 January 2024 in “Advanced Science”
January 2024 in “Advanced Science” New microspheres help heal skin wounds and regrow hair without scarring.
 December 2023 in “The journal of cell biology/The Journal of cell biology”
December 2023 in “The journal of cell biology/The Journal of cell biology” The mTurq2-Col4a1 mouse model shows how the basement membrane develops in live mammals.
 November 2023 in “ACS Omega”
November 2023 in “ACS Omega” New liposome treatment successfully delivers CRISPR to deactivate a key enzyme in androgen-related disorders.

New treatments for hair loss should target eight main causes and use specific plant compounds and peptides for better results.
 May 2023 in “IntechOpen eBooks”
May 2023 in “IntechOpen eBooks” More research is needed to understand how testosterone is maintained in adult males.
 February 2023 in “IntechOpen eBooks”
February 2023 in “IntechOpen eBooks” Testosterone replacement therapy helps manage deficiency and has various methods, but requires careful monitoring to avoid side effects.
 June 2022 in “Authorea (Authorea)”
June 2022 in “Authorea (Authorea)” Efficient delivery systems are needed for the clinical use of CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing.
April 2022 in “JAAD case reports” Alitretinoin helped clear up a skin condition called generalized granuloma annulare in an elderly man.
 January 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings”
January 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings” The 2015 Hair Research Congress concluded that stem cells, maraviroc, and simvastatin could potentially treat Alopecia Areata, topical minoxidil, finasteride, and steroids could treat Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia, and PTGDR2 antagonists could also treat alopecia. They also found that low-level light therapy could help with hair loss, a robotic device could assist in hair extraction, and nutrition could aid hair growth. They suggested that Alopecia Areata is an inflammatory disorder, not a single disease, indicating a need for personalized treatments.
 13 citations,
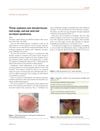
October 2015 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
13 citations,
October 2015 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” The document concludes that early recognition and appropriate treatment of red scalp, red ear, and red scrotum syndromes can lead to remission.
 6 citations,
August 2016 in “Journal of women & aging”
6 citations,
August 2016 in “Journal of women & aging” Older women reported negative physical and psychological effects from Botox and facial fillers, feeling neglected by the medical system.
 3 citations,
May 2011 in “Practice nursing”
3 citations,
May 2011 in “Practice nursing” As skin ages, it gets thinner, paler, and more wrinkled, and protection and care like sunblock and moisturizers are important.
 90 citations,
October 1998 in “Animal Reproduction Science”
90 citations,
October 1998 in “Animal Reproduction Science” Mouflon rams mature gradually with changes in body, horns, and hormones linked to age and seasons, reaching full sexual maturity well after puberty.
 144 citations,
July 2015 in “Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology”
144 citations,
July 2015 in “Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology” Alopecia areata is a common autoimmune disease affecting about 2% of people, causing significant disability and often associated with mental health issues and other autoimmune conditions.
 37 citations,
April 2008 in “The Cochrane library”
37 citations,
April 2008 in “The Cochrane library” 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors can lower prostate cancer risk but may increase high-grade tumors and cause sexual side effects.
 6 citations,
January 2014 in “Journal of pediatric endocrinology & metabolism/Journal of pediatric endocrinology and metabolism”
6 citations,
January 2014 in “Journal of pediatric endocrinology & metabolism/Journal of pediatric endocrinology and metabolism” Three siblings with a genetic form of rickets showed different symptoms of the disease.
 253 citations,
March 1994 in “Developmental dynamics”
253 citations,
March 1994 in “Developmental dynamics” Apoptosis is essential for human skin development and forming a functional epidermis.
 55 citations,
July 1999 in “Clinics in Sports Medicine”
55 citations,
July 1999 in “Clinics in Sports Medicine” Athletes use steroids to enhance performance despite health risks and legal issues, and education on their dangers is needed.
 6 citations,
November 2010 in “International Journal of Andrology”
6 citations,
November 2010 in “International Journal of Andrology” New oral testosterone formulations show potential for safer, effective hormone replacement in men with low testosterone.
 30 citations,
January 2023 in “EFSA journal”
30 citations,
January 2023 in “EFSA journal” Adults should not consume more than 255 micrograms of selenium per day to avoid risk of hair loss and other side effects.
 March 2015 in “Surgery (oxford)”
March 2015 in “Surgery (oxford)” Critical illness can lead to long-lasting physical and psychological problems, requiring ongoing, specialized care and rehabilitation.
 109 citations,
May 2011 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
109 citations,
May 2011 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Alopecia areata is a type of hair loss that can lead to complete baldness, often associated with other autoimmune conditions, and half of the cases may see hair return within a year.

The pandemic worsened mental health and healthcare access for middle-aged women, leading to negative changes in their lifestyle.
 4025 citations,
December 2003 in “Human Reproduction”
4025 citations,
December 2003 in “Human Reproduction” The 2003 consensus updated PCOS diagnosis criteria and linked PCOS to higher risks of diabetes and heart problems, recommending lifestyle changes to lower these risks.
 119 citations,
January 2012 in “Nutrition & Metabolism”
119 citations,
January 2012 in “Nutrition & Metabolism” Modern lifestyles, including poor diet, stress, and long-term use of certain medications, hinder the body's ability to heal from inflammation, leading to chronic diseases.
 1 citations,
October 2022 in “Cureus”
1 citations,
October 2022 in “Cureus” Over half of the participants in a Saudi Arabian survey experienced hair loss after COVID-19, affecting women and younger people more, with a small percentage feeling a severe impact on their lives.
 3 citations,
May 2023 in “Frontiers in Public Health”
3 citations,
May 2023 in “Frontiers in Public Health” Most severe COVID-19 patients in Mexico experienced long-lasting symptoms that worsened their quality of life.
 43 citations,
January 2016 in “International Journal of Andrology”
43 citations,
January 2016 in “International Journal of Andrology” Finasteride caused long-term sexual and non-sexual side effects in young men with hair loss.
 30 citations,
November 2018 in “Fertility and Sterility”
30 citations,
November 2018 in “Fertility and Sterility” Young women with PCOS have a higher risk of high blood pressure and metabolic syndrome, but these risks may decrease after age 40.
 12 citations,
November 2021 in “Journal of Clinical Medicine”
12 citations,
November 2021 in “Journal of Clinical Medicine” Kidney transplant patients who had COVID-19 experienced a significant drop in their quality of life due to long-lasting symptoms.





























