 June 2018 in “International journal of trend in scientific research and development”
June 2018 in “International journal of trend in scientific research and development” The review explains how hair products work and the science of different hair types to help improve hair care research.
 January 2018 in “Journal of cosmetology & trichology”
January 2018 in “Journal of cosmetology & trichology” The Automatic Biofibre® Hair Implant is a fast and effective hair restoration method that provides immediate cosmetic benefits and good results in over 90% of cases, but requires proper care to avoid complications.
 December 2008 in “Dermatologic Surgery”
December 2008 in “Dermatologic Surgery” The new powered hair transplant method is faster and damages fewer grafts than the manual technique.
 June 2018 in “Advances in Cosmetic Surgery”
June 2018 in “Advances in Cosmetic Surgery” Hair loss caused by genetics and hormones; more research needed for treatments.
 December 2020 in “Journal of Aesthetic Nursing”
December 2020 in “Journal of Aesthetic Nursing” Injecting platelet-rich plasma into the scalp stimulates hair growth, increases hair density, and treats hair loss effectively with minimal side effects.
 October 2020 in “Journal of Aesthetic Nursing”
October 2020 in “Journal of Aesthetic Nursing” Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections effectively treat hair loss and thinning in both men and women, with high satisfaction and no major side effects.
 December 2016 in “Journal of Dermatology and Dermatologic Surgery”
December 2016 in “Journal of Dermatology and Dermatologic Surgery” IFHUT shows better hair growth than FUE, but needs improvements in positioning, speed, and accuracy.
 200 citations,
November 1997 in “Planta”
200 citations,
November 1997 in “Planta” Calcium affects where root hairs grow, but other unknown factors determine their growth direction.
 3 citations,
April 2011 in “Microscopy research and technique”
3 citations,
April 2011 in “Microscopy research and technique” Teratoma hair is similar to scalp hair but has a rougher surface and lower adhesive force.
 1 citations,
December 2018 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
1 citations,
December 2018 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” Men with thinner hair from genetic hair loss may be more likely to have an enlarged prostate.
 42 citations,
April 2011 in “Annals of Pharmacotherapy”
42 citations,
April 2011 in “Annals of Pharmacotherapy” Flutamide effectively treats female pattern hair loss with low doses showing good liver tolerance.
 40 citations,
August 2006 in “Current Drug Safety”
40 citations,
August 2006 in “Current Drug Safety” Some drugs can cause hair loss, excessive growth, or color changes, often reversible but sometimes permanent.
 November 2011 in “Advanced Materials Research”
November 2011 in “Advanced Materials Research” Adding 1% hair fibers to brake materials improves friction and wear, making them more effective.
 December 2024 in “Tropical Journal of Natural Product Research”
December 2024 in “Tropical Journal of Natural Product Research” CTUMP's Herb shampoo promotes faster and denser hair growth.

A 15-year-old boy's smelly, yellow armpit hair improved with clindamycin treatment.
 March 2021 in “CRC Press eBooks”
March 2021 in “CRC Press eBooks” Hair loss without scarring is more common than permanent hair loss with scarring, and is often due to genetic factors.
 May 2017 in “InTech eBooks”
May 2017 in “InTech eBooks” Trichoscopy and trichogram are useful for diagnosing hair and scalp conditions.
 38 citations,
January 2009 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
38 citations,
January 2009 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” A woman developed hair loss after starting a treatment with adalimumab, suggesting this medication might cause hair loss.
 25 citations,
April 2018 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
25 citations,
April 2018 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” PRP injections increase hair density and diameter in female androgenetic alopecia patients.
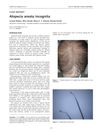 19 citations,
January 2011 in “Clinics”
19 citations,
January 2011 in “Clinics” A young woman with a rare hair loss condition improved with steroid and biotin treatment.
 17 citations,
January 2010 in “International journal of trichology”
17 citations,
January 2010 in “International journal of trichology” A man experienced hair loss from radiotherapy, which can be temporary or permanent depending on radiation dose, with potential treatments available.
 11 citations,
August 2004 in “Facial Plastic Surgery”
11 citations,
August 2004 in “Facial Plastic Surgery” The endobrow-midface lift is a safe and effective way to rejuvenate the upper face with minimal complications and rare temporary hair loss.
 4 citations,
August 2018 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
4 citations,
August 2018 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” Wound tension after hair transplant surgery increases with strip size and is higher on the sides, affecting scarring.
 4 citations,
October 2011 in “Pediatric dermatology”
4 citations,
October 2011 in “Pediatric dermatology” Head lice can cause unusual patchy hair loss.
 4 citations,
January 2007 in “Australian Veterinary Journal”
4 citations,
January 2007 in “Australian Veterinary Journal” A horse's sudden hair loss was caused by an allergic reaction to a coat conditioning powder.
 June 2021 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)”
June 2021 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)” KIF18B is important for correctly positioning cell division machinery in skin cells, affecting hair follicle development.
 199 citations,
April 2010 in “Nature”
199 citations,
April 2010 in “Nature” A gene called APCDD1, which controls hair growth, is found to be faulty in a type of hair loss called hereditary hypotrichosis simplex.
 198 citations,
October 2011 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft”
198 citations,
October 2011 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft” Use minoxidil for hair loss; finasteride and dutasteride for men, dutasteride for women.
 126 citations,
April 2006 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
126 citations,
April 2006 in “International Journal of Dermatology” The conclusion is that FFA and LPP have similar scalp biopsy features, making them hard to distinguish histologically, and FFA may be a specific kind of scarring hair loss.
74 citations,
March 2006 in “Journal of Chromatography B” Hair analysis is promising for detecting drug misuse in livestock.





























