 19 citations,
May 2019 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
19 citations,
May 2019 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” Platelet-rich plasma is a safe and effective treatment for hair loss, with fewer relapses than steroid treatment.
[object Object]  16 citations,
July 2016 in “Journal of Dermatological Science”
16 citations,
July 2016 in “Journal of Dermatological Science” Regenerated hairs can regain their color if the wound occurs during a certain stage of hair growth, and this process is helped by specific skin cells and proteins.
 13 citations,
January 2014 in “Postępy Dermatologii i Alergologii”
13 citations,
January 2014 in “Postępy Dermatologii i Alergologii” Patchy alopecia areata can affect only pigmented hairs, leaving gray hairs untouched.
 37 citations,
February 2019 in “Experimental Dermatology”
37 citations,
February 2019 in “Experimental Dermatology” Spiny mice are better at regenerating hair after injury than laboratory mice and could help us understand how to improve human skin repair.
 19 citations,
December 2008 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
19 citations,
December 2008 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” The authors suggest that a new type of hair loss exists, which is different from alopecia areata.
 January 2023 in “Indian Dermatology Online Journal”
January 2023 in “Indian Dermatology Online Journal” Bimatoprost and clobetasol are both effective for scalp hair loss, but bimatoprost works faster, has fewer side effects, and grows more colored hair.
 67 citations,
August 2013 in “International Journal of Cosmetic Science”
67 citations,
August 2013 in “International Journal of Cosmetic Science” Hair greying is caused by oxidative stress damaging hair follicles and melanocytes.
 6 citations,
March 1982 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology”
6 citations,
March 1982 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology” The document says that hair loss in women is often due to androgenic alopecia, similar to male baldness, and that hirsutism is treated with hormonal and cosmetic methods.
 25 citations,
June 2015 in “Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology”
25 citations,
June 2015 in “Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology” Microneedling helps increase the absorption of a melanin product into hair follicles, which may improve laser hair removal effectiveness.
 19 citations,
July 2006 in “Lasers in medical science”
19 citations,
July 2006 in “Lasers in medical science” Laser hair removal is safe and effective for fair-skinned people with dark hair, and using eflornithine with laser treatments can improve results.
 July 2023 in “Clinical dermatology review”
July 2023 in “Clinical dermatology review” Intralesional triamcinolone acetonide is better than PRP for treating scalp alopecia areata, leading to faster and more complete hair regrowth.
 June 2012 in “Expert Review of Dermatology”
June 2012 in “Expert Review of Dermatology” Japanese researchers created new hair follicles from human cells that grew hair when put into mice, and other findings showed a link between eye disease severity and corneal thickness, gene mutations affecting hearing and touch, and the safety of the shingles vaccine for adults over 50.
46 citations,
April 1982 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Isotretinoin shrinks sebaceous glands without affecting hair or skin color, unlike etretinate.
 36 citations,
June 2009 in “Archives of Dermatology”
36 citations,
June 2009 in “Archives of Dermatology” Marie Antoinette syndrome causes sudden hair whitening, but its exact cause is unknown.
 33 citations,
September 2012 in “Wound Repair and Regeneration”
33 citations,
September 2012 in “Wound Repair and Regeneration” Applying calreticulin can speed up wound healing in diabetics.
 31 citations,
April 2019 in “Cell reports”
31 citations,
April 2019 in “Cell reports” Patient-derived melanocytes can potentially treat vitiligo by restoring skin pigmentation.
 30 citations,
December 2001 in “Experimental dermatology”
30 citations,
December 2001 in “Experimental dermatology” Gonadal hormones significantly affect the severity of alopecia areata in mice.
 April 2015 in “Archives of disease in childhood”
April 2015 in “Archives of disease in childhood” A chubby child can still be malnourished.

Melanocyte transplantation can safely restore skin color, especially in stable vitiligo, but must be chosen carefully based on the disease phase.
 33 citations,
December 2005 in “Archives of dermatology”
33 citations,
December 2005 in “Archives of dermatology” Alefacept showed some effectiveness for alopecia areata but needs more research.
 18 citations,
April 2004 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
18 citations,
April 2004 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Skin patterns are formed by simple reaction-diffusion mechanisms.
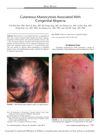 3 citations,
February 2012 in “The American Journal of Dermatopathology”
3 citations,
February 2012 in “The American Journal of Dermatopathology” A 3-year-old girl with skin mast cell buildup and congenital baldness improved with treatment, suggesting a rare link between these conditions.
 73 citations,
April 1999 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
73 citations,
April 1999 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Lasers and light sources can effectively remove hair, work best on fair skin with dark hair, and usually need multiple treatments.
 14 citations,
October 2020 in “Scientific reports”
14 citations,
October 2020 in “Scientific reports” Hair greying is linked to reduced ATM protein in hair cells, which protects against stress and damage.
 209 citations,
September 2008 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
209 citations,
September 2008 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Androgens can both increase and decrease hair growth in different parts of the body.
 207 citations,
January 2011 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
207 citations,
January 2011 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Laser hair removal is the most requested cosmetic procedure and has become a scientifically-based treatment suitable for all skin types.
[object Object]  130 citations,
August 2015 in “Experimental Dermatology”
130 citations,
August 2015 in “Experimental Dermatology” Human hair follicle organ culture is a useful model for hair research with potential for studying hair biology and testing treatments.
 112 citations,
July 1998 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
112 citations,
July 1998 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Ruby laser pulses best destroy hair follicles during the growth phase and effectiveness varies with laser intensity; melanin is key for targeting, and timing treatments can improve results.
 109 citations,
December 1998 in “The Journal of Dermatology”
109 citations,
December 1998 in “The Journal of Dermatology” Manipulating the catagen and telogen phases of hair growth could lead to treatments for hair disorders.
 107 citations,
December 2013 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
107 citations,
December 2013 in “International Journal of Dermatology” The document concludes that hair is complex, with a detailed growth cycle, structure, and clinical importance, affecting various scientific and medical fields.





























