9 citations,
January 2013 in “International journal of trichology” 88% phenol is effective for treating alopecia areata.
 July 2023 in “International journal of trichology”
July 2023 in “International journal of trichology” Injectable platelet-rich fibrin may stop hair loss from Discoid lupus erythematosus.
 1 citations,
January 2019 in “Paediatrics and Child Health”
1 citations,
January 2019 in “Paediatrics and Child Health” The document concludes that understanding hair biology and recognizing hair conditions are crucial for managing and treating hair loss in children.
March 2022 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Discoid Lupus Erythematosus causes scalp plaques that can lead to hair loss, and antimalarial drugs are effective treatments.
 January 2023 in “International Journal of Homoeopathic Sciences”
January 2023 in “International Journal of Homoeopathic Sciences” Homoeopathic treatment may help restore hair in Alopecia Areata by balancing the immune system.
 May 2015 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
May 2015 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Combination therapy with cyclosporine and low-dose corticosteroid shows favorable long-term results for treating alopecia areata.
 30 citations,
May 2004 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft”
30 citations,
May 2004 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft” The document concludes that early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for children with hair loss to prevent permanent damage, although not all conditions can be effectively treated.
 September 2024 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
September 2024 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” The patient responded well to treatment with no disease progression.
 25 citations,
July 2017 in “Archives of Dermatological Research”
25 citations,
July 2017 in “Archives of Dermatological Research” Herbal products might promote hair growth with fewer side effects, but more research is needed to confirm their safety and effectiveness.
 34 citations,
June 2007 in “The Journal of Dermatology”
34 citations,
June 2007 in “The Journal of Dermatology” Most Korean systemic lupus erythematosus patients experienced hair loss, often as non-scarring diffuse hair loss, with non-scarring patch alopecia also common.
 30 citations,
October 2013 in “Lupus”
30 citations,
October 2013 in “Lupus” Hair loss in lupus is different from hair loss in alopecia areata and may indicate lupus activity.
 January 2018 in “Springer eBooks”
January 2018 in “Springer eBooks” Trichotillomania is a condition where people repeatedly pull out their hair, which can be triggered by stress and has various physical signs.
 5 citations,
October 1984 in “The BMJ”
5 citations,
October 1984 in “The BMJ” Up to 50% of scalp hair can be lost before it appears thin, and treatment is only needed for hair loss caused by diseases or deficiencies.
 27 citations,
September 2012 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
27 citations,
September 2012 in “Dermatologic Clinics” The document concludes that using specific tools and tests is essential for identifying the cause of hair loss and deciding on the right treatment.
 6 citations,
August 1991 in “Pediatric Clinics of North America”
6 citations,
August 1991 in “Pediatric Clinics of North America” The document concludes that various hair and scalp disorders in children have specific treatments and proper diagnosis is essential.
 April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks”
April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks” The document concludes that diagnosing hair loss requires evaluating multiple histological features, as no single feature is definitive on its own.
 39 citations,
October 2010 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
39 citations,
October 2010 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Some patients with mycosis fungoides or Sézary syndrome experience hair loss, which may be similar to alopecia areata or linked to skin lesions, possibly due to abnormal T cells, and bexarotene can help treat it.
63 citations,
January 2006 in “Journal of cosmetic and laser therapy” The pulsed infrared diode laser is effective for treating hair loss in alopecia areata.
6 citations,
November 2020 in “Clinical Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology” Both concentrations of triamcinolone acetonide are effective for hair regrowth in patchy alopecia areata, but 5 mg/mL is recommended to reduce side effects.
 30 citations,
January 2013 in “International Journal of Trichology”
30 citations,
January 2013 in “International Journal of Trichology” The most common causes of hair loss in Jordanian children are fungal infections, autoimmune hair loss, and hair shedding after fever, with zinc deficiency also being a notable cause.
 72 citations,
February 2011 in “The American Journal of Dermatopathology”
72 citations,
February 2011 in “The American Journal of Dermatopathology” Anti-TNF therapy can cause a unique type of hair loss that may get better with topical treatments without stopping the therapy.
 10 citations,
August 2011 in “Clinics”
10 citations,
August 2011 in “Clinics” The author clarified that Alopecia Areata Incognita (AAI) and diffuse Alopecia Areata (AA) are different conditions and the case discussed was actually AA, not AAI.
 37 citations,
May 2016 in “Deutsches Arzteblatt International”
37 citations,
May 2016 in “Deutsches Arzteblatt International” Hair loss requires customized treatments based on its various causes and types.
 31 citations,
April 2010 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement”
31 citations,
April 2010 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement” Frontal fibrosing alopecia can cause sudden hair loss on limbs, similar to scalp hair loss.
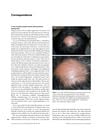 11 citations,
July 2008 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
11 citations,
July 2008 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Greying hairs may be protected from alopecia areata.
 April 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Removing STAT5 from 3D-cultured human skin cells reduces their ability to grow hair.
 July 2013 in “Our Dermatology Online”
July 2013 in “Our Dermatology Online” Minoxidil 2% is more effective than tacrolimus 0.1% for hair regrowth in mild to moderate patchy hair loss, and combining both might give better results.
 49 citations,
July 2009 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
49 citations,
July 2009 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Some people experienced hair loss after mesotherapy treatments for hair loss.
 15 citations,
February 2017 in “Nursing Clinics of North America”
15 citations,
February 2017 in “Nursing Clinics of North America” Targeted cancer therapies can cause skin side effects, which should be treated early to help patients' quality of life and treatment adherence.
 32 citations,
January 2014 in “Dermatology Research and Practice”
32 citations,
January 2014 in “Dermatology Research and Practice” Trichoscopy can effectively tell apart tinea capitis and alopecia areata in children by looking for specific hair shapes.

























