 December 2004 in “Medicine”
December 2004 in “Medicine” Pregnancy can cause skin changes and may affect pre-existing skin conditions, with some treatments not safe for use during pregnancy.
 51 citations,
February 2006 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
51 citations,
February 2006 in “Clinics in Dermatology” Pregnant women often experience skin and hair changes, with over half getting stretch marks and pigment changes, and should be cautious with cosmetic procedures due to potential risks.
 15 citations,
December 2016 in “Obstetrics & Gynecology”
15 citations,
December 2016 in “Obstetrics & Gynecology” Most skin changes during pregnancy are harmless and moles don't significantly change, but many women experience pigmentation changes due to hormones and sun exposure.
 7 citations,
August 2016 in “Nursing for Women's Health”
7 citations,
August 2016 in “Nursing for Women's Health” To prevent and treat Hair-thread tourniquet syndrome in infants, keep a close eye on their limbs, manage maternal hair loss, and educate parents and healthcare providers.
 23 citations,
October 1971 in “BMJ”
23 citations,
October 1971 in “BMJ” Stopping the pill and giving birth both caused hair loss.
 4 citations,
January 2019 in “PubMed”
4 citations,
January 2019 in “PubMed” Patterned hair loss in women is linked to hormonal imbalances and biochemical changes, and should be evaluated for underlying health issues.
6 citations,
January 2015 in “Il Giornale di Chirurgia” Hair tourniquet syndrome can cause serious harm if not treated quickly, especially in infants.
 3 citations,
April 2002 in “The American Journal of Medicine”
3 citations,
April 2002 in “The American Journal of Medicine” The document concludes that early diagnosis of Balint's syndrome is crucial for effective treatment and that understanding drug interactions, like between ritonavir and statins, is important for patient care.
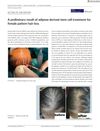 April 2021 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
April 2021 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” Stem cell treatment improved hair density in female hair loss patient.
 37 citations,
May 2016 in “Deutsches Arzteblatt International”
37 citations,
May 2016 in “Deutsches Arzteblatt International” Hair loss requires customized treatments based on its various causes and types.
 33 citations,
August 2006 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft”
33 citations,
August 2006 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft” Pregnancy can cause specific skin conditions that need correct diagnosis and treatment to protect both mother and baby.
 22 citations,
March 2000 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
22 citations,
March 2000 in “Clinics in Dermatology” Many treatments for hair loss lack proper testing and FDA approval, so their effectiveness is uncertain.
 20 citations,
June 2012 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
20 citations,
June 2012 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Bleaching hair damages protein structure, especially keratin, leading to weakened hair.
 8 citations,
June 2016 in “Journal of Pediatric Orthopaedics B”
8 citations,
June 2016 in “Journal of Pediatric Orthopaedics B” Washing baby socks without flipping them inside out may increase the risk of Hair Tourniquet Syndrome.
 4 citations,
September 2014 in “Elsevier eBooks”
4 citations,
September 2014 in “Elsevier eBooks” Use some skin medications with caution during pregnancy; avoid strong steroids, certain eczema treatments, and systemic retinoids, but many topical treatments and nasal sprays are safe.
 1113 citations,
August 1999 in “The New England Journal of Medicine”
1113 citations,
August 1999 in “The New England Journal of Medicine” Hair follicle biology advancements may lead to better hair growth disorder treatments.
 36 citations,
December 2016 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
36 citations,
December 2016 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” The normal range for the hair pull test is 2 hairs or fewer, and washing or brushing hair before the test does not affect the results.
 25 citations,
June 2003 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings”
25 citations,
June 2003 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings” Phototrichogram and hair diameter measurements are effective, noninvasive ways to assess hair growth and detect early hair loss, with the most common pattern being reduced hair density.
 22 citations,
June 1980 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
22 citations,
June 1980 in “International Journal of Dermatology” The document concludes that correct diagnosis of alopecia types is crucial, scalp biopsies are important, and more research is needed.
 16 citations,
February 2014 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
16 citations,
February 2014 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Researchers developed a mouse model that tracks hair growth using bioluminescence, improving accuracy in studying hair cycles.
 10 citations,
August 2012 in “Current Problems in Pediatric and Adolescent Health Care”
10 citations,
August 2012 in “Current Problems in Pediatric and Adolescent Health Care” Hair changes can indicate systemic diseases or medication effects.
 3 citations,
January 1996 in “Pharmacotherapy: The Journal of Human Pharmacology and Drug Therapy”
3 citations,
January 1996 in “Pharmacotherapy: The Journal of Human Pharmacology and Drug Therapy” Zidovudine may cause hair loss in advanced-stage HIV patients.
 2 citations,
January 2018 in “Dermatology Review/Przegląd Dermatologiczny”
2 citations,
January 2018 in “Dermatology Review/Przegląd Dermatologiczny” Use trichoscopy to diagnose hair loss; treat with minoxidil, finasteride, or dutasteride; consider platelet-rich plasma and spironolactone.
 1 citations,
August 2020 in “Food Research”
1 citations,
August 2020 in “Food Research” Plant extracts like Avicennia marina, Boehmeria nipononivea, and Camellia sinensis could potentially treat hair loss with fewer side effects than synthetic drugs.
 December 2022 in “Journal of complementary medicine & alternative healthcare”
December 2022 in “Journal of complementary medicine & alternative healthcare” Traditional Chinese medicine improved hair loss in a teenager with alopecia.
 June 2021 in “Journal of Emerging Technologies and Innovative Research”
June 2021 in “Journal of Emerging Technologies and Innovative Research” Rice water and hibiscus can help improve hair health and growth.
 40 citations,
April 2014 in “Genes & Development”
40 citations,
April 2014 in “Genes & Development” Hormones during pregnancy and lactation keep skin stem cells inactive, preventing hair growth.
 37 citations,
March 1990 in “The Journal of Pediatrics”
37 citations,
March 1990 in “The Journal of Pediatrics” Toxic shock syndrome is caused by a complex interaction of bacterial toxins and the immune system, and understanding this can help improve diagnosis and treatment.
 34 citations,
June 2014 in “The BMJ”
34 citations,
June 2014 in “The BMJ” Pregnancy can change skin disease severity, with some conditions improving and others worsening, and treatment should balance benefits and fetal safety.
 34 citations,
August 2003 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology”
34 citations,
August 2003 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology” Pregnant women's hair gets thicker.





























