
Eye drops with β-blockers may cause hair loss.
 50 citations,
December 2009 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
50 citations,
December 2009 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Latanoprost can effectively treat eyelash hair loss, with 45% of patients showing hair regrowth and no reported side effects.
 20 citations,
November 2009 in “European Journal of Dermatology”
20 citations,
November 2009 in “European Journal of Dermatology” Latanoprost, a glaucoma treatment, was found ineffective in treating hair loss in eyebrows and eyelashes.
 6 citations,
October 2022 in “American journal of clinical dermatology”
6 citations,
October 2022 in “American journal of clinical dermatology” The review shows how to properly diagnose and treat the loss of eyebrow and eyelash hair.
27 citations,
February 2006 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Some children and young adults with eyebrow and eyelash hair loss actually have a hair-pulling disorder, often with related psychological issues.
 162 citations,
August 2002 in “Survey of Ophthalmology”
162 citations,
August 2002 in “Survey of Ophthalmology” Latanoprost can make eyelashes longer, thicker, and darker.
6 citations,
March 2021 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” The Brigham Eyelash Tool for Alopecia (BELA) is a reliable way to measure eyelash loss in alopecia areata patients.
 38 citations,
March 2017 in “Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs”
38 citations,
March 2017 in “Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs” Bimatoprost is promising for treating some types of hair loss but needs more testing for androgenetic alopecia.
 11 citations,
August 2012 in “Canadian journal of ophthalmology”
11 citations,
August 2012 in “Canadian journal of ophthalmology” Eyelash alopecia areata often goes undiagnosed and can lead to complete eyelash regrowth, especially in younger patients.
69 citations,
April 2010 in “Clinical ophthalmology” Bimatoprost is effective for growing longer, thicker, and darker eyelashes.
 9 citations,
December 2020 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
9 citations,
December 2020 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Certain drugs are effective for skin conditions like psoriasis, vitiligo, and hair loss.
 37 citations,
January 2010 in “International Journal of Trichology”
37 citations,
January 2010 in “International Journal of Trichology” Bimatoprost helped eyelash growth in nearly half of the patients with a type of eyelash hair loss.
 16 citations,
March 2016 in “Clinical ophthalmology”
16 citations,
March 2016 in “Clinical ophthalmology” Bimatoprost is safe and improves eyelash growth in healthy kids but not in those with eyelash loss from chemotherapy or alopecia.
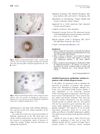 30 citations,
August 2009 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
30 citations,
August 2009 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Bimatoprost is safe but not effective for severe eyelash loss from alopecia areata, possibly helping those with less loss.
 7 citations,
April 2021 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
7 citations,
April 2021 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Topical tofacitinib may effectively and safely regrow facial hair in some people with alopecia areata.
 24 citations,
October 2018 in “JAAD Case Reports”
24 citations,
October 2018 in “JAAD Case Reports” A woman's eyelash regrowth was successful using tofacitinib solution for alopecia areata.
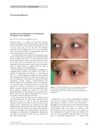 15 citations,
November 2009 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology”
15 citations,
November 2009 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology” Bimatoprost helped a girl grow her eyelashes back quickly and without serious side effects.
 81 citations,
August 2011 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
81 citations,
August 2011 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Latanoprost 0.1% may effectively treat hair loss.
 31 citations,
January 2015 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
31 citations,
January 2015 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Prostaglandin F2α analogs show promise for treating certain types of hair loss but need more research for other skin conditions.
 8 citations,
January 2015 in “Scars, burns & healing”
8 citations,
January 2015 in “Scars, burns & healing” Hair transplantation effectively treats burn scar alopecia, improving self-esteem and confidence.
 May 2023 in “Dermatology and therapy”
May 2023 in “Dermatology and therapy” The document concludes that identifying the cause of eyebrow and eyelash loss is key to treating it and improving quality of life.

The study concluded that Frontal fibrosing alopecia can affect younger people, is often missed in men, and may be autoimmune-related.
67 citations,
July 2011 in “Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology” The document suggests a personalized treatment plan for alopecia areata based on the patient's age and hair loss severity, using a range of therapies ranked by effectiveness and safety.
 36 citations,
May 2011 in “Dermatologic therapy”
36 citations,
May 2011 in “Dermatologic therapy” No treatments fully cure or prevent alopecia areata; some help but have side effects or need more research.
 72 citations,
July 2014 in “American journal of clinical dermatology”
72 citations,
July 2014 in “American journal of clinical dermatology” Some treatments, like corticosteroids and sensitizing agents, can help with alopecia areata, but more high-quality research is needed.
14 citations,
September 2015 in “PubMed” Alopecia areata can be managed with various treatments, and severe cases should be referred to dermatologists.
 August 2022 in “IntechOpen eBooks”
August 2022 in “IntechOpen eBooks” The best treatment for Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia and Lichen Planopilaris combines oral and topical medications to reduce symptoms and stop hair loss.

Different scalp and hair disorders are more common in certain ethnic groups, with the most common being androgenetic alopecia, which is treated with medications like minoxidil and finasteride.
2 citations,
January 2021 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology” Betamethasone is more effective for hair regrowth than latanoprost but has more side effects.
 4 citations,
August 2018 in “JEADV. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology/Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
4 citations,
August 2018 in “JEADV. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology/Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” There is an urgent need for better treatments for hair loss caused by chemotherapy.
























