 12 citations,
January 2005 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
12 citations,
January 2005 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” AGA affects many, progresses differently, and early treatment is crucial.
 10 citations,
January 2019 in “Skin Research and Technology”
10 citations,
January 2019 in “Skin Research and Technology” Southern Chinese women with female pattern hair loss have less, thinner hair and smaller hair follicles.
 4 citations,
September 2017 in “Skin appendage disorders”
4 citations,
September 2017 in “Skin appendage disorders” The dog with an Alopecia Areata-like condition showed signs of an autoimmune disease and partially regrew hair without treatment, suggesting dogs could be models for human AA research.
 4 citations,
January 2010 in “Acta dermato-venereologica”
4 citations,
January 2010 in “Acta dermato-venereologica” Low androgen levels can still cause female pattern hair loss.
 3 citations,
January 2018 in “Dermatology”
3 citations,
January 2018 in “Dermatology” Scalp biopsies help tell apart androgenetic alopecia and alopecia areata.
 2 citations,
October 2017 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
2 citations,
October 2017 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Focal atrichia helps diagnose female pattern hair loss.
 2 citations,
April 2017 in “PubMed”
2 citations,
April 2017 in “PubMed” Fat cells near hair follicles may affect hair growth and could help treat baldness.
May 2023 in “Journal of Cosmetic and Laser Therapy” Using multiple treatments together works better for female hair loss than using one treatment alone.
August 2021 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Newer contraceptives with less androgenic progestins may reduce female hair loss.
 January 2009 in “CRC Press eBooks”
January 2009 in “CRC Press eBooks” Androgenetic alopecia, or common baldness, is the main cause of hair loss in men due to shrinking hair follicles from hormones, and it's normal but can be a problem if it's too much or too early.
 43 citations,
May 2011 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
43 citations,
May 2011 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Recognizing the different stages of alopecia areata is crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
 3 citations,
January 1989 in “PubMed”
3 citations,
January 1989 in “PubMed” The review found that specific changes in scalp tissue can help diagnose different types of hair loss.
 10 citations,
January 2000 in “Journal Of Cutaneous Laser Therapy”
10 citations,
January 2000 in “Journal Of Cutaneous Laser Therapy” Laser hair removal might also work by damaging blood vessels around hair follicles.
 6 citations,
October 2015 in “International Journal of Women's Dermatology”
6 citations,
October 2015 in “International Journal of Women's Dermatology” Hair aging is inevitable, but using the right hair care products can help maintain hair health.
 4 citations,
October 2012 in “Archives of Dermatology”
4 citations,
October 2012 in “Archives of Dermatology” Hair diameter diversity is a key sign for diagnosing and managing male pattern baldness.
 52 citations,
April 2004 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
52 citations,
April 2004 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Male pattern baldness involves three mechanisms and finasteride can help reverse it.
 13 citations,
November 2009 in “Journal of Dermatological Science”
13 citations,
November 2009 in “Journal of Dermatological Science” A gene mutation causes woolly hair in a Syrian patient.
 November 2014 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
November 2014 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Hair loss is due to thinner hairs, not less hairs; hair diameter indicates balding progression and treatment effectiveness.
 January 2003 in “Springer eBooks”
January 2003 in “Springer eBooks” Androgenic alopecia is a type of hair loss that's partly inherited and can be due to hormonal imbalance.
 144 citations,
July 2002 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology”
144 citations,
July 2002 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology” Telogen effluvium is a common type of hair loss that can resolve on its own or become chronic, with treatment depending on early diagnosis.
 11 citations,
May 2009 in “Medical Hypotheses”
11 citations,
May 2009 in “Medical Hypotheses” Male pattern baldness is an unintended side effect of the body's use of androgens for muscle growth, especially in those genetically prone to it.
 4 citations,
April 2016 in “Experimental Dermatology”
4 citations,
April 2016 in “Experimental Dermatology” AGA causes hair loss through follicle miniaturization and hair cycle changes; regrowth depends on anagen initiation in kenogen follicles.
 June 2018 in “Advances in Cosmetic Surgery”
June 2018 in “Advances in Cosmetic Surgery” Hair loss caused by genetics and hormones; more research needed for treatments.
 30 citations,
September 2017 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
30 citations,
September 2017 in “Clinics in Dermatology” Men with common hair loss may have a higher risk of heart disease and diabetes, and should be checked for these conditions.
 14 citations,
March 2012 in “Lasers in Surgery and Medicine”
14 citations,
March 2012 in “Lasers in Surgery and Medicine” A low-power, fast laser safely reduces hair with minimal pain and few side effects.
 1 citations,
July 2017 in “Clinical research in dermatology”
1 citations,
July 2017 in “Clinical research in dermatology” Hair loss, known as Androgenetic Alopecia, is often caused by hormones and can be diagnosed using noninvasive techniques. Treatments include topical minoxidil and oral finasteride, with new treatments being explored. There may also be a link between this type of hair loss and heart disease risk.
 1 citations,
August 2002 in “Zeitschrift für Hautkrankheiten”
1 citations,
August 2002 in “Zeitschrift für Hautkrankheiten” Male androgenetic alopecia involves hair follicle miniaturization due to DHT, with potential treatments using inhibitors and blockers.
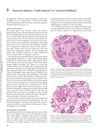 April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks”
April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks” Senescent alopecia is a type of hair loss that occurs after age 50, not caused by genetics, and involves a gradual thinning of hair without significant inflammation.
 7 citations,
January 1981 in “Springer eBooks”
7 citations,
January 1981 in “Springer eBooks” The document concludes that hair biology is complex and there are still unanswered questions about hair loss and follicle changes.
 June 2024 in “Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal”
June 2024 in “Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal” Multi-omics techniques help understand the molecular causes of androgenetic alopecia.




























