 8 citations,
June 2017 in “JAMA Dermatology”
8 citations,
June 2017 in “JAMA Dermatology” Women pay more for the same 5% minoxidil foam than men, but prices for liquid solutions are similar.
8 citations,
March 2015 in “PubMed” 5% minoxidil foam effectively treats female hair loss.
 January 2022 in “Experimental Dermatology”
January 2022 in “Experimental Dermatology” Minoxidil solution and foam both increase hair growth, but the solution works better than the foam.
1 citations,
January 2023 in “Journal of Clinical Medicine” Minoxidil can cause a skin reaction called ALEP.
 1 citations,
April 2019 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
1 citations,
April 2019 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Oral minoxidil can potentially increase hair growth in people suffering from Central Centrifugal Cicatricial Alopecia.
 April 2008 in “Medical & surgical dermatology”
April 2008 in “Medical & surgical dermatology” Certain hairstyles can cause scalp diseases, smoking is linked to hair loss, 5% minoxidil foam is effective for hair loss treatment, and various factors influence wound healing and hair growth.
 7 citations,
January 2021 in “Cureus”
7 citations,
January 2021 in “Cureus” A woman had an allergic skin reaction to a hair loss treatment containing minoxidil and should not use it.
November 2022 in “Research Square (Research Square)” Topical minoxidil 5% is better for treating female pattern hair loss than topical sildenafil 1%.
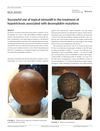 1 citations,
August 2019 in “Pediatric dermatology”
1 citations,
August 2019 in “Pediatric dermatology” Topical minoxidil helped an 8-year-old boy with a genetic hair disorder grow hair.
 January 2024 in “Pediatric Dermatology”
January 2024 in “Pediatric Dermatology” Minoxidil improved hair growth in a child with a rare genetic disorder.

Effective treatment for midlife women's hair loss is limited, with 5% minoxidil foam being the only proven option for the most common type.
 17 citations,
October 2013 in “F1000Research”
17 citations,
October 2013 in “F1000Research” A 2-year-old boy grew excessive hair after using minoxidil for hair loss, but it improved when the treatment stopped.
 5 citations,
January 2018 in “Javma-journal of The American Veterinary Medical Association”
5 citations,
January 2018 in “Javma-journal of The American Veterinary Medical Association” A dog fully recovered from minoxidil poisoning after receiving treatment.
 74 citations,
April 2005 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
74 citations,
April 2005 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Minoxidil and finasteride are effective for male hair loss, minoxidil for female hair loss, and various treatments like corticosteroids work for alopecia areata; treatment should be tailored to the individual.

Topical minoxidil and oral finasteride and dutasteride are the most effective treatments for male and female pattern hair loss, but study quality varies.
 145 citations,
November 2017 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
145 citations,
November 2017 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Use minoxidil for hair loss treatment; assess results after 6 months.

Microneedling is an effective way to treat hair loss from androgenetic alopecia.
December 2018 in “International journal of women’s dermatology” FFA in young women is often missed, and no single treatment works best.
 January 2017 in “Springer eBooks”
January 2017 in “Springer eBooks” Over 40% of postmenopausal women experience hair loss, with treatments aiming to stop further loss and possibly thicken hair.
 2 citations,
September 2022 in “Dermatologic therapy”
2 citations,
September 2022 in “Dermatologic therapy” Microneedling helps reduce hair-pulling and promotes hair regrowth in trichotillomania patients.
 3 citations,
December 2020 in “International Journal of Women's Dermatology”
3 citations,
December 2020 in “International Journal of Women's Dermatology” Scalp micro-wounding helps promote hair growth in female pattern hair loss.
 1 citations,
January 2015 in “Side effects of drugs annual”
1 citations,
January 2015 in “Side effects of drugs annual” The document concludes that various dermatological treatments and drugs can cause skin reactions and side effects.
 January 2018 in “Karger Kompass”
January 2018 in “Karger Kompass” Skin symptoms like fragile skin and easy bruising can indicate Cushing's syndrome, which requires early diagnosis and treatment to prevent serious health issues.
 16 citations,
June 2021 in “Journal of Dermatological Treatment”
16 citations,
June 2021 in “Journal of Dermatological Treatment” Minoxidil effectively treats hair loss, especially androgenetic alopecia, but needs more research for better understanding.
 14 citations,
January 2015 in “Skin appendage disorders”
14 citations,
January 2015 in “Skin appendage disorders” Minoxidil treatment for hair loss can cause scalp allergy and severe hair loss.
 12 citations,
September 2018 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
12 citations,
September 2018 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Daily low-dose aspirin lowers minoxidil's effectiveness for hair loss treatment.
 8 citations,
April 2020 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
8 citations,
April 2020 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Oral minoxidil is a reasonably safe alternative for patients allergic to the topical form.
 1 citations,
August 2020 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
1 citations,
August 2020 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” The "After Minoxidil" spray makes hair easier to style, less greasy, and encourages people to keep using the treatment.
 27 citations,
September 2018 in “Medicines”
27 citations,
September 2018 in “Medicines” Oleic acid nanovesicles improve minoxidil absorption in hair follicles for alopecia treatment.
 25 citations,
January 2010 in “International Journal of Pharmaceutics”
25 citations,
January 2010 in “International Journal of Pharmaceutics” Particle properties affect drug retention and release in minoxidil foams, with lipid nanoparticles having higher loading capacity.


























