 July 2023 in “Deleted Journal”
July 2023 in “Deleted Journal” Alopecia areata is the most common type of baldness treated with corticosteroids and minoxidil.
 September 1987 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
September 1987 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Dr. Baral observed that applying minoxidil can cause hair to grow in areas other than where it was applied.
June 1986 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Topical minoxidil showed promise for early male pattern baldness.
[object Object]  164 citations,
April 2008 in “Cochrane library”
164 citations,
April 2008 in “Cochrane library” Current treatments for alopecia show no significant long-term benefits.
67 citations,
July 2011 in “Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology” The document suggests a personalized treatment plan for alopecia areata based on the patient's age and hair loss severity, using a range of therapies ranked by effectiveness and safety.
 48 citations,
October 1996 in “Dermatologic clinics”
48 citations,
October 1996 in “Dermatologic clinics” Some treatments can help with hair regrowth in alopecia areata, but results vary and long-term use is often needed without changing the disease's outcome.
 34 citations,
April 2009 in “Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy”
34 citations,
April 2009 in “Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy” Some treatments work for common baldness, but there's less evidence for other hair loss types, and more research is needed.
 14 citations,
January 2011 in “International Journal of Trichology”
14 citations,
January 2011 in “International Journal of Trichology” Some people with severe, long-lasting baldness responded well to a specific combination treatment.
 7 citations,
September 2015 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas”
7 citations,
September 2015 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas” Hair transplantation for Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia may work if done after the disease is inactive for 2 years and with ongoing treatment after surgery.
 7 citations,
April 1987 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
7 citations,
April 1987 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Stopping imipramine reduced the woman's hair loss.
 2 citations,
January 2023 in “Journal of Dermatology”
2 citations,
January 2023 in “Journal of Dermatology” Some types of hair loss can continue for a long time after recovering from a severe drug reaction known as DRESS.
 1 citations,
July 2023 in “Journal of Clinical Medicine”
1 citations,
July 2023 in “Journal of Clinical Medicine” Different causes of beard hair loss have various treatments, including medications, lifestyle changes, and procedures to stimulate hair growth.
1 citations,
May 2022 in “Journal of Drugs in Dermatology” Low-dose naltrexone and platelet-rich plasma can regrow hair in lichen planopilaris.
 1 citations,
March 2020 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology”
1 citations,
March 2020 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology” The paper concludes that recognizing bitemporal alopecia areata is important for early treatment and preventing its progression.
1 citations,
August 2005 in “Springer eBooks” Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disease with genetic links, treatable with certain medications, and can affect mental health.
[object Object] 
Baricitinib helped treat a man's beard hair loss when steroids didn't work.
 September 2023 in “Journal of the Dermatology Nurses’ Association”
September 2023 in “Journal of the Dermatology Nurses’ Association” Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) may be a safe and effective treatment for hair loss caused by Alopecia Areata.
 August 2023 in “JAAD Case Reports”
August 2023 in “JAAD Case Reports” A woman with lupus experienced hair regrowth after treatment, but hair transplantation is not advised for her condition.
 June 2023 in “JAAD case reports”
June 2023 in “JAAD case reports” A rare scalp condition, cutis verticis gyrata, was found in a woman with primary scarring alopecia.
 January 2023 in “International journal of sciences”
January 2023 in “International journal of sciences” Platelet-Rich Plasma therapy helped significantly in hair recovery for a hair loss condition after infection.
 March 2018 in “Dermatología Argentina”
March 2018 in “Dermatología Argentina” The study found that the average age of women diagnosed with Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia in Argentina is higher than in other countries, but their symptoms are similar.

No treatment alters the natural progression of alopecia areata, and effectiveness varies, with some possibly working better in children.
 April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks”
April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks” Alopecia areata is a common autoimmune condition causing varying hair loss, diagnosed by specific patterns of inflammation around hair follicles, with several treatment options available.
 182 citations,
December 2017 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
182 citations,
December 2017 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Some treatments can help with a hair loss condition called alopecia areata, but none ensure lasting results; choices depend on the person, with JAK inhibitors showing promise for severe cases.
 123 citations,
August 2005 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
123 citations,
August 2005 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” The study found that Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia affects a broader age range of women and early treatment can help stop hair loss.
 95 citations,
November 2016 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
95 citations,
November 2016 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Treatments for permanent hair loss from scarring aim to stop further loss, not regrow hair, and vary by condition, with partial success common.
 85 citations,
October 2012 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
85 citations,
October 2012 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Alopecia Areata is an autoimmune condition often starting before age 20, with varied treatment success and a need for personalized treatment plans.
71 citations,
December 2013 in “The journal of investigative dermatology. Symposium proceedings/The Journal of investigative dermatology symposium proceedings” There are no FDA-approved treatments for Alopecia Areata, and current options have varying success and relapse rates.
 53 citations,
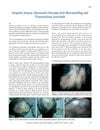
January 2014 in “Journal of Cutaneous and Aesthetic Surgery”
53 citations,
January 2014 in “Journal of Cutaneous and Aesthetic Surgery” Microneedling combined with triamcinolone can safely stimulate faster hair regrowth in people with Alopecia Areata.
 49 citations,
April 2000 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
49 citations,
April 2000 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Despite progress in treatment, the exact cause of Alopecia areata is still unknown.

























