 April 2023 in “Medizinische Genetik”
April 2023 in “Medizinische Genetik” New research has found 14 genes linked to the risk of developing alopecia areata, improving understanding and treatment options.
 August 2023 in “International Ayurvedic medical journal”
August 2023 in “International Ayurvedic medical journal” Ayurvedic treatment successfully regrew hair in a 7-year-old girl with alopecia areata.
77 citations,
September 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” TRPV3 in skin cells causes inflammation and cell death.
 December 2023 in “International journal of research in dermatology”
December 2023 in “International journal of research in dermatology” Adding PRP to topical mometasone improves and speeds up alopecia areata treatment.
September 2013 in “Canadian Medical Association Journal” Alopecia areata causes sudden hair loss, often resolves within a year, but can recur.
 May 2017 in “InTech eBooks”
May 2017 in “InTech eBooks” Some hair loss disorders cause permanent loss due to scarring, and treatments like steroids don't always work well.
 9 citations,
July 2009 in “Journal Of Endocrinology, Metabolism And Diabetes Of South Africa”
9 citations,
July 2009 in “Journal Of Endocrinology, Metabolism And Diabetes Of South Africa” The document concludes that managing PCOS involves treating symptoms and reducing long-term metabolic risks, with lifestyle changes being important.
 1 citations,
April 2010 in “Expert Review of Dermatology”
1 citations,
April 2010 in “Expert Review of Dermatology” The document concludes that early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for managing rare hair loss disorders and that more research is needed to improve treatment strategies.
 18 citations,
July 2022 in “Frontiers in Immunology”
18 citations,
July 2022 in “Frontiers in Immunology” Volatile organic compounds can cause inflammation and increase the risk of autoimmune diseases.
 28 citations,
November 2019 in “Frontiers in Endocrinology”
28 citations,
November 2019 in “Frontiers in Endocrinology” Vegetarian Indian women with PCOS have higher inflammation levels than non-vegetarians.
 23 citations,
January 2020 in “Central-European Journal of Immunology/Central European Journal of Immunology”
23 citations,
January 2020 in “Central-European Journal of Immunology/Central European Journal of Immunology” Alopecia areata, a type of hair loss, is likely an autoimmune disease with a genetic link, but its exact cause is still unknown.
 29 citations,
March 2019 in “JEADV. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology/Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
29 citations,
March 2019 in “JEADV. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology/Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Older age at onset of alopecia areata leads to less severe and shorter episodes, with most patients experiencing significant hair regrowth.
 January 2018 in “Springer eBooks”
January 2018 in “Springer eBooks” Terbinafine is the most effective medicine for fungal nail infections, especially for diabetics and those with weak immune systems.
 3 citations,
August 2015 in “Diabetes and Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research and Reviews”
3 citations,
August 2015 in “Diabetes and Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research and Reviews” Married women with type 2 diabetes had a surprisingly low infertility rate, suggesting type 2 diabetes and PCOS may be different conditions.
 January 2015 in “Przegla̧d dermatologiczny”
January 2015 in “Przegla̧d dermatologiczny” Intralesional triamcinolone is the most effective treatment for alopecia areata, followed by excimer light therapy, and then topical minoxidil. The scalp responds better to treatment than the beard area.
 7 citations,
January 2015 in “Current problems in dermatology”
7 citations,
January 2015 in “Current problems in dermatology” Hair loss can be caused by stress, infections, drugs, and various diseases, with treatment depending on accurate diagnosis.
 January 2015 in “Journal of clinical & experimental dermatology research”
January 2015 in “Journal of clinical & experimental dermatology research” A protein combining parathyroid hormone and collagen helped hair regrow in mice with a hair loss condition.
 3 citations,
May 2023 in “Biomedicines”
3 citations,
May 2023 in “Biomedicines” PCOS causes infertility mainly due to hormonal imbalances, insulin resistance, and chronic inflammation.
 76 citations,
July 2011 in “Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology”
76 citations,
July 2011 in “Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology” The document concludes that proper diagnosis and FDA-approved treatments for different types of hair loss exist, but treatments for severe cases often fail and future improvements may focus on hair follicle stem cells.
44 citations,
August 2014 in “Anais brasileiros de dermatologia/Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia” Methotrexate is a promising and safe treatment for severe alopecia areata, with better results when combined with corticosteroids.
 51 citations,
January 2014 in “Pediatric Clinics of North America”
51 citations,
January 2014 in “Pediatric Clinics of North America” The guide explains how to identify and treat children's hair loss, including fungal infections, autoimmune disorders, hairstyle changes, self-correcting conditions, and behavioral therapy for hair-pulling.
 35 citations,
May 2012 in “Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy”
35 citations,
May 2012 in “Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy” The document concludes that there are various treatments for different types of alopecia, but more research is needed for evidence-based treatments.
 2 citations,
January 2018 in “International journal of research in dermatology”
2 citations,
January 2018 in “International journal of research in dermatology” Intralesional corticosteroids are the best for limited alopecia areata, oral steroids are less effective, and PRP is safe and promising, especially for children and severe cases.
 10 citations,
February 2011 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft”
10 citations,
February 2011 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft” The document concludes that proper diagnosis and evidence-based treatments are crucial for managing hair diseases, and psychological support for patients is important.
 71 citations,
November 2013 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
71 citations,
November 2013 in “Clinics in Dermatology” Acne is a chronic disease linked to various systemic conditions and has significant psychological and social effects.
 8 citations,
September 2015 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
8 citations,
September 2015 in “Clinics in Dermatology” Hair loss in children is diagnosed and treated differently than in adults, with different common causes and a focus on less invasive methods.
 1 citations,
July 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks”
1 citations,
July 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks” Alopecia Areata is an autoimmune hair loss condition, with various treatments showing mixed effectiveness and no guaranteed cure.
 30 citations,
May 2016 in “Expert Opinion on Biological Therapy”
30 citations,
May 2016 in “Expert Opinion on Biological Therapy” New treatments targeting immune pathways show promise for severe hair loss but need more research for safety and effectiveness.
 60 citations,
September 2015 in “Expert Review of Clinical Immunology”
60 citations,
September 2015 in “Expert Review of Clinical Immunology” Lymphocytes, especially CD8+ T cells, play a key role in causing alopecia areata, and targeting them may lead to new treatments.
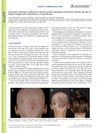 24 citations,
June 2016 in “Acta dermato-venereologica”
24 citations,
June 2016 in “Acta dermato-venereologica” Tofacitinib helped a young woman's severe hair loss and arthritis but not her plaque psoriasis.



























