169 citations,
September 2002 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement” ZD1839 (Iressa) causes skin and hair side effects, treatable with tretinoin cream and minocycline.
 1 citations,
March 2004 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
1 citations,
March 2004 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” ZD1839, a cancer drug, can cause mild skin rashes that are treatable without stopping the medication.
 192 citations,
January 2015 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
192 citations,
January 2015 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Targeted cancer therapies often cause serious skin problems that need careful management.
[object Object]  138 citations,
February 2007 in “European journal of cancer”
138 citations,
February 2007 in “European journal of cancer” EGFR inhibitors often cause skin problems and other side effects, but these are usually reversible and can be managed to keep patients comfortable.
 78 citations,
June 2005 in “Annals of oncology”
78 citations,
June 2005 in “Annals of oncology” Cetuximab can cause excessive eyelash growth.
 53 citations,
April 2018 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
53 citations,
April 2018 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Cancer treatments often cause hair disorders, significantly affecting patients' quality of life, and better management methods are needed.
 44 citations,
April 2006 in “Expert opinion on drug safety”
44 citations,
April 2006 in “Expert opinion on drug safety” Gefitinib can cause skin problems, diarrhea, and nausea, but rarely causes severe lung disease or hair loss.
 42 citations,
April 2012 in “Seminars in Oncology”
42 citations,
April 2012 in “Seminars in Oncology” Targeted cancer therapies often cause skin problems that need careful management to improve patient quality of life and treatment success.
 32 citations,
January 2012 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
32 citations,
January 2012 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Skin side effects from EGFR inhibitor cancer treatment can be managed effectively, often without stopping the medication.
 30 citations,
August 2010 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology”
30 citations,
August 2010 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology” Cetuximab can cause eyelash growth, which is rare but manageable.
 29 citations,
September 2017 in “Oncology and therapy”
29 citations,
September 2017 in “Oncology and therapy” The document provides advice on how to recognize and treat skin-related side effects of cancer drugs known as EGFR inhibitors.
 28 citations,
December 2006 in “Clinical lung cancer”
28 citations,
December 2006 in “Clinical lung cancer” Early recognition and management of skin side effects from new cancer therapies can prevent treatment delays.
 26 citations,
October 2018 in “Clinical & Translational Oncology”
26 citations,
October 2018 in “Clinical & Translational Oncology” Spanish experts provided guidelines for treating skin side effects in cancer patients on new therapies, stressing early action and teamwork.
 25 citations,
March 2012 in “Journal of oncology pharmacy practice”
25 citations,
March 2012 in “Journal of oncology pharmacy practice” An 81-year-old man's white hair began to regain its original color while he was treated with lenalidomide, suggesting that graying hair might be reversible.
 24 citations,
May 2012 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
24 citations,
May 2012 in “International Journal of Dermatology” The document concludes that eyelash trichomegaly, which is the abnormal growth of eyelashes, can be present from birth, caused by diseases, or result from certain medications.
 19 citations,
October 2011 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
19 citations,
October 2011 in “Clinics in Dermatology” New chemotherapy drugs cause skin side effects, but treatments like minocycline and tetracycline can help reduce them.
 19 citations,
October 2008 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft”
19 citations,
October 2008 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft” Anti-cancer treatments can cause reversible hair loss, skin sensitivity, pigmentation changes, nail damage, and skin reactions, with a need for more research on managing these side effects.
 18 citations,
July 2008 in “Current Oncology Reports”
18 citations,
July 2008 in “Current Oncology Reports” EGFR cancer drugs often cause a rash, which can lead to distress and isolation, but may also improve outcomes for some cancer patients. Current treatments for the rash are limited, but a compound called menadione shows promise.
 3 citations,
January 2011 in “Annals of Dermatology”
3 citations,
January 2011 in “Annals of Dermatology” Blocking EGFR in skin cells doesn't majorly increase inflammation markers.
 2 citations,
January 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks”
2 citations,
January 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks” Targeted therapies for lung cancer are effective but require careful management of side effects to benefit patients.
 2 citations,
October 2016
2 citations,
October 2016 Chemotherapy and radiotherapy can cause skin side effects like rashes, hair loss, and nail changes, which are usually managed with conservative treatments.
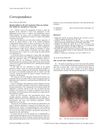 2 citations,
June 2005 in “Clinical Oncology”
2 citations,
June 2005 in “Clinical Oncology” A man's bald spot grew hair after starting cancer treatment with gefitinib.
 1 citations,
January 2010 in “Elsevier eBooks”
1 citations,
January 2010 in “Elsevier eBooks” Any drug can cause skin reactions, but antibiotics, NSAIDs, and psychotropic drugs are more common, with some reactions being life-threatening.
 October 2021 in “International journal of basic and clinical pharmacology”
October 2021 in “International journal of basic and clinical pharmacology” Excessive eyelash growth from erlotinib may indicate positive tumor response and help treat madarosis.
[object Object] 1 citations,
February 2020 in “The Journal of clinical investigation/The journal of clinical investigation” Certain cancer drugs interact with skin bacteria to cause acne-like rashes.
 January 2023 in “Applied sciences”
January 2023 in “Applied sciences” Gefitinib and Sasam-Kyeongokgo together significantly reduce cancer growth and improve immune response in mice.























