 15 citations,
March 2004 in “American Journal of Ophthalmology”
15 citations,
March 2004 in “American Journal of Ophthalmology” Using bimatoprost on one side of the face caused increased cheek hair growth in a patient.
[object Object]  April 2023 in “Tikrit Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences”
April 2023 in “Tikrit Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences” Deferasirox effectively reduces iron overload in ß-thalassemia patients but may cause some manageable side effects.
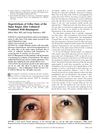
 216 citations,
October 1997 in “American Journal of Ophthalmology”
216 citations,
October 1997 in “American Journal of Ophthalmology” Using the eye pressure medication latanoprost can cause excessive hair growth and darker eyelashes on the treated eye.
 55 citations,
July 2016 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
55 citations,
July 2016 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Multiple treatments work best for hair loss.
 38 citations,
February 2002 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement”
38 citations,
February 2002 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement” Two patients with porphyria cutanea tarda experienced their grey hair turning dark again.
 33 citations,
August 2018 in “Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America”
33 citations,
August 2018 in “Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America” The document explains hair biology, the causes of hair loss, and reviews various hair loss treatments.
 33 citations,
September 2016 in “Lasers in Surgery and Medicine”
33 citations,
September 2016 in “Lasers in Surgery and Medicine” Fractional resurfacing is safe and effective for certain skin conditions in Asian patients, but care must be taken to avoid skin pigmentation issues.
 19 citations,
April 2015 in “European Journal of Pharmacology”
19 citations,
April 2015 in “European Journal of Pharmacology” Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) doesn't affect rat skin cell growth, but it does change cell cycle, protein levels, and other cell functions, potentially shortening hair growth cycle.
 8 citations,
April 2020 in “Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America”
8 citations,
April 2020 in “Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America” Minoxidil, finasteride, and low-level laser light therapy are effective FDA-approved treatments for hair loss.
 4 citations,
September 2019 in “Journal of cosmetic dermatology”
4 citations,
September 2019 in “Journal of cosmetic dermatology” Topical bimatoprost 0.01% improves eyebrow density and diameter, especially at the tail.
 4 citations,
September 2011 in “Expert Review of Dermatology”
4 citations,
September 2011 in “Expert Review of Dermatology” Various treatments exist for alopecia areata, but none are completely satisfactory; choice depends on age, disease extent, and preference.
 1 citations,
July 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks”
1 citations,
July 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks” Heredity and hormones cause common hair loss, and topical minoxidil is the first recommended treatment.
 1 citations,
January 2014 in “Hair therapy & transplantation”
1 citations,
January 2014 in “Hair therapy & transplantation” Platelet-rich plasma treatment is not very effective for chronic severe alopecia areata.
 1 citations,
January 2001 in “Journal of Toxicology-cutaneous and Ocular Toxicology”
1 citations,
January 2001 in “Journal of Toxicology-cutaneous and Ocular Toxicology” Hair follicles could be used to deliver drugs effectively, with the right understanding and methods.
 July 2024 in “Forum Dermatologicum”
July 2024 in “Forum Dermatologicum” Topical treatments for hair loss can be effective but need careful safety evaluation.
 February 2021 in “Journal of pharmaceutical and biological sciences”
February 2021 in “Journal of pharmaceutical and biological sciences” No cure exists for alopecia areata, and treatments are personalized.
[object Object]  November 2019 in “Harper's Textbook of Pediatric Dermatology”
November 2019 in “Harper's Textbook of Pediatric Dermatology” Understanding normal hair growth and loss in children is key to diagnosing and treating hair disorders.
 April 2016 in “Plastic and reconstructive surgery. Global open”
April 2016 in “Plastic and reconstructive surgery. Global open” The supplement highlighted advancements and challenges in plastic and reconstructive surgery, including the impact of smoking, chemotherapy, and new treatments like Tafluprost for hair loss.
June 1986 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Topical minoxidil showed promise for early male pattern baldness.
110 citations,
December 2013 in “The journal of investigative dermatology. Symposium proceedings/The Journal of investigative dermatology symposium proceedings” Alopecia areata is a genetic and immune-related hair loss condition that is often associated with other autoimmune diseases and does not typically cause permanent damage to hair follicles.
11 citations,
March 2021 in “Cleveland Clinic Journal of Medicine” Treating hair loss in both men and women is effective and improves quality of life.
 August 2024 in “Stem Cell Research & Therapy”
August 2024 in “Stem Cell Research & Therapy” New regenerative therapies show promise for treating hair loss.
103 citations,
April 2005 in “Experimental dermatology” Prostaglandin F2alpha and related compounds can increase hair growth and darken hair in mice.
 218 citations,
April 2012 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
218 citations,
April 2012 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Guidelines suggest various treatments for alopecia areata, but leaving it untreated is also an option as 80% cases may recover on their own.
 39 citations,
April 2001 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
39 citations,
April 2001 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Latanoprost, a glaucoma medication, caused excessive eyelid hair growth in many patients.
 November 2024 in “Postępy Biochemii”
November 2024 in “Postępy Biochemii” Latanoprost may be a promising new treatment for hair loss.
 June 2012 in “Nature digest”
June 2012 in “Nature digest” A substance called prostaglandin D2 is linked to stopping hair growth in men with common baldness.
 21 citations,
June 2017 in “Journal of Dermatological Treatment”
21 citations,
June 2017 in “Journal of Dermatological Treatment” Topical cetirizine improves hair density and thickness in androgenetic alopecia, but more research is needed.
 35 citations,
May 2012 in “Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy”
35 citations,
May 2012 in “Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy” The document concludes that there are various treatments for different types of alopecia, but more research is needed for evidence-based treatments.
 3 citations,
March 2018 in “Pediatric Dermatology”
3 citations,
March 2018 in “Pediatric Dermatology” Two children grew extra hair from taking omeprazole, which went away after they stopped the medication.


























