 1 citations,
August 2022 in “JAAD case reports”
1 citations,
August 2022 in “JAAD case reports” Tofacitinib and oral minoxidil may help treat Sisaipho alopecia areata.
 August 2024 in “Skin Appendage Disorders”
August 2024 in “Skin Appendage Disorders” Alopecia areata can look like male or female pattern hair loss, needing a new subtype for better diagnosis and treatment.
1 citations,
February 2000 in “PubMed”  7 citations,
August 2013 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
7 citations,
August 2013 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Less than a quarter of alopecia areata cases were unusual forms or had paradoxical regrowth.
 January 2014 in “International Journal of Trichology”
January 2014 in “International Journal of Trichology” A man had an unusual type of hair loss that didn't match known patterns and didn't improve with treatment.
April 2022 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Androgenetic alopecia causes hair thinning due to increased androgen activity, treatable with minoxidil and finasteride.
 89 citations,
March 2018 in “The Journal of Dermatology”
89 citations,
March 2018 in “The Journal of Dermatology” Trichoscopy helps diagnose and monitor alopecia areata by looking at a combination of specific hair and scalp features.
 56 citations,
January 2021 in “Clinical and Experimental Medicine”
56 citations,
January 2021 in “Clinical and Experimental Medicine” The document concludes that while there are various treatments for Alopecia Areata, there is no cure, and individualized treatment plans are essential due to varying effectiveness.
 39 citations,
July 2015 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
39 citations,
July 2015 in “British Journal of Dermatology” The pseudo 'fringe sign' can also appear in frontal fibrosing alopecia, not just in traction alopecia, showing that this condition may be more common than thought.
 26 citations,
August 2013 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology”
26 citations,
August 2013 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology” Certain scalp patterns can indicate the severity and activity of hair loss in Turkish alopecia patients.
 11 citations,
May 2009 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas”
11 citations,
May 2009 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas” Some treatments can help hair regrowth in alopecia areata, but none offer a cure, and effectiveness varies.
 1 citations,
March 2020 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology”
1 citations,
March 2020 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology” The paper concludes that recognizing bitemporal alopecia areata is important for early treatment and preventing its progression.
 1 citations,
August 2019 in “Australasian journal of dermatology”
1 citations,
August 2019 in “Australasian journal of dermatology” Immunotherapy can help treat severe alopecia areata.
 1 citations,
April 2019 in “Acta Medica Philippina”
1 citations,
April 2019 in “Acta Medica Philippina” Azathioprine may help treat severe alopecia areata, but more research is needed.
 1 citations,
July 2018 in “Journal of Pakistan Association of Dermatology”
1 citations,
July 2018 in “Journal of Pakistan Association of Dermatology” Microneedling with PRP is a safe and effective way to treat chronic alopecia areata, improving hair regrowth with minimal side effects.
 1 citations,
July 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks”
1 citations,
July 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks” Alopecia Areata is an autoimmune hair loss condition, with various treatments showing mixed effectiveness and no guaranteed cure.
 1 citations,
January 2017 in “Springer eBooks”
1 citations,
January 2017 in “Springer eBooks” Understanding the immune-related causes of Alopecia Areata has led to potential treatments like JAK inhibitors.
 January 2023 in “Frontiers in medicine”
January 2023 in “Frontiers in medicine” Early diagnosis and personalized treatments are crucial for better hair loss management.
 April 2022 in “Cermin Dunia Kedokteran”
April 2022 in “Cermin Dunia Kedokteran” Accurate diagnosis and understanding of alopecia areata in children are crucial for proper treatment.
 March 2022 in “Nepal Journal of Dermatology Venereology & Leprology”
March 2022 in “Nepal Journal of Dermatology Venereology & Leprology” Methotrexate with steroids is slightly more effective than azathioprine with steroids for treating severe alopecia areata.
 October 2021 in “International journal of research in dermatology”
October 2021 in “International journal of research in dermatology” No link between scalp patterns and alopecia severity in children, but more severe cases often had nail abnormalities.
 October 2021 in “The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine”
October 2021 in “The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine” Alopecia areata causes patchy hair loss and involves immune system disruptions.
 October 2020 in “International journal of Ayurvedic medicine”
October 2020 in “International journal of Ayurvedic medicine” Leech therapy and Ayurvedic treatment can effectively regrow hair in recent Alopecia areata cases.
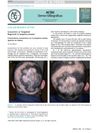 April 2016 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas”
April 2016 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas” The document concludes that a unique target-like hair regrowth pattern in alopecia areata may be more common than thought and should be properly identified.

The patient with total hair loss did not regrow hair despite treatment, indicating a poor outlook for this type of hair loss.
 290 citations,
December 2017 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
290 citations,
December 2017 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Alopecia areata is an autoimmune condition causing hair loss, influenced by genetics, stress, and diet, and may be prevented by a high soy oil diet.
 67 citations,
January 2013 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology”
67 citations,
January 2013 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology” The document concludes that alopecia areata is an autoimmune disease without a definitive cure, but treatments like corticosteroids are commonly used.
 40 citations,
July 2017 in “Frontiers in Medicine”
40 citations,
July 2017 in “Frontiers in Medicine” Early and personalized treatment for hair loss in young people is crucial to prevent permanent damage and should include psychological support.
 35 citations,
January 2013 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology”
35 citations,
January 2013 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology” Intralesional triamcinolone acetonide is effective for treating patchy hair loss, and dermoscopy helps detect treatment response and side effects early.
 30 citations,
January 2014 in “Annals of Dermatology”
30 citations,
January 2014 in “Annals of Dermatology” Scalp dermatoscopy helps diagnose and monitor hair loss severity.




























