13 citations,
November 2022 in “Biomaterials Science” The microneedle patch effectively promotes hair regrowth by delivering miR-218.
 4 citations,
November 2022 in “Frontiers in Immunology”
4 citations,
November 2022 in “Frontiers in Immunology” Lung and liver macrophages protect our tissues and their dysfunction can cause various diseases.
 1 citations,
April 2023 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
1 citations,
April 2023 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” New CRISPR/Cas9 variants and nanotechnology-based delivery methods are improving cancer treatment, but choosing the best variant and overcoming certain limitations remain challenges.
[object Object]  August 2022 in “IARS international research journal”
August 2022 in “IARS international research journal” The document concludes that drug repurposing, which is reusing known medicines for new illnesses, can provide faster, cheaper treatment options for various serious diseases, including cancer, COVID-19, and rare diseases.
 April 2011 in “한국생물공학회 학술대회”
April 2011 in “한국생물공학회 학술대회” Lotion with fucoidan from brown seaweed improved skin and reduced allergy symptoms in mice with dermatitis.
 165 citations,
February 2014 in “Phytotherapy Research”
165 citations,
February 2014 in “Phytotherapy Research” Myrtle has various health benefits and potential for medicine development.
1 citations,
May 2024 in “Pharmaceutics” Hemp is a promising ingredient for skin products due to its healing and soothing properties.
1 citations,
February 2024 in “Cosmetics” Cannabidiol shows promise as an effective treatment for acne.
 17 citations,
February 2011 in “Expert Opinion on Drug Safety”
17 citations,
February 2011 in “Expert Opinion on Drug Safety” Manage side effects of hepatitis C treatment with dose changes and medications, which may improve patient adherence and treatment success.
 17 citations,
January 2011 in “The Korean Journal of Hepatology”
17 citations,
January 2011 in “The Korean Journal of Hepatology” Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada disease can develop during interferon therapy for chronic hepatitis C.
11 citations,
April 2014 in “Journal of Clinical Virology” Older age, pre-existing skin conditions, cirrhosis, and pegylated interferon use increase the risk of skin issues during hepatitis C treatment.
 10 citations,
September 2014 in “European Journal of Dermatology”
10 citations,
September 2014 in “European Journal of Dermatology” A woman's hair loss worsened after starting hepatitis C treatment due to immune changes in her hair follicles.
 9 citations,
November 2012 in “Hepatology Research”
9 citations,
November 2012 in “Hepatology Research” A man lost all his hair permanently after hepatitis C treatment, a side effect not seen before.
 7 citations,
May 2016 in “European Polymer Journal”
7 citations,
May 2016 in “European Polymer Journal” The new nanocarriers improve how well water-insoluble drugs dissolve and allow for controlled drug release.
 6 citations,
October 2016 in “Journal of Chemotherapy”
6 citations,
October 2016 in “Journal of Chemotherapy” A man lost all his hair as a rare side effect after hepatitis C treatment.
 3 citations,
March 2014 in “Annals of Hepatology”
3 citations,
March 2014 in “Annals of Hepatology” A man lost all his hair after stopping hepatitis C treatment and it didn't grow back.
 2 citations,
March 2015 in “Hepatitis Monthly”
2 citations,
March 2015 in “Hepatitis Monthly” A woman's hair loss during Hepatitis C treatment with PEG-INF-a-2a and Ribavirin was reversible after stopping the medication.
 April 2024 in “Journal of applied cosmetology”
April 2024 in “Journal of applied cosmetology” Using hyaluronic acid fillers in the temple area of the face can improve looks but has risks, so choosing the right technique and product is important for safety.
 January 2014 in “대한피부과학회지”
January 2014 in “대한피부과학회지” A hepatitis B patient lost hair in patches after starting and stopping a treatment with pegylated interferon alpha2a.
2 citations,
November 2004 in “Hospital pharmacy” Certain medications can cause serious side effects, so it's important to report them.
[object Object]  26 citations,
June 2005 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
26 citations,
June 2005 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Some patients receiving pegylated interferon alfa injections developed skin necrosis, requiring treatment adjustments or discontinuation.
 32 citations,
October 2004 in “Pharmacotherapy”
32 citations,
October 2004 in “Pharmacotherapy” Peginterferon alfa-2b and ribavirin therapy for hepatitis C can cause serious side effects, some different from those reported in clinical trials.
 29 citations,
December 2017 in “Molecular therapy”
29 citations,
December 2017 in “Molecular therapy” Enzyme replacement therapy improved multiple symptoms of homocystinuria in mice.
 4 citations,
August 2007 in “PubMed”
4 citations,
August 2007 in “PubMed” A woman lost all her body hair after hepatitis C treatment, but it started to grow back a year after stopping the treatment.
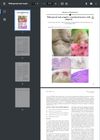 November 2022 in “JAAD case reports”
November 2022 in “JAAD case reports” A man with skin and hair symptoms improved partially with specific treatment.
 January 2011 in “Annals of dermatology/Annals of Dermatology”
January 2011 in “Annals of dermatology/Annals of Dermatology” A woman's psoriasis improved after hepatitis C treatment with interferon, despite interferon's risk of worsening skin conditions.
March 2019 in “SLAS TECHNOLOGY” New technologies show promise in healing wounds, treating cancer, autoimmune diseases, and genetic disorders.
 January 2003 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology”
January 2003 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology” Various drugs caused different skin reactions, including allergic and inflammatory responses.
 1 citations,
January 2014 in “Hair therapy & transplantation”
1 citations,
January 2014 in “Hair therapy & transplantation” The combination therapy of PEG-IFN α-2a and Ribavirin can cause widespread hair loss and skin reactions.
 41 citations,
August 2007 in “European Journal of Gastroenterology & Hepatology”
41 citations,
August 2007 in “European Journal of Gastroenterology & Hepatology” A woman's total hair loss from hepatitis C treatment grew back after stopping the medication.























