 34 citations,
February 1993 in “Journal of steroid biochemistry and molecular biology/The Journal of steroid biochemistry and molecular biology”
34 citations,
February 1993 in “Journal of steroid biochemistry and molecular biology/The Journal of steroid biochemistry and molecular biology” Certain 4-azasteroids are effective at blocking the enzyme that processes testosterone in human skin and could help treat acne, excessive hair growth, and male pattern baldness.
 32 citations,
June 2015 in “PLOS ONE”
32 citations,
June 2015 in “PLOS ONE” Olive leaf compound oleuropein helps grow hair in mice.
 41 citations,
March 1992 in “Archives of Dermatology”
41 citations,
March 1992 in “Archives of Dermatology” The review suggests that understanding and treating the psychological aspect of skin disorders is important and calls for more collaboration in this field.
 2 citations,
February 2014 in “Animal Biotechnology”
2 citations,
February 2014 in “Animal Biotechnology” The PTGER2 gene is highly active in Cashmere goat skin and its activity changes with the hair growth cycle.
 40 citations,
July 2007 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
40 citations,
July 2007 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Systemic glucocorticosteroids are a primary treatment for various skin conditions but require careful management due to potential side effects and relapses.
 5 citations,
December 2011 in “Canadian Journal of Plastic Surgery”
5 citations,
December 2011 in “Canadian Journal of Plastic Surgery” Hair grafts can successfully reconstruct a beard on reconstructed jaw skin, improving appearance and patient satisfaction.
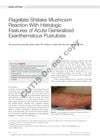 2 citations,
September 2021 in “Cutis”
2 citations,
September 2021 in “Cutis” Eating shiitake mushrooms caused a man to develop a rash similar to a skin condition known as AGEP.
1 citations,
September 2021 in “Rossijskij žurnal kožnyh i veneričeskih boleznej” Osteoma cutis is a rare, benign skin condition where bone forms in the skin.

Psoriasis is a common, genetically influenced skin disease worsened by stress and lifestyle, but targeted treatments are promising.
 September 2011 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology”
September 2011 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology” The birth control pill containing ethinylestradiol and chlormadinone may help treat acne and other skin and hair conditions related to hormones.
 July 2017 in “Journal of Young Pharmacists”
July 2017 in “Journal of Young Pharmacists” Nothopanax scutellarium leaves can promote hair growth but may mildly irritate the skin.
 October 2007 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
October 2007 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” The meeting highlighted the genetic basis of female pattern hair loss and various skin health insights.
 5 citations,
January 1987 in “Gynecologic and obstetric investigation”
5 citations,
January 1987 in “Gynecologic and obstetric investigation” Cyproterone acetate implants were more effective at reducing facial hair and improving skin in severe hirsutism than oral treatment.
 June 2023 in “Romanian Medical Journal”
June 2023 in “Romanian Medical Journal” The case shows how hard it is to tell apart Multiple Autoimmune Syndrome from other similar autoimmune conditions, but correct diagnosis is key for treatment to work.
 56 citations,
January 2004 in “Dermatology”
56 citations,
January 2004 in “Dermatology” Most patients treated with low-dose alpha-interferon for malignant melanoma experienced skin side effects, with hair loss being the most frequent.
14 citations,
January 2013 in “Journal of the Egyptian Women's Dermatologic Society /Journal of the Egyptian Women's Dermatologic Society”  53 citations,
October 1993 in “Drug Safety”
53 citations,
October 1993 in “Drug Safety” Oral retinoids can cause side effects ranging from mild to severe, including birth defects, and require careful monitoring and contraception.
 September 1998 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
September 1998 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Old people's nails often have problems due to body changes, more diseases, and self-care difficulties, affecting their movement and hand use.
 34 citations,
October 2007 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
34 citations,
October 2007 in “International Journal of Dermatology” The most common causes of hair loss in children in South-East Nigeria are fungal infections and alopecia areata.
September 1993 in “PubMed” The document concludes that antiandrogenic drugs like cyproterone acetate and spironolactone are effective but not permanent treatments for skin-related androgenization in women.
1 citations,
November 2022 in “Animals” The research found specific genes and pathways that control fur development and color in young American minks.
 March 2023 in “Journal of clinical pharmacy and therapeutics”
March 2023 in “Journal of clinical pharmacy and therapeutics” Isoliensinine, a natural compound, prevents stress-related hair greying by blocking a specific receptor on hair cells.
 25 citations,
April 2015 in “Current problems in dermatology”
25 citations,
April 2015 in “Current problems in dermatology” Hair regrowth slows with age and can be affected by treatments that change enzyme activity in the skin.
 August 1986 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
August 1986 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Minoxidil showed a 30% success rate for hair growth in a study, and various skin treatments were effective, but some had limitations or side effects.
 August 2011 in “Planta Medica”
August 2011 in “Planta Medica” 4-O-methylhonokiol from Magnolia Officinalis may promote hair growth by interfering with TGF-β1 effects in skin cells.

Different hair and nail conditions can indicate health issues and have specific treatments; accurate diagnosis is crucial before treatment.
 35 citations,
April 2006 in “Ocular Surface”
35 citations,
April 2006 in “Ocular Surface” Cosmetics and procedures can cause eye issues, from mild discomfort to serious conditions, due to allergies, toxins, or poor care.
 November 2015 in “Springer eBooks”
November 2015 in “Springer eBooks” Hair loss treated with minoxidil, finasteride, laser/light, hair transplant, and scalp prostheses; more research needed for skin of color.
 18 citations,
January 2008 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
18 citations,
January 2008 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Certain proteins and their receptors are more active during the growth phase of human hair and could be targeted to treat hair disorders.
November 1993 in “PubMed” Hirsutism, excessive male-pattern hair in women, can be caused by high androgens or skin sensitivity, diagnosed by testosterone levels, and treated with hair removal and hormone therapy.
























