 321 citations,
December 2009 in “Journal of Dermatological Science”
321 citations,
December 2009 in “Journal of Dermatological Science” Dermal cells are key in controlling hair growth and could potentially be used in hair loss treatments, but more research is needed to improve hair regeneration methods.
11 citations,
January 2019 in “International Journal of Trichology” Mesotherapy is not significantly better than minoxidil for treating male hair loss.
[object Object] 3 citations,
January 2020 in “International journal of trichology” Congenital triangular alopecia is a hair loss condition present from birth or early childhood with no effective treatment needed.

Combining stress management and Minoxidil helps treat stress-related hair loss and improve well-being.
 January 2024 in “Journal of Biosciences and Medicines”
January 2024 in “Journal of Biosciences and Medicines” Future treatments for androgenic alopecia may focus on reactivating hair follicle stem cells and improving drug delivery.
 November 2023 in “International Journal of Trichology”
November 2023 in “International Journal of Trichology” Trichoscopic features help diagnose and assess female pattern hair loss severity, with inflammation playing a key role.

New treatments for hair loss should target eight main causes and use specific plant compounds and peptides for better results.

Different genes cause Female Pattern Hair Loss compared to male hair loss, and treatments vary, but more research is needed to understand it fully.
February 2023 in “Materials today bio” The treatment effectively promotes hair regrowth in androgenetic alopecia without causing skin irritation.
 19 citations,
January 2017 in “International Journal of Trichology”
19 citations,
January 2017 in “International Journal of Trichology” The document concludes that injecting platelet-rich plasma can effectively treat androgenetic alopecia, a type of hair loss.
 13 citations,
September 2019 in “Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology”
13 citations,
September 2019 in “Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology” Early treatment of EPDS can improve outcomes and reduce recurrence risk.
11 citations,
March 2021 in “Cleveland Clinic Journal of Medicine” Treating hair loss in both men and women is effective and improves quality of life.
 June 2024 in “Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal”
June 2024 in “Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal” Multi-omics techniques help understand the molecular causes of androgenetic alopecia.
January 2023 in “Indian Dermatology Online Journal” Female pattern hair loss in Western India is common and often linked to metabolic syndrome.
 19 citations,
December 2001 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
19 citations,
December 2001 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Horizontal scalp biopsy sections are better for diagnosing alopecia areata, showing fewer hair follicles and more miniaturized hairs.
 39 citations,
January 2011 in “Archives of Dermatology”
39 citations,
January 2011 in “Archives of Dermatology” Reflectance confocal microscopy confirms that yellow dots are signs of damaged hair follicles in alopecia areata.
 January 2018 in “Springer eBooks”
January 2018 in “Springer eBooks” Congenital triangular alopecia is a harmless, non-spreading hair loss condition often seen in young children.
 47 citations,
September 2008 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
47 citations,
September 2008 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Ludwig pattern hair loss in women results from varying sensitivity in hair follicles, causing fewer visible hairs.
 11 citations,
January 2017 in “Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine”
11 citations,
January 2017 in “Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine” DA-5512 effectively improves hair growth and health, performing better than minoxidil.
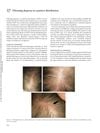 April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks”
April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks” Fibrosing alopecia in a pattern distribution is a unique hair loss condition with inflammation and scarring, resembling but distinct from common balding.
 7 citations,
December 2016 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
7 citations,
December 2016 in “British Journal of Dermatology” The report suggests that hair loss in Cronkhite-Canada syndrome may be caused by alopecia areata incognita, as shown by a patient's improvement with treatment.
 June 2022 in “International journal of drug delivery technology”
June 2022 in “International journal of drug delivery technology” Convolvulus arvensis ethanolic extract can potentially promote hair growth and reduce hair loss.
 3 citations,
March 2014 in “Annals of Hepatology”
3 citations,
March 2014 in “Annals of Hepatology” A man lost all his hair after stopping hepatitis C treatment and it didn't grow back.
2 citations,
September 2023 in “International journal of molecular sciences” Special proteins are important for skin balance, healing, and aging, and affect skin stem cells.
 January 2020 in “Przegla̧d dermatologiczny”
January 2020 in “Przegla̧d dermatologiczny” A 5-year-old boy was diagnosed with congenital triangular alopecia, a type of hair loss without skin changes, usually starting between ages 2-5, with no specific treatment.
231 citations,
December 1999 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Hair follicle size is mainly influenced by the number of cells and extracellular matrix volume, with cell number having a larger impact.
[object Object] 
Androgenetic alopecia, or hair loss, is caused by a mix of genetics, hormones, and environment, where testosterone affects hair growth and causes hair to become smaller and grow for a shorter time.
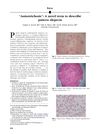 25 citations,
April 2007 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
25 citations,
April 2007 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” The document suggests "anisotrichosis" as a new term for hair thickness variation in common baldness.
 77 citations,
March 2001 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
77 citations,
March 2001 in “Clinics in Dermatology” Androgenetic alopecia involves genetics, hormones, and can be treated with medications or surgery.
 40 citations,
October 2012 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
40 citations,
October 2012 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Minoxidil helps regrow hair in female pattern hair loss, but more research needed for other treatments.























