3 citations,
February 1983 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Hair plucking quickly increases antizyme, reducing a specific enzyme activity in rats.
1 citations,
September 2020 in “Sahel Journal of Veterinary Sciences” Switching to coarser feed and providing hay improved the sheep's health.
 4 citations,
July 2020 in “International Journal of Cosmetic Science”
4 citations,
July 2020 in “International Journal of Cosmetic Science” All hair removal methods irritate underarm skin and cause dryness, with shaving being less irritating but more drying than plucking or waxing.
 1 citations,
November 2017 in “International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences”
1 citations,
November 2017 in “International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences” Dermoscopy helps distinguish between scarring and non-scarring hair loss and accurately diagnoses hair and scalp conditions without needing hair plucking.
 139 citations,
July 1991 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
139 citations,
July 1991 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Understanding hair follicle anatomy helps diagnose hair disorders.
73 citations,
November 2000 in “Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America” There are two ways to start hair growth: one needs Stat3 and the other does not, but both need PI3K activation.
 7 citations,
January 1981 in “Springer eBooks”
7 citations,
January 1981 in “Springer eBooks” The document concludes that hair biology is complex and there are still unanswered questions about hair loss and follicle changes.

Hair microscopy is a useful and affordable way to diagnose hair disorders.
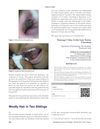 January 2012 in “International Journal of Trichology”
January 2012 in “International Journal of Trichology” Two siblings have a rare genetic condition causing curly, coarse hair.
Trichotillometry can measure hair plucking force, aiding alopecia treatment evaluation.
 1 citations,
March 2018 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)”
1 citations,
March 2018 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)” The hair treatment made hair grow faster and thicker and strengthened the hair roots.
 September 2022 in “F1000Research”
September 2022 in “F1000Research” Removing hair from mice without reproductive glands led to grey hair, possibly helping to understand greying in aging.
 20 citations,
December 2003 in “Journal of Cosmetic and Laser Therapy”
20 citations,
December 2003 in “Journal of Cosmetic and Laser Therapy” An 800nm diode laser safely and effectively reduces hair for about 8 months, with most patients satisfied and few side effects.
 9 citations,
August 2013 in “Journal of Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine”
9 citations,
August 2013 in “Journal of Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine” Transplanted baby mouse skin cells grew normal hair using a new, efficient method.
 66 citations,
February 2013 in “Pediatric Dermatology”
66 citations,
February 2013 in “Pediatric Dermatology” Dermoscopy improves diagnosis and treatment monitoring for children's skin infections, inflammations, and hair disorders.
 14 citations,
March 2010 in “Gynecological endocrinology”
14 citations,
March 2010 in “Gynecological endocrinology” New treatments for excessive hair growth in women include insulin modulators and enzyme inhibitors.
 7 citations,
January 2020 in “Scientific Reports”
7 citations,
January 2020 in “Scientific Reports” Rabbit skin analysis showed changes in hair growth and identified miRNAs that may regulate hair follicle development.
January 1999 in “대한피부과학회지” Trichotillomania is more common in young females and often linked to stress and psychiatric conditions, with hair loss and increased catagen hair observed.
 37 citations,
February 2019 in “Experimental Dermatology”
37 citations,
February 2019 in “Experimental Dermatology” Spiny mice are better at regenerating hair after injury than laboratory mice and could help us understand how to improve human skin repair.
 24 citations,
March 2018 in “Pigment Cell & Melanoma Research”
24 citations,
March 2018 in “Pigment Cell & Melanoma Research” The environment around melanocyte stem cells is key for hair regeneration and color, with certain injuries affecting hair color and potential treatments for pigmentation disorders.
 April 2016 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2016 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Phenylephrine may help prevent hair loss from pulling on the hair roots.
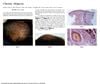 June 1995 in “Archives of Dermatology”
June 1995 in “Archives of Dermatology” A woman's hair loss was due to trichotillomania, which is often misdiagnosed and can require different treatments based on age and underlying conditions.
 21 citations,
April 2019 in “Endocrinology and Metabolism Clinics of North America”
21 citations,
April 2019 in “Endocrinology and Metabolism Clinics of North America” Transgender patients need proper skin care, especially when undergoing hormone treatments, to manage issues like acne and hair loss.
 74 citations,
January 2013 in “Expert Opinion on Biological Therapy”
74 citations,
January 2013 in “Expert Opinion on Biological Therapy” The conclusion is that hair growth can be improved by activating hair cycles, changing the surrounding environment, healing wounds to create new hair follicles, and using stem cell technology.
 26 citations,
March 1986 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology”
26 citations,
March 1986 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology” Scalp hair grows at 0.37 mm/day, forearm hair at 0.18 mm/day, and thigh hair at 0.30 mm/day, with no significant differences found in people with certain hair conditions.
 25 citations,
April 2015 in “Current problems in dermatology”
25 citations,
April 2015 in “Current problems in dermatology” Hair regrowth slows with age and can be affected by treatments that change enzyme activity in the skin.
 24 citations,
January 2011 in “International Journal of Trichology”
24 citations,
January 2011 in “International Journal of Trichology” Light microscopy is useful for diagnosing different hair disorders.
 18 citations,
November 2020 in “Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology”
18 citations,
November 2020 in “Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology” Inflammation plays a key role in activating skin stem cells for hair growth and wound healing, but more research is needed to understand how it directs cell behavior.
 16 citations,
February 2014 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
16 citations,
February 2014 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Researchers developed a mouse model that tracks hair growth using bioluminescence, improving accuracy in studying hair cycles.
 7 citations,
July 2020 in “Pigment cell & melanoma research”
7 citations,
July 2020 in “Pigment cell & melanoma research” RT1640 treatment reverses gray hair and promotes hair growth in mice.
























