 5 citations,
December 1981 in “PubMed”
5 citations,
December 1981 in “PubMed” Metoprolol, a blood pressure medication, was linked to reversible hair loss.
 June 1982 in “Reactions (Auckland)”
June 1982 in “Reactions (Auckland)” Metoprolol and propranolol may cause hair loss.
 54 citations,
September 2012 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
54 citations,
September 2012 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Some medications can cause hair loss, but stopping the drug usually leads to recovery within 3 months.
 35 citations,
February 2012 in “The New England Journal of Medicine”
35 citations,
February 2012 in “The New England Journal of Medicine” Early diagnosis and treatment of TPP can prevent complications.
 3 citations,
February 1985 in “PubMed”
3 citations,
February 1985 in “PubMed” Stopping the beta-blocker nadolol led to quick hair regrowth and improved scalp condition.
 January 1983 in “Side effects of drugs annual”
January 1983 in “Side effects of drugs annual” Beta-blockers and anti-anginal medications have various side effects and interactions that require careful monitoring and individualized treatment.
 January 1982 in “Clin-Alert”
January 1982 in “Clin-Alert” Some medications caused temporary health issues that improved after stopping the drugs, but two patients died from liver problems linked to carbamazepine.
 13 citations,
January 2015 in “Molecular Pharmaceutics”
13 citations,
January 2015 in “Molecular Pharmaceutics” Minoxidil works well as a high permeability reference drug for biopharmaceutics classification.
 55 citations,
September 2017 in “Expert Opinion on Drug Discovery”
55 citations,
September 2017 in “Expert Opinion on Drug Discovery” Different factors affect where drugs are absorbed in the small intestine, which is important for effective medication use.
 44 citations,
July 1990 in “Journal of the American College of Cardiology”
44 citations,
July 1990 in “Journal of the American College of Cardiology” Captopril reduces heart mass, while minoxidil has opposite effects and side effects.
 30 citations,
May 1991 in “Psychosomatics”
30 citations,
May 1991 in “Psychosomatics” Some psychiatric medications can cause reversible hair loss.
 25 citations,
March 2012 in “Journal of oncology pharmacy practice”
25 citations,
March 2012 in “Journal of oncology pharmacy practice” An 81-year-old man's white hair began to regain its original color while he was treated with lenalidomide, suggesting that graying hair might be reversible.
 9 citations,
January 2007 in “Endocrine Practice”
9 citations,
January 2007 in “Endocrine Practice” A woman's male-like symptoms and high testosterone were due to ovarian hilus-cell hyperplasia, which improved after surgery.
 6 citations,
September 1988 in “Drug intelligence & clinical pharmacy”
6 citations,
September 1988 in “Drug intelligence & clinical pharmacy” Minoxidil caused a severe rash in a patient, which improved after stopping the drug.
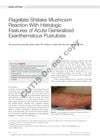 2 citations,
September 2021 in “Cutis”
2 citations,
September 2021 in “Cutis” Eating shiitake mushrooms caused a man to develop a rash similar to a skin condition known as AGEP.
 1 citations,
March 2018 in “Dermatologie pro praxi”
1 citations,
March 2018 in “Dermatologie pro praxi” Most over-the-counter hair loss treatments lack strong evidence of effectiveness, except for minoxidil, which works but stops working if you stop using it.
 291 citations,
January 2014 in “The Scientific World Journal”
291 citations,
January 2014 in “The Scientific World Journal” Lichen Planus is a less common condition affecting skin and mucous membranes, with various types and associated risk factors, challenging to diagnose, significantly impacts life quality, and may have a risk of cancerous changes in oral lesions.
 214 citations,
March 1993 in “Archives of Dermatology”
214 citations,
March 1993 in “Archives of Dermatology” Telogen effluvium is a reversible hair loss condition that requires a detailed diagnosis and often resolves on its own.
 147 citations,
April 1994 in “Drug Safety”
147 citations,
April 1994 in “Drug Safety” Some drugs can cause hair loss or increase hair growth, but these effects are usually reversible when the drug is stopped.
 119 citations,
June 2005 in “Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology”
119 citations,
June 2005 in “Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology” Potassium channel openers are effective in treating heart conditions, high blood pressure, pulmonary diseases, bladder issues, and hair loss, but more selective drugs are needed.
 110 citations,
April 2002 in “The Journal of clinical endocrinology and metabolism/Journal of clinical endocrinology & metabolism”
110 citations,
April 2002 in “The Journal of clinical endocrinology and metabolism/Journal of clinical endocrinology & metabolism” Dihydrotestosterone gel improved well-being and sexual function in older men without negatively affecting prostate health.
 86 citations,
August 2014 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
86 citations,
August 2014 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” To diagnose hair loss, use a systematic approach including history, exams, and tests.
 86 citations,
September 1977 in “BMJ”
86 citations,
September 1977 in “BMJ” Minoxidil effectively controls blood pressure in severe cases, but has serious side effects and causes hair growth in women.
 85 citations,
April 2007 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
85 citations,
April 2007 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Some drugs can cause hair loss, change hair color and shape, or increase hair growth, and treatment may involve stopping the drug or using specific hair growth treatments.
 83 citations,
May 1999 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
83 citations,
May 1999 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Hair loss that spreads out can often fix itself or be treated by finding and handling the cause.
 77 citations,
March 2001 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
77 citations,
March 2001 in “Clinics in Dermatology” Androgenetic alopecia involves genetics, hormones, and can be treated with medications or surgery.
 73 citations,
September 2016 in “Journal of Translational Medicine”
73 citations,
September 2016 in “Journal of Translational Medicine” Some heart drugs show promise for other conditions, but more research is needed to confirm their effectiveness and safety.
 69 citations,
July 2015 in “Pharmacotherapy”
69 citations,
July 2015 in “Pharmacotherapy” Low-dose finasteride may cause lasting sexual dysfunction and suicidal thoughts in young men.
 63 citations,
March 1995 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
63 citations,
March 1995 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Some drugs can cause hair loss, and stopping these drugs often leads to hair regrowth.
 57 citations,
May 2014 in “Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution”
57 citations,
May 2014 in “Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution” The research found how GPCR Class A Rhodopsin receptors are related and suggested possible substances they interact with.






























