 January 2007 in “Elsevier eBooks”
January 2007 in “Elsevier eBooks” Alopecia areata is a reversible, autoimmune-related hair loss that can have significant emotional impact and uncertain treatment effectiveness.
[object Object] 
A patient with patchy hair loss was successfully treated for Tumid Lupus Erythematosus after other treatments failed.
 January 2021 in “International journal of dermatology, venereology and leprosy sciences”
January 2021 in “International journal of dermatology, venereology and leprosy sciences” Trichoscopy shows black dots, yellow dots, and empty follicles are common in Alopecia Areata, with broken and exclamation mark hair as typical patterns.
 July 2023 in “IntechOpen eBooks”
July 2023 in “IntechOpen eBooks” Some types of hair loss can be reversed, others are permanent, and treatments vary by type.
 3 citations,
December 2020 in “Polski merkuriusz lekarski : organ Polskiego Towarzystwa Lekarskiego”
3 citations,
December 2020 in “Polski merkuriusz lekarski : organ Polskiego Towarzystwa Lekarskiego” People with androgenetic alopecia often experience high stress, but the stress doesn't affect how the disease progresses or how well different treatments work.
 November 2019 in “Journal of Aesthetic Nursing”
November 2019 in “Journal of Aesthetic Nursing” The article concludes that a thorough diagnosis and treatment plan, including medications, non-invasive methods, or surgery, is important for managing hair loss, with a combination of minoxidil and finasteride being particularly effective.
 December 2023 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
December 2023 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” Baricitinib effectively and safely improves hair growth in patients with severe alopecia areata.
 January 2025 in “Clinical Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology”
January 2025 in “Clinical Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology” Pediatric alopecia areata is more immune-active than adult cases, suggesting age-specific treatments and potential use of JAK inhibitors.

Minoxidil and finasteride are the only FDA-approved treatments for hair loss caused by genetic and hormonal factors, but their effectiveness is often doubted, indicating a need for new treatments.
 13 citations,
October 2017 in “Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia”
13 citations,
October 2017 in “Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia” Yellow dots in hair and scalp examinations are important for diagnosing different scalp conditions.
1 citations,
March 2022 in “Dermatology Research and Practice” Higher CD70 and CD27 gene expression in alopecia areata lesions predicts disease severity and activity.
 2 citations,
January 2022 in “Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology”
2 citations,
January 2022 in “Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology” The refined wash test is a reliable way to measure daily hair loss and can tell the difference between different types of hair loss.
 June 2023 in “Stem cell reviews and reports”
June 2023 in “Stem cell reviews and reports” Stem cell therapies could be a promising alternative for hair loss treatment, but more research is needed to understand their full potential and safety.
2 citations,
January 2022 in “Anais brasileiros de dermatologia/Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia” Chemical hair straighteners can cause scalp and hair damage, but long-term effects are unclear.
1 citations,
April 2024 in “Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology” Microneedles combined with conventional therapies show promise in treating alopecia areata.
 9 citations,
June 2008 in “Springer eBooks”
9 citations,
June 2008 in “Springer eBooks” Understanding hair follicle structure is key for treating hair disorders and could help develop new treatments.
 37 citations,
October 2015 in “Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia”
37 citations,
October 2015 in “Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia” Lichen planopilaris mostly affects women with fair skin and can look different on each person, needing early treatment to prevent hair loss.
 July 2024 in “Dermatology Practical & Conceptual”
July 2024 in “Dermatology Practical & Conceptual” COVID-19-related hair loss may have unique features compared to hair loss from other causes.
 1 citations,
November 2015 in “Journal of Evolution of Medical and Dental Sciences”
1 citations,
November 2015 in “Journal of Evolution of Medical and Dental Sciences” Certain skin symptoms can help detect and manage systemic lupus.
 14 citations,
October 2006 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
14 citations,
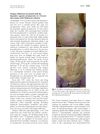
October 2006 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” A woman with Parkinson's disease experienced hair loss from the Parkinson's medication pramipexole, which improved after stopping the drug.
 6 citations,
June 2018 in “Journal of Stomatology, Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery”
6 citations,
June 2018 in “Journal of Stomatology, Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery” Nanofat grafting is better for delicate areas and combining it with lipofilling might improve hair loss treatment.
 September 2023 in “Çukurova medical journal (Online)/Çukurova medical journal”
September 2023 in “Çukurova medical journal (Online)/Çukurova medical journal” EZH2 levels decrease as fetuses develop and are higher in adult skin, which may affect skin growth and repair.
 January 2019 in “International journal of dermatology, venereology and leprosy sciences”
January 2019 in “International journal of dermatology, venereology and leprosy sciences” Hair loss in young adults is common and varies in pattern, cause, and type.
 14 citations,
April 2021 in “Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology”
14 citations,
April 2021 in “Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology” COVID-19 may trigger sudden temporary hair loss.
 1 citations,
May 2022 in “Frontiers in Psychiatry”
1 citations,
May 2022 in “Frontiers in Psychiatry” Hair loss was the first sign of a brain-related complication in a woman with lupus, and early treatment helped her hair grow back.
[object Object]  18 citations,
March 2022 in “Drug design, development and therapy”
18 citations,
March 2022 in “Drug design, development and therapy” Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) may help with various hair loss types, but more research is needed to find the best use method.
 December 2023 in “Portuguese journal of dermatology and venereology”
December 2023 in “Portuguese journal of dermatology and venereology” Trichoscopy can reliably distinguish between alopecia areata and trichotillomania.
 10 citations,
February 2020 in “Endocrine”
10 citations,
February 2020 in “Endocrine” Finasteride safely treats hair loss without harming hormones or reproduction, but may slightly reduce sexual function.
 8 citations,
December 2020 in “Skin appendage disorders”
8 citations,
December 2020 in “Skin appendage disorders” Low-dose oral minoxidil helped regrow eyebrows in women with Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia.
 2 citations,
April 2019 in “Acta medica Philippina/Acta Medica Philippina”
2 citations,
April 2019 in “Acta medica Philippina/Acta Medica Philippina” People with alopecia areata often have lower vitamin D levels than healthy people.



























