 37 citations,
March 1990 in “The Journal of Pediatrics”
37 citations,
March 1990 in “The Journal of Pediatrics” Toxic shock syndrome is caused by a complex interaction of bacterial toxins and the immune system, and understanding this can help improve diagnosis and treatment.
 12 citations,
June 2019 in “Actas dermo-sifiliográficas/Actas dermo-sifiliográficas”
12 citations,
June 2019 in “Actas dermo-sifiliográficas/Actas dermo-sifiliográficas” Proper skin toxicity management in chemotherapy is key to continuing treatment and keeping patient quality of life high.
 1 citations,
December 2021 in “Medical Records”
1 citations,
December 2021 in “Medical Records” The COVID-19 pandemic led to fewer dermatology visits, older and more male patients, and more stress-related skin issues.

COVID-19 can cause skin problems and affect dermatology treatments, with recommendations for skin care and cautious use of certain drugs.
 1 citations,
November 2020 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
1 citations,
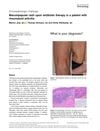
November 2020 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Methotrexate caused a rare skin rash in a rheumatoid arthritis patient, which resolved after stopping the drug.
 November 2023 in “Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology”
November 2023 in “Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology” A man's rash caused by Finasteride improved after stopping the drug and starting new treatments.
 July 2023 in “The Journal of Family Practice”
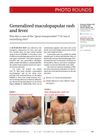
July 2023 in “The Journal of Family Practice” The man was diagnosed with lupus and improved with treatment.
December 2013 in “American journal of transplantation” The patient improved after antiviral treatment for a viral infection.
 176 citations,
May 2020 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
176 citations,
May 2020 in “Dermatologic Therapy” COVID-19 can cause different skin symptoms that may help with early diagnosis and show how severe the disease is.
82 citations,
March 2013 in “PLoS ONE” Vemurafenib causes skin side effects similar to RASopathies, requiring regular skin checks and UVA protection.
4 citations,
October 2013 in “PLoS ONE” Vemurafenib causes significant skin side effects, requiring regular dermatologist care and sun protection.
 1 citations,
July 2022 in “BMJ Case Reports”
1 citations,
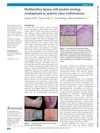
July 2022 in “BMJ Case Reports” A woman was wrongly diagnosed with lupus but actually had leprosy.
1 citations,
November 2020 in “Cermin Dunia Kedokteran” COVID-19 can cause various skin issues, helping doctors diagnose it early.
 August 2024 in “Journal of Research in Clinical Medicine”
August 2024 in “Journal of Research in Clinical Medicine” COVID-19 can cause various skin issues, with some linked to how severe the illness is.
 May 2023 in “Dermatology Reports”
May 2023 in “Dermatology Reports” The study found that skin conditions in COVID-19 patients can signal serious internal organ damage and may be life-threatening.
May 2019 in “Journal of clinical oncology” Topical calcitriol was safe and well-tolerated for potential hair loss prevention in chemotherapy patients.
 March 2024 in “Poster presentations”
March 2024 in “Poster presentations” A woman with lupus and Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease improved with treatment.
 January 2014 in “Reactions Weekly”
January 2014 in “Reactions Weekly” A woman experienced unusual hair loss and skin reactions after taking phenobarbital, but her hair grew back after treatment.
 October 2011 in “Reactions Weekly”
October 2011 in “Reactions Weekly” A man had a severe allergic reaction to sulfasalazine, with symptoms improving after treatment and follow-up.
December 2008 in “中華皮膚科醫學雜誌” The man's hair loss was due to syphilis, and his hair regrew after treatment.
 3 citations,
June 2020 in “Open access rheumatology”
3 citations,
June 2020 in “Open access rheumatology” A patient with Rhupus was diagnosed with Rowell syndrome and treated with various medications.
 1 citations,
July 1988 in “JAMA”
1 citations,
July 1988 in “JAMA” Metronidazole can cause lung disease.

COVID-19 can lead to different skin symptoms and might trigger autoimmune diseases in genetically susceptible people.
 April 2023 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2023 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Using DNase enzymes to break down harmful NETs could be a new treatment for Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis.
The man likely has secondary syphilis affecting his nervous system.
 18 citations,
October 1984 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
18 citations,
October 1984 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Lithium therapy may cause temporary hair loss, with possible regrowth if treatment is stopped or continued.
 179 citations,
October 2018 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology”
179 citations,
October 2018 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology” Cancer treatments targeting specific cells and the immune system can cause skin, mouth, hair, and nail problems, affecting patients' quality of life and treatment adherence.
 130 citations,
October 2006 in “Allergy”
130 citations,
October 2006 in “Allergy” Allergic reactions to blood thinners are rare but can be serious, requiring careful testing and alternative treatments.
 32 citations,
March 2021 in “Journal of cosmetic dermatology (Print)”
32 citations,
March 2021 in “Journal of cosmetic dermatology (Print)” COVID-19 infection may trigger alopecia areata in some patients.
 7 citations,
November 2006 in “Pediatric Dermatology”
7 citations,
November 2006 in “Pediatric Dermatology” A newborn with congenital syphilis had unusual hair loss possibly caused by the infection.























