 12 citations,
June 1999 in “Dermatologic Surgery”
12 citations,
June 1999 in “Dermatologic Surgery” Hair restoration surgery can effectively increase pubic hair density, with patient satisfaction and natural results largely depending on the chosen hair pattern and graft design.
[object Object]  January 2023 in “Pesquisa Veterinária Brasileira”
January 2023 in “Pesquisa Veterinária Brasileira” A KRT71 mutation in Hereford cattle in Uruguay causes thin, curly hair and scaly skin.
 7 citations,
May 2005 in “Experimental Dermatology”
7 citations,
May 2005 in “Experimental Dermatology” Two mouse mutations cause similar hair loss despite different skin changes.
35 citations,
August 2009 in “Differentiation” Desmoglein 4 is controlled by specific proteins that affect hair growth.
 May 2018 in “European Journal of Dermatology”
May 2018 in “European Journal of Dermatology” The first Japanese family with Marie Unna hereditary hypotrichosis showed hair condition improvement in a child and highlighted the risk of misdiagnosis.

Inhibiting AP-1 changes skin tumor types and affects tumor cell identity.
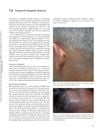 April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks”
April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks” Temporal triangular alopecia is a lifelong condition with hairless patches on the side of the head that may be present from birth.
11 citations,
January 2010 in “Springer eBooks”  July 2023 in “New phytologist”
July 2023 in “New phytologist” The BUZZ gene is important for root hair growth and overall root structure in the plant Brachypodium distachyon.
2 citations,
May 2022 in “Stem cell research & therapy” Disrupted stem cell signals in hairpoor mice cause hair loss.
51 citations,
September 2008 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Vitamin D receptor may help protect against UV-induced skin cancer.
[object Object]  May 2018 in “European Journal of Dermatology”
May 2018 in “European Journal of Dermatology” Adjusting the medication tacrolimus resolved a boy's red nail beds after a stem cell transplant.
 5 citations,
June 2017 in “in Vivo”
5 citations,
June 2017 in “in Vivo” Vitamin C deficiency changes gene expression, affecting skin and hair health.
9 citations,
August 2021 in “International journal of molecular sciences” PPARγ is essential for maintaining healthy skin, controlling inflammation, and ensuring proper skin barrier function.
107 citations,
April 2014 in “The Plant cell” The CAP1 gene helps control ammonium levels and is necessary for the proper growth of root hairs in Arabidopsis.
 109 citations,
October 2007 in “American Journal of Human Genetics”
109 citations,
October 2007 in “American Journal of Human Genetics” Giving a special protein to dogs with a certain genetic disease improved their symptoms but didn't help with hair growth.
 3 citations,
May 2021 in “Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine”
3 citations,
May 2021 in “Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine” Some traditional Chinese medicines may have anti-aging benefits and could help with hair growth, but more research is needed.
May 2023 in “International journal of molecular sciences” The ABCA4 gene protects hair follicle stem cells from toxic vitamin A byproducts.
 October 2024 in “Comprehensive Health and Biomedical Studies”
October 2024 in “Comprehensive Health and Biomedical Studies” Smoking and alcohol worsen hair transplant results.
 10 citations,
June 2005 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
10 citations,
June 2005 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” FP-1 is a key protein in rat hair growth, active only during the growth phase.
11 citations,
May 2012 in “Genesis” Bmpr2 and Acvr2a receptors are crucial for hair retention and color.
 August 2023 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)”
August 2023 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)” Too much β-catenin activity can mess up the development of mammary glands and make them more like hair follicles.
 5 citations,
October 2014 in “Methods”
5 citations,
October 2014 in “Methods” The document explains how to create detailed biological pathways using genomic data and tools, with examples of hair and breast development.
 67 citations,
November 2019 in “Molecules”
67 citations,
November 2019 in “Molecules” Tea, especially green tea, shows promise in cosmetics for skin and hair benefits but more research is needed for effective use.
 5 citations,
November 2011 in “Expert Review of Dermatology”
5 citations,
November 2011 in “Expert Review of Dermatology” The document concludes that early diagnosis and a comprehensive treatment plan are crucial for managing hair loss in children, with a focus on both medical and psychological support.
44 citations,
February 2023 in “Cell” Fingerprints form uniquely before birth due to specific genetic pathways and local signals.
 271 citations,
March 1999 in “Developmental biology”
271 citations,
March 1999 in “Developmental biology” The research shows that a gene called Wnt3 affects hair growth and structure, causing short hair and balding when overactive.
 82 citations,
March 2012 in “Development”
82 citations,
March 2012 in “Development” Drosha and Dicer are essential for hair follicle health and preventing DNA damage in skin cells.
9 citations,
October 2017 in “Frontiers in plant science” The peach gene CTG134 helps control the interaction between auxin and ethylene, which could lead to new agricultural chemicals.
 July 2023 in “Photodermatology, Photoimmunology and Photomedicine”
July 2023 in “Photodermatology, Photoimmunology and Photomedicine” Infrared radiation can cause skin aging and cancer at high temperatures but may have therapeutic benefits at controlled levels.



















