 38 citations,
September 2017 in “Oncologist”
38 citations,
September 2017 in “Oncologist” Scalp cooling can help prevent chemotherapy-induced hair loss with a 50-90% success rate and is safe for patients.
 April 2003 in “Experimental Dermatology”
April 2003 in “Experimental Dermatology” The workshop highlighted the genetic links and psychological impacts of hair loss and skin disorders.
 1 citations,
May 2023 in “European Journal of Human Genetics”
1 citations,
May 2023 in “European Journal of Human Genetics” Rare ULBP3 gene changes may raise the risk of Alopecia areata, a certain FAS gene deletion could cause a dysfunctional protein in an immune disorder, and having one copy of a specific genetic deletion is okay, but two copies cause sickle cell disease.
 9 citations,
January 2015 in “Springer eBooks”
9 citations,
January 2015 in “Springer eBooks” The document concludes that managing PCOS involves treating symptoms, regulating periods, and reducing health risks, with specific medications for fertility and metabolic issues.
 June 2023 in “International journal of biology, pharmacy and allied sciences”
June 2023 in “International journal of biology, pharmacy and allied sciences” New medications are improving depression treatment, emphasizing accurate diagnosis and chronic care.
 1 citations,
October 2022 in “Springer eBooks”
1 citations,
October 2022 in “Springer eBooks” Testosterone is key for male sexual function, and treating hormone imbalances can improve sexual issues.
 June 1996 in “Irish Journal of Medical Science (1971 -)”
June 1996 in “Irish Journal of Medical Science (1971 -)” The document summarizes medical findings on topics like heart rhythm treatment, sleep apnea therapy, and various health conditions and treatments.
 2 citations,
June 2011 in “Expert Review of Dermatology”
2 citations,
June 2011 in “Expert Review of Dermatology” Female pattern hair loss involves thinning hair on crown and frontal scalp, diagnosed by hair ratio, and treated with minoxidil, antiandrogens, or hair transplantation.
 October 2024 in “Journal of the Endocrine Society”
October 2024 in “Journal of the Endocrine Society” Leydig cell tumors can cause high testosterone and symptoms like hair loss in postmenopausal women, but surgery can improve these symptoms.
 October 2024 in “Journal of the Endocrine Society”
October 2024 in “Journal of the Endocrine Society” Leydig cell tumors can cause high testosterone and symptoms in postmenopausal women, and removing them improves symptoms.
 2 citations,
April 2016 in “Más dermatología”
2 citations,
April 2016 in “Más dermatología” The supplement with Serenoa repens and Pygeum africanum significantly increased active hair growth and decreased rest phase hair in post-menopausal women with hair loss, with only mild digestive side effects.
 130 citations,
May 1988 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
130 citations,
May 1988 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” "Male-pattern" hair loss is common in women, especially after menopause, and doesn't always mean there's a problem with hormone balance.
 1 citations,
November 2002 in “Endocrine practice”
1 citations,
November 2002 in “Endocrine practice” The patient's high testosterone was reduced by a medication that suppresses gonadotropin.
 4 citations,
January 2015 in “Endocrinology & metabolic syndrome”
4 citations,
January 2015 in “Endocrinology & metabolic syndrome” Testosterone can cause acne and male-pattern baldness, affects hair growth in men and women, and makes male skin more sensitive.

Finasteride and low-level laser therapy are similarly effective for frontal pattern hair loss.
 17 citations,
April 2006 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
17 citations,
April 2006 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Older women face various skin issues like dryness and thinning, and treatments are available but can have side effects; proper skin care and legal health decisions are important.
 10 citations,
December 2010 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
10 citations,
December 2010 in “British Journal of Dermatology” After menopause, some women lose scalp hair and gain facial hair, with patterns suggesting different underlying causes.
 38 citations,
December 2011 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
38 citations,
December 2011 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Menopause-related hormonal changes affect hair but are not the only cause of hair changes in middle-aged women.
 14 citations,
July 1987 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
14 citations,
July 1987 in “Dermatologic Clinics” The document concludes that treating female hair loss should target reducing excess androgen and blocking its effects on hair follicles, with the best treatments being hormonal therapy, adrenal suppression, and topical minoxidil.
 May 2021 in “Journal of the Endocrine Society”
May 2021 in “Journal of the Endocrine Society” A rare ovarian cancer with a good outlook was found in a woman with unusual hair growth and abdominal symptoms.
 January 2013 in “Revista Clínica Española”
January 2013 in “Revista Clínica Española” A postmenopausal woman's increased male hormone levels were successfully treated with surgery.
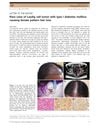 August 2019 in “Journal of Dermatology”
August 2019 in “Journal of Dermatology” Woman with diabetes had hair loss due to rare ovarian tumor; surgery improved hair growth.
 3 citations,
September 2014 in “Journal of obstetrics and gynaecology Canada”
3 citations,
September 2014 in “Journal of obstetrics and gynaecology Canada” Menopause often leads to lower sexual desire and discomfort during sex, but treatment should be personalized and only if it bothers the woman.
 June 2003 in “Obstetrical & Gynecological Survey”
June 2003 in “Obstetrical & Gynecological Survey” After chemotherapy for a gestational trophoblastic tumor, normal pregnancy rates are possible, but there's a slightly higher risk of the tumor reoccurring in future pregnancies.
 370 citations,
September 1999 in “The New England Journal of Medicine”
370 citations,
September 1999 in “The New England Journal of Medicine” Finasteride and minoxidil are effective for hair loss, but continued research is needed for better treatments.
 8 citations,
March 2006 in “Seminars in Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
8 citations,
March 2006 in “Seminars in Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” Hair transplantation has improved to look more natural, but managing patient expectations and using precise techniques are key for the best outcomes.
 4 citations,
March 2021 in “Case Reports”
4 citations,
March 2021 in “Case Reports” A woman's excessive hair growth and masculine features were due to a rare benign ovarian tumor and endometrial cancer, which improved after surgery.
 3 citations,
January 2007 in “Elsevier eBooks”
3 citations,
January 2007 in “Elsevier eBooks” The document concludes that individualized treatment and lifestyle changes are important for managing menopause symptoms and health risks.
 2 citations,
October 2015 in “The New England Journal of Medicine”
2 citations,
October 2015 in “The New England Journal of Medicine” The woman's surgery lowered her testosterone and improved scalp hair loss but did not change her excessive body hair.
 September 2014 in “Springer eBooks”
September 2014 in “Springer eBooks” Men and women experience skin aging differently due to changes in sex hormone levels with age.






























