127 citations,
January 2000 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Cytotoxic T cells cause hair loss in chronic alopecia areata.
 63 citations,
December 1988 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
63 citations,
December 1988 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Vitiligo causes white skin patches and is linked to autoimmune issues.
 October 2021 in “The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine”
October 2021 in “The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine” Alopecia areata causes patchy hair loss and involves immune system disruptions.
 46 citations,
January 1996 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
46 citations,
January 1996 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” People with late-stage HIV-1 often experience a specific type of hair loss linked to multiple factors, including nutritional issues and immune responses.
 April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks”
April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks” Syphilitic alopecia is a rare hair loss condition in secondary syphilis that looks similar to another condition but can be diagnosed with specific tests and responds to antibiotics.
 43 citations,
May 2011 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
43 citations,
May 2011 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Recognizing the different stages of alopecia areata is crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
 15 citations,
March 2016 in “The American Journal of Dermatopathology”
15 citations,
March 2016 in “The American Journal of Dermatopathology” Demodex mites rarely cause scalp infections leading to hair loss, but when they do, treatment is effective.
 19 citations,
December 2001 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
19 citations,
December 2001 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Horizontal scalp biopsy sections are better for diagnosing alopecia areata, showing fewer hair follicles and more miniaturized hairs.
 15 citations,
July 1999 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
15 citations,
July 1999 in “Dermatologic Clinics” The document concludes that immune system abnormalities cause alopecia areata, but the exact process is still not completely understood.
 18 citations,
January 2017 in “Annals of dermatology/Annals of Dermatology”
18 citations,
January 2017 in “Annals of dermatology/Annals of Dermatology” Certain immune cells contribute to severe hair loss in chronic alopecia areata, with Th17 cells possibly having a bigger impact than cytotoxic T cells.
18 citations,
June 2010 in “Cell Stress and Chaperones” Heat treatment increases hair loss in certain mice.
 61 citations,
September 2010 in “Genomics”
61 citations,
September 2010 in “Genomics” The study found that immune responses disrupt hair growth cycles, causing hair loss in alopecia areata.
 2 citations,
September 2018 in “Tissue Engineering Part A”
2 citations,
September 2018 in “Tissue Engineering Part A” Xeno-free three-dimensional stem cell masses are safe and effective for improving blood flow and tissue repair in limb ischemia.
 23 citations,
January 2010 in “Journal of Medical Primatology”
23 citations,
January 2010 in “Journal of Medical Primatology” Hair loss in Rhesus macaques may be caused by a skin allergy-related condition.
 150 citations,
October 2010 in “The American Journal of Pathology”
150 citations,
October 2010 in “The American Journal of Pathology” The document concludes that more research is needed to better understand and treat primary cicatricial alopecias, and suggests a possible reclassification based on molecular pathways.
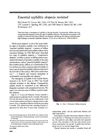 53 citations,
May 1995 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
53 citations,
May 1995 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Syphilis can cause hair loss that looks like other conditions, but it improves with treatment.
 23 citations,
June 2003 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings”
23 citations,
June 2003 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings” Alopecia Areata is an autoimmune disease affecting hair follicles, influenced by genetic and environmental factors, with rodent models being essential for research.
 22 citations,
June 2013 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology”
22 citations,
June 2013 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology” Early stage bald spots are linked to skin inflammation and damage to the upper part of the hair follicle.
 131 citations,
November 1998 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
131 citations,
November 1998 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Skin grafts on mice can cause an immune response leading to hair loss, useful for studying human hair loss conditions.
 12 citations,
May 2001 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement”
12 citations,
May 2001 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement” A rare benign skin tumor showed unusual features of sebaceous and sweat glands, important for correct diagnosis.
 1 citations,
March 2004 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
1 citations,
March 2004 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” ZD1839, a cancer drug, can cause mild skin rashes that are treatable without stopping the medication.
 January 2017 in “Springer eBooks”
January 2017 in “Springer eBooks” The document explains various skin conditions and their treatments.
 59 citations,
September 2008 in “Experimental dermatology”
59 citations,
September 2008 in “Experimental dermatology” Both mouse and rat models are effective for testing alopecia areata treatments.
 October 2015 in “Elsevier eBooks”
October 2015 in “Elsevier eBooks” Aldesleukin can treat certain cancers and increase HIV patient CD4+ counts but often causes severe side effects.
 January 2017 in “Springer eBooks”
January 2017 in “Springer eBooks” The document concludes that Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus has different forms, is influenced by genetic and environmental factors, and can be treated with various medications, but more targeted therapies are needed.
 60 citations,
September 2015 in “Expert Review of Clinical Immunology”
60 citations,
September 2015 in “Expert Review of Clinical Immunology” Lymphocytes, especially CD8+ T cells, play a key role in causing alopecia areata, and targeting them may lead to new treatments.
 36 citations,
January 2006 in “Veterinary Dermatology”
36 citations,
January 2006 in “Veterinary Dermatology” Cyclosporin effectively and safely treated skin diseases in three pets with no side effects.
 12 citations,
November 2003 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
12 citations,
November 2003 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Topical diphencyprone helped regrow hair in mice and rats with a condition similar to human hair loss.
 January 2020 in “International Journal of PharmTech Research”
January 2020 in “International Journal of PharmTech Research” A man with severe leprosy developed painless ulcers and numbness, treated successfully with multiple drugs and vitamins.
 9 citations,
June 2017 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology”
9 citations,
June 2017 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology” People with pemphigus vulgaris and pemphigus foliaceus often have smaller sebaceous glands on their scalp.



























