 5 citations,
August 2015 in “Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry”
5 citations,
August 2015 in “Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry” Obese mice with a leptin gene mutation have a longer resting phase in their hair cycle, which may help understand certain hair loss conditions.
[object Object] 9 citations,
April 2019 in “Bioscience, biotechnology, and biochemistry” Ten miRNAs may play key roles in starting secondary hair follicle development in sheep foetuses.
 February 2014 in “Medicine - Programa De Formación Médica Continuada Acreditado”
February 2014 in “Medicine - Programa De Formación Médica Continuada Acreditado” The document concludes that non-scarring alopecias can be reversed, but scarring alopecias cause permanent hair loss.
 March 2009 in “Medical & surgical dermatology”
March 2009 in “Medical & surgical dermatology” Women with androgenetic alopecia have fewer terminal hairs, phenol in nail surgery is safe, and a new hair transplant method is faster and less damaging.
 28 citations,
March 2016 in “Toxicologic pathology”
28 citations,
March 2016 in “Toxicologic pathology” Dogs could be good models for studying human hair growth and hair loss.
 42 citations,
July 2012 in “PLOS ONE”
42 citations,
July 2012 in “PLOS ONE” Estrogen can temporarily slow down hair growth but this can be reversed.
 January 2012 in “Journal of the Dermatology Nurses’ Association”
January 2012 in “Journal of the Dermatology Nurses’ Association” The document explains hair growth, hair loss types, and other hair-related terms.
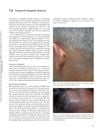 April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks”
April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks” Temporal triangular alopecia is a lifelong condition with hairless patches on the side of the head that may be present from birth.
 June 2018 in “Advances in Cosmetic Surgery”
June 2018 in “Advances in Cosmetic Surgery” Hair loss caused by genetics and hormones; more research needed for treatments.
 April 2021 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
April 2021 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” 6.1% of patients seeking PRP for hair loss had undiagnosed cicatricial alopecia, which PRP cannot treat.
 7 citations,
November 2000 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
7 citations,
November 2000 in “Clinics in Dermatology” Most hair loss in children is caused by a few common conditions and is easy to diagnose, but rare types require careful evaluation.
[object Object]  4 citations,
March 2013 in “The American Journal of Cosmetic Surgery”
4 citations,
March 2013 in “The American Journal of Cosmetic Surgery” Melanin absorbing light is necessary but not enough for effective hair removal by light treatment.
 59 citations,
March 2020 in “Journal of Biomedical Science”
59 citations,
March 2020 in “Journal of Biomedical Science” Understanding how hair follicle stem cells work can help find new ways to prevent hair loss and promote hair growth.
 66 citations,
July 2015 in “Journal of Molecular Biology”
66 citations,
July 2015 in “Journal of Molecular Biology” The document concludes that for hair and feather growth, it's better to target the environment around stem cells than the cells themselves.
11 citations,
May 2012 in “Genesis” Bmpr2 and Acvr2a receptors are crucial for hair retention and color.
 37 citations,
June 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
37 citations,
June 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Blocking a protein called CXXC5 with a specific peptide can stimulate hair regrowth and new hair growth in wounds.
 38 citations,
June 2017 in “The Journal of Dermatology”
38 citations,
June 2017 in “The Journal of Dermatology” Aging in hair follicle stem cells leads to hair graying, thinning, and loss.
 January 2019 in “Springer eBooks”
January 2019 in “Springer eBooks” Micrografts are useful for healing wounds, regenerating bone and periodontal tissues, and improving hair transplantation outcomes.
 88 citations,
July 2019 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
88 citations,
July 2019 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” Using human fat tissue derived stem cells in micrografts can safely and effectively increase hair density in people with hair loss.
 8 citations,
March 2019 in “Open Biology”
8 citations,
March 2019 in “Open Biology” The document concludes that regenerating functional ectodermal organs like teeth and hair is promising for future therapies.
 12 citations,
May 1989 in “Postgraduate Medicine”
12 citations,
May 1989 in “Postgraduate Medicine” The document concludes that hair loss is common and can be treated with medications like minoxidil or surgical options, and it significantly affects people's psychological well-being.
 6 citations,
January 2010 in “Springer eBooks”
6 citations,
January 2010 in “Springer eBooks” SA linked to mitochondrial issues and oxidative stress, while AGA involves disrupted hair growth genes.
 3 citations,
April 2011 in “Expert Review of Dermatology”
3 citations,
April 2011 in “Expert Review of Dermatology” Male hair loss is caused by inactive hair follicle stem cells.
 19 citations,
November 2011 in “Journal of Dermatological Science”
19 citations,
November 2011 in “Journal of Dermatological Science” TGF-β1 increases androgen receptor activity in hair loss, but Hic-5/ARA55 can counter this effect.
 21 citations,
December 2013 in “Archives of Dermatological Research”
21 citations,
December 2013 in “Archives of Dermatological Research” No link found between new male baldness genes and female hair loss.
 4 citations,
December 2022 in “Advanced science”
4 citations,
December 2022 in “Advanced science” SCD1 is important for hair growth by keeping the connection in skin cells where hair stem cells live stable.
 103 citations,
March 2015 in “Nature Communications”
103 citations,
March 2015 in “Nature Communications” A genetic region near the PAX1 gene is linked to a higher risk of scoliosis in females.
 1 citations,
September 2011 in “Journal of Dermatology”
1 citations,
September 2011 in “Journal of Dermatology” A woman with a new PTCH gene mutation has both Gorlin syndrome and severe hair loss.
 26 citations,
October 2011 in “International Journal of Biological Macromolecules”
26 citations,
October 2011 in “International Journal of Biological Macromolecules” Some newly made compounds are promising for treating enlarged prostate, hair loss, viruses, and prostate cancer, and might be better than current drugs.
 19 citations,
May 2020 in “Cells”
19 citations,
May 2020 in “Cells” Substance from human umbilical cord blood cells promotes hair growth.




























