 8 citations,
January 1996 in “Springer eBooks”
8 citations,
January 1996 in “Springer eBooks” Male pattern baldness may be caused by factors like poor blood circulation, scalp tension, stress, and hormonal imbalances, but the exact causes are still unclear.
 5 citations,
December 1979 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology”
5 citations,
December 1979 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology” Anti-androgens are effective for female acne but less so for male-pattern hair loss, with side effects similar to birth control pills.
 4 citations,
October 2012 in “Archives of Dermatology”
4 citations,
October 2012 in “Archives of Dermatology” Hair diameter diversity is a key sign for diagnosing and managing male pattern baldness.
 3 citations,
June 2000 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
3 citations,
June 2000 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Men with balding at age 45 had higher IGF-1 and lower IGFBP-3 levels, suggesting these factors might influence male pattern baldness.
 1 citations,
April 2016 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
1 citations,
April 2016 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” UV photography can help identify people at higher risk for skin cancer, and male pattern baldness at age 45 is linked to a higher risk of certain skin cancers.
 November 2020 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
November 2020 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Men with male pattern baldness may be more at risk for severe COVID-19, and anti-androgen treatments could offer protection.
 April 2016 in “Journal of Aesthetic Nursing”
April 2016 in “Journal of Aesthetic Nursing” Men are increasingly removing body hair for looks and cleanliness, and while hair loss can cause distress, it doesn't affect their self-esteem as much as it does in women.
 February 2011 in “Expert Review of Dermatology”
February 2011 in “Expert Review of Dermatology” Researchers found potential new targets for treating melanoma and nonmelanoma skin cancers, and identified a possible cause and treatment for male pattern baldness and eczema.
 35 citations,
March 2014 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
35 citations,
March 2014 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Hair loss in male pattern baldness involves muscle degeneration and increased scalp fat.
 27 citations,
January 2002 in “Exogenous Dermatology”
27 citations,
January 2002 in “Exogenous Dermatology” Chronic exposure to sunlight may worsen male pattern baldness and protecting the scalp from the sun could slow it down.
 27 citations,
February 2017 in “Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology”
27 citations,
February 2017 in “Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology” New compounds were found to help increase hair growth and decrease hair loss.
 20 citations,
August 2005 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology”
20 citations,
August 2005 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology” The protein ARA70/ELE1 is involved in male pattern baldness, and lower levels of its short form may lead to hair thinning.
 January 2008 in “Annals of Nutrition and Metabolism”
January 2008 in “Annals of Nutrition and Metabolism” Parthenolide promotes hair growth in mice and may influence pathways related to male pattern baldness.
 June 2020 in “Aesthetic Surgery Journal”
June 2020 in “Aesthetic Surgery Journal” Estradiol-rich plasma can increase hair density faster and more effectively in male pattern baldness treatment than regular plasma.
 25 citations,
November 2005 in “Facial Plastic Surgery”
25 citations,
November 2005 in “Facial Plastic Surgery” The article concludes that surgeons should tailor facial surgery techniques for Asian males to their unique cultural and anatomical needs.

Botox is effective for urinary incontinence, chronic migraines, and male pattern hair loss, and a new test for Botox antibodies is more humane.
 14 citations,
September 2020 in “Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology”
14 citations,
September 2020 in “Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology” The hair serum significantly improved hair growth and reduced hair fall without causing any skin issues.
 September 2009 in “European Urology Supplements”
September 2009 in “European Urology Supplements” After prostate removal surgery, higher initial prostate size was linked to higher urethral PSA levels and more severe male pattern baldness.
 24 citations,
January 2010 in “Endocrine Regulations”
24 citations,
January 2010 in “Endocrine Regulations” Taking 1mg of finasteride daily can mildly improve metabolic health and glucose regulation in men with male pattern baldness.
 20 citations,
February 2002 in “Expert Opinion on Therapeutic Patents”
20 citations,
February 2002 in “Expert Opinion on Therapeutic Patents” New research is needed to create better drugs that block the enzyme responsible for conditions like male baldness and prostate enlargement.
 6 citations,
October 2005 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology”
6 citations,
October 2005 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology” The document discusses male and female pattern hair loss, its diagnosis methods, FDA-approved treatments like finasteride and minoxidil, their side effects, and the role of lifestyle changes.
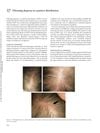 April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks”
April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks” Fibrosing alopecia in a pattern distribution is a unique hair loss condition with inflammation and scarring, resembling but distinct from common balding.
 158 citations,
February 2000 in “Archives of dermatology”
158 citations,
February 2000 in “Archives of dermatology” Some people with pattern hair loss may also have scalp inflammation and scarring similar to lichen planopilaris.
 101 citations,
April 1994 in “Baillière's clinical endocrinology and metabolism”
101 citations,
April 1994 in “Baillière's clinical endocrinology and metabolism” 5α-reductase is essential for male sexual development and its inhibitors have potential in treating various conditions related to hormone action.
 45 citations,
January 2006 in “Endocrine journal”
45 citations,
January 2006 in “Endocrine journal” To diagnose Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome, two out of three signs—irregular periods, high male hormone levels, or cysts on the ovaries—are needed.
 11 citations,
November 2012 in “Seminars in Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
11 citations,
November 2012 in “Seminars in Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” Genetic factors affect hair loss, and molecular testing may help predict, diagnose, and treat it.
 August 2023 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
August 2023 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” Both minoxidil-spironolactone and minoxidil-finasteride treatments work for hair loss, but minoxidil-spironolactone is slightly more effective, especially in women.
 November 1983 in “American Biology Teacher”
November 1983 in “American Biology Teacher” Pattern baldness is likely caused by a dominant gene influenced by testosterone levels, making it more common in men.
1 citations,
December 2019 in “Journal of skin and stem cell” PRP shows promise for short-term hair growth, especially in young men.
 176 citations,
August 2000 in “The Journal of clinical endocrinology and metabolism/Journal of clinical endocrinology & metabolism”
176 citations,
August 2000 in “The Journal of clinical endocrinology and metabolism/Journal of clinical endocrinology & metabolism” Hormone treatments in transsexual individuals reduce hair growth and oil production in male-to-females and increase them in female-to-males.





























