 June 2021 in “Dermatology Online Journal”
June 2021 in “Dermatology Online Journal” A girl with a rare genetic condition affecting hair and nails also developed a common type of hair loss, suggesting a possible genetic link.
 1 citations,
September 2020 in “Cochrane library (CD-ROM)”
1 citations,
September 2020 in “Cochrane library (CD-ROM)” The analysis aims to identify the most effective and safest treatments for alopecia areata.
 September 2023 in “Medical and Clinical Case Reports”
September 2023 in “Medical and Clinical Case Reports” People with Alopecia Areata often have thyroid problems like Hashimoto thyroiditis and hypothyroidism.
 April 2021 in “Sohag Medical Journal”
April 2021 in “Sohag Medical Journal” Superficial cryotherapy is effective and safe for treating alopecia areata, especially eyebrow hair loss.
 20 citations,
March 2019 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
20 citations,
March 2019 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Minoxidil effectively and safely treats patchy hair loss, but more research needed.
 January 2023 in “Voprosy kurortologii fizioterapii i lechebnoĭ fizicheskoĭ kultury”
January 2023 in “Voprosy kurortologii fizioterapii i lechebnoĭ fizicheskoĭ kultury” COVID-19 may cause hair loss, often after recovery, with androgenetic alopecia being the most common type.
 1 citations,
July 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks”
1 citations,
July 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks” Alopecia Areata is an autoimmune hair loss condition, with various treatments showing mixed effectiveness and no guaranteed cure.
 May 2017 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
May 2017 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Certain factors like patchy hair loss at the back of the head, being female, and younger age at diagnosis can lead to a worse outcome for alopecia areata.
 16 citations,
November 2005 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings”
16 citations,
November 2005 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings” Blocking interferon-gamma helps prevent and treat hair loss in Alopecia Areata.
 13 citations,
December 2001 in “Dermatologic therapy”
13 citations,
December 2001 in “Dermatologic therapy” Alopecia areata causes varying hair loss patterns, affecting hair, nails, and possibly glands, with treatment outcomes depending on disease duration and extent.
36 citations,
July 2007 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Certain HLA class II alleles increase or decrease the risk of alopecia areata.
 24 citations,
January 2012 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology”
24 citations,
January 2012 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology” Diffuse alopecia areata involves more inflammation and higher allergy-related antibodies than patchy types.
 June 2022 in “Journal of pharmaceutical research international”
June 2022 in “Journal of pharmaceutical research international” Alopecia causes patchy hair loss and can be diagnosed with new techniques; treatments like strong creams and contact immunotherapy can help.
 August 2023 in “Medical Hypotheses”
August 2023 in “Medical Hypotheses” Metformin, usually used for diabetes, can also help treat hair loss from alopecia areata due to its ability to reduce inflammation and stimulate new hair growth.
 March 2023 in “International journal of trichology”
March 2023 in “International journal of trichology” Six genetic conditions are often linked to complete scalp hair loss in children.
 45 citations,
December 2014 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
45 citations,
December 2014 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Plasmacytoid dendritic cells are a key factor in causing hair loss in alopecia areata and could help differentiate it from other hair loss conditions.
 1 citations,
October 2020 in “International Journal of Research in Dermatology”
1 citations,
October 2020 in “International Journal of Research in Dermatology” The study concluded that short vellus hair and yellow dots were the most common signs of alopecia areata, indicating disease activity and remission.
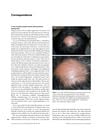 11 citations,
July 2008 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
11 citations,
July 2008 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Greying hairs may be protected from alopecia areata.
January 2014 in “DOAJ (DOAJ: Directory of Open Access Journals)” Minoxidil can effectively treat patchy hair loss by stimulating hair growth.
 December 2024 in “Journal of Clinical Medicine”
December 2024 in “Journal of Clinical Medicine” Minoxidil shows promise for alopecia areata, but more research is needed before it can be recommended as a primary treatment.
 30 citations,
May 2004 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft”
30 citations,
May 2004 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft” The document concludes that early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for children with hair loss to prevent permanent damage, although not all conditions can be effectively treated.
 35 citations,
January 1993 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
35 citations,
January 1993 in “International Journal of Dermatology” People with HIV and low T cell counts have more hair and scalp problems.
75 citations,
June 2005 in “Archives of Dermatology” Etanercept may not prevent alopecia areata from coming back.
April 2024 in “Cosmetics” Wigs help improve self-esteem and quality of life for people with hair loss from alopecia areata.
April 2017 in “Al-Azhar Medical Journal” PRP is an effective and safe treatment for alopecia areata.
 February 2024 in “Actas dermo-sifiliográficas/Actas dermo-sifiliográficas”
February 2024 in “Actas dermo-sifiliográficas/Actas dermo-sifiliográficas” Most alopecia areata patients in the study were women, aged 15-49, with patchy hair loss and often had other health conditions.
November 2021 in “CRC Press eBooks” Tinea capitis is a fungal infection of the scalp that mainly affects children and can cause symptoms from mild itching to severe inflammation.
 January 2025 in “Journal of Personalized Medicine”
January 2025 in “Journal of Personalized Medicine” People with Alopecia Areata are more likely to have prediabetes and obesity.

Alopecia areata, a type of hair loss, may be passed through T cells and has genetic links, while treatments vary in effectiveness. Male pattern baldness can be treated with finasteride and is influenced by androgens in hair follicles.
 36 citations,
January 2015 in “Dermatology”
36 citations,
January 2015 in “Dermatology” Bimatoprost was found to be safer and more effective than mometasone furoate for treating scalp hair loss.
























