 17 citations,
February 2003 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology”
17 citations,
February 2003 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology” Hair loss in postmenopausal woman caused by ovarian issue.
 40 citations,
October 2012 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
40 citations,
October 2012 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Minoxidil helps regrow hair in female pattern hair loss, but more research needed for other treatments.
 May 2006 in “Women's Health Medicine”
May 2006 in “Women's Health Medicine” Excessive hair growth in women, often from high androgen levels, is usually caused by PCOS, and can be treated with hair removal, medication, and possibly weight loss.
 1 citations,
December 2010 in “InnovAiT”
1 citations,
December 2010 in “InnovAiT” The document concludes that accurate diagnosis and appropriate management are crucial for treating various hair disorders, which have significant psychological impacts.
 207 citations,
April 2006 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
207 citations,
April 2006 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Iron deficiency may be related to hair loss, but there's not enough evidence to recommend iron screening or supplements for all hair loss patients.
 39 citations,
May 2011 in “European Journal of Clinical Investigation”
39 citations,
May 2011 in “European Journal of Clinical Investigation” Hirsutism can be caused by various conditions besides PCOS, and it's important to treat the underlying issue and manage symptoms with medication and cosmetic approaches.
 8 citations,
March 2021 in “Medicina-lithuania”
8 citations,
March 2021 in “Medicina-lithuania” PRP treatment may promote hair growth and improve hair density in women with AGA, but more research is needed.
 3 citations,
April 2012 in “Osteoporosis International”
3 citations,
April 2012 in “Osteoporosis International” A woman experienced hair loss after taking strontium ranelate for osteoporosis.
 28 citations,
January 2012 in “International Journal of Trichology”
28 citations,
January 2012 in “International Journal of Trichology” Genetics affect early female hair loss, severity depends on duration, and low ferritin levels not significant.
 75 citations,
February 2016 in “The Journal of Sexual Medicine”
75 citations,
February 2016 in “The Journal of Sexual Medicine” Androgens play a role in female sexual function, and testosterone therapy can help women with low sexual desire, but more research is needed on treatments and long-term safety.
 December 2023 in “International journal of research in dermatology”
December 2023 in “International journal of research in dermatology” The ayurvedic hair oil is safe and effective for reducing hair fall, promoting hair growth, and improving scalp health.
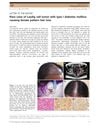 August 2019 in “Journal of Dermatology”
August 2019 in “Journal of Dermatology” Woman with diabetes had hair loss due to rare ovarian tumor; surgery improved hair growth.
 28 citations,
August 2000 in “Current Opinion in Chemical Biology”
28 citations,
August 2000 in “Current Opinion in Chemical Biology” Future osteoporosis treatments should focus on increasing bone growth, with many promising options available.
74 citations,
February 2018 in “Stroke” Women have unique stroke risks due to hormones, contraceptives, pregnancy, and menopause.
 112 citations,
May 2019 in “Pharmacological Research”
112 citations,
May 2019 in “Pharmacological Research” Lignans and neolignans from plants may help protect against various health issues, including cancer and heart disease.
 October 2023 in “Dermatological reviews”
October 2023 in “Dermatological reviews” Fibroblast-derived growth factors and exosomes can significantly improve skin aging.
 22 citations,
November 2018 in “Breast Cancer Research and Treatment”
22 citations,
November 2018 in “Breast Cancer Research and Treatment” The medications 5α-reductase inhibitors and spironolactone are generally safe for breast cancer patients on endocrine therapies and do not significantly increase breast cancer risk.
 1533 citations,
October 2008 in “Endocrine reviews”
1533 citations,
October 2008 in “Endocrine reviews” Mice without the vitamin D receptor have bone issues and other health problems, suggesting vitamin D is important for preventing various diseases in humans.
 1 citations,
December 2005 in “Therapeutische Umschau”
1 citations,
December 2005 in “Therapeutische Umschau” The document concludes that protecting skin from the sun, avoiding smoking, and using treatments like Minoxidil and Finasteride can help manage skin and hair aging.
26 citations,
July 2012 in “Journal of family planning and reproductive health care” The document says that hirsutism in women usually needs hair removal and hormone treatment to manage symptoms and improve well-being.
 44 citations,
March 2008 in “European journal of endocrinology”
44 citations,
March 2008 in “European journal of endocrinology” Women with PCOS have lower ghrelin levels and a weaker response to sugar, which might affect their feeling of fullness and lead to overeating.
89 citations,
August 2013 in “PloS one” Androgen receptors are active in many tissues of both male and female mice, not just reproductive organs.
 1 citations,
August 2023 in “Curēus”
1 citations,
August 2023 in “Curēus” Metformin helps reduce PCOS-related infertility by improving insulin sensitivity and inducing ovulation.
 August 2019 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
August 2019 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” 5% minoxidil foam effectively regrows hair in women, with postmenopausal women seeing the most improvement.
 3 citations,
March 2019 in “Post Reproductive Health”
3 citations,
March 2019 in “Post Reproductive Health” Testosterone replacement can help menopausal women with various symptoms, but should be used carefully and is not yet officially licensed in the UK for women.
24 citations,
May 2015 in “Molecular and clinical oncology” Honey and bee pollen can help reduce menopausal symptoms in breast cancer patients.
 January 2018 in “Springer eBooks”
January 2018 in “Springer eBooks” Lasers are less favored for hair transplant surgery but show promise for hair growth in controlled trials.
 34 citations,
May 2013 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
34 citations,
May 2013 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Hair growth slows and shedding increases after childbirth, but most women don't experience excessive hair loss.
 39 citations,
October 1967 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
39 citations,
October 1967 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Hair loss in women often doesn't follow a pattern, isn't linked to age, may be genetic, and can be related to thyroid issues or other health factors.
 November 2022 in “Journal of the Endocrine Society”
November 2022 in “Journal of the Endocrine Society” Removing the ovarian tumor improved the woman's hormonal symptoms.


























