 22 citations,
February 2008 in “Journal of Neurochemistry”
22 citations,
February 2008 in “Journal of Neurochemistry” Minoxidil prevents serotonin loss from MDMA by affecting potassium channels and increasing Akt phosphorylation.
 88 citations,
July 2014 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
88 citations,
July 2014 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Targeted cancer therapies often cause skin reactions, so dermatologists must manage these effects.
 September 2023 in “Frontiers in medicine”
September 2023 in “Frontiers in medicine” The mTOR signaling pathway is crucial for hair health and targeting it may lead to new hair loss treatments.
 506 citations,
January 2012 in “Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology”
506 citations,
January 2012 in “Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology” Melatonin affects many body functions beyond sleep by interacting with specific receptors in various tissues.
 71 citations,
February 2020 in “Journal of Translational Medicine”
71 citations,
February 2020 in “Journal of Translational Medicine” Progress has been made in skin and nerve regeneration, but more research is needed to improve methods and ensure safety.
 8 citations,
May 2010 in “Dermatologic clinics”
8 citations,
May 2010 in “Dermatologic clinics” New treatments for skin conditions in children include a preferred drug for birthmark reduction, proactive creams for eczema and vitiligo, a safe psoriasis medication, and special tissues and socks for eczema and fungal infections.
 5 citations,
November 2016 in “Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine”
5 citations,
November 2016 in “Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine” BeauTop improves hair growth in androgenetic alopecia patients.
 24 citations,
September 2005 in “Journal of Cellular Biochemistry”
24 citations,
September 2005 in “Journal of Cellular Biochemistry” Retinoids increase steroid sulfatase activity in leukemia cells through RARα/RXR and involves certain pathways like phosphoinositide 3-kinase and ERK-MAP kinase.
 234 citations,
September 2004 in “Clinical cancer research”
234 citations,
September 2004 in “Clinical cancer research” BAY 43-9006 helps control kidney cancer growth but doesn't significantly increase overall survival.
26 citations,
September 2012 in “Cell Reports” B-Raf and C-Raf are essential for maintaining melanocyte stem cells to prevent hair graying.
 46 citations,
February 2012 in “Oncology Reports”
46 citations,
February 2012 in “Oncology Reports” Sorafenib helps some advanced cancers alone or with other treatments, but not all, and research continues to improve its use.
 21 citations,
February 2013 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
21 citations,
February 2013 in “Clinics in Dermatology” New treatments for advanced skin cancer are improving patient outcomes, but drug resistance and finding the right treatment combinations are still big challenges.
 15 citations,
December 2014 in “Dermatology and therapy”
15 citations,
December 2014 in “Dermatology and therapy” Sorafenib can cause facial acne-like eruptions, which improve after reducing the dose or stopping the drug.
 1 citations,
August 2012 in “Food Science and Biotechnology”
1 citations,
August 2012 in “Food Science and Biotechnology” The essence made from fermented products increased hair growth in mice better than minoxidil.
 January 2016 in “Elsevier eBooks”
January 2016 in “Elsevier eBooks” The conclusion is that grasping how cells determine their roles through evolution is key, with expected progress from new research models and genome editing.
188 citations,
October 2014 in “Thyroid” Dabrafenib was effective and well tolerated in treating thyroid cancer with a specific mutation.
37 citations,
November 2017 in “Medical Sciences” Melanoma's complexity requires personalized treatments due to key genetic mutations and tumor-initiating cells.
 46 citations,
August 2003 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
46 citations,
August 2003 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Phosphatidic acid may help hair grow by affecting cell growth pathways.
 356 citations,
March 2012 in “Trends in Plant Science”
356 citations,
March 2012 in “Trends in Plant Science” Auxin and ethylene hormones both work together and against each other to control plant growth.
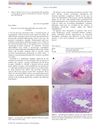 5 citations,
August 2014 in “Australasian journal of dermatology”
5 citations,
August 2014 in “Australasian journal of dermatology” Sorafenib can cause delayed skin problems, so patients need careful monitoring.
 510 citations,
August 2006 in “Endocrinology”
510 citations,
August 2006 in “Endocrinology” The vitamin D receptor is involved in multiple body functions beyond calcium regulation, including immune response and rapid reactions not related to gene activity.

The vitamin D receptor has many roles in the body beyond managing calcium, affecting the immune system, hair growth, muscles, fat, bone marrow, and cancer cells.
 6 citations,
July 2018 in “Scientific Reports”
6 citations,
July 2018 in “Scientific Reports” Methamphetamine affects gene expression in rat whisker follicles, with key genes linked to addiction.
 4 citations,
October 2014 in “Springer eBooks”
4 citations,
October 2014 in “Springer eBooks” Ethylene and auxin hormones interact in complex ways that are essential for plant growth and development.

research Acne
2 citations,
May 2011 in “Harper's Textbook of Pediatric Dermatology” Acne is a common skin condition linked to diet, hormones, and genetics, and early treatment can prevent scarring.
200 citations,
August 2009 in “Experimental dermatology” Eating high-glycemic foods and drinking milk may worsen acne by increasing insulin and IGF-1 levels.
7 citations,
August 2017 in “Journal of dermatological science” Sorafenib causes skin reactions by increasing the number and activity of skin mast cells.
10 citations,
September 2016 in “Journal of cutaneous medicine and surgery” Patients on dabrafenib and trametinib for melanoma often experience skin side effects.
39 citations,
June 2019 in “Frontiers in Endocrinology” Lenvatinib and sorafenib are generally safe but need dose adjustments due to side effects.
 21 citations,
March 2019 in “Critical Reviews in Clinical Laboratory Sciences”
21 citations,
March 2019 in “Critical Reviews in Clinical Laboratory Sciences” The androgen receptor is a promising target for breast cancer treatment, especially in triple-negative cases, but more research is needed for personalized therapies.























