8 citations,
February 2022 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Lipids are crucial for healthy hair, protecting it from damage and breakage.
 4 citations,
April 2019 in “Cosmetics”
4 citations,
April 2019 in “Cosmetics” Hair stiffness is higher when it has more para-like cortical cells.
 4 citations,
July 2012 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
4 citations,
July 2012 in “Dermatologic Clinics” New biopsy techniques and tools improve alopecia diagnosis, and both too much and too little selenium can cause hair loss.
[object Object] 
Optical Coherence Tomography has potential in diagnosing hair loss and monitoring blood clotting, and could be improved for deeper tissue observation and better hair loss understanding.
 June 1996 in “Journal of Dermatological Science”
June 1996 in “Journal of Dermatological Science” Vitamin D3 applied to mouse skin caused more wrinkles and sagging due to changes in the skin's outer layer.
 25 citations,
October 2017 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
25 citations,
October 2017 in “Clinics in Dermatology” Older adults commonly experience hair loss and nail disorders due to aging and health changes, affecting their quality of life.
 12 citations,
February 1999 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
12 citations,
February 1999 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Minoxidil increased small openings in blood vessel walls near growing hair in rats.
 June 2020 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
June 2020 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” The technique effectively shows how human skin and hair cells form into ball-like structures.
 1 citations,
January 2013 in “The Journal of Dermatology”
1 citations,
January 2013 in “The Journal of Dermatology” A skin condition called pyodermatitis vegetans was found in a patient with multiple myeloma for the first time.
 1 citations,
November 2004 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology”
1 citations,
November 2004 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology” Most bald men don't protect their scalp from the sun, and doctors should encourage prevention.
 128 citations,
July 2009 in “International Journal of Pharmaceutics”
128 citations,
July 2009 in “International Journal of Pharmaceutics” PEVs improve minoxidil skin penetration, increasing hair growth.
 95 citations,
February 2018 in “Dermatology and Therapy”
95 citations,
February 2018 in “Dermatology and Therapy” Nutraceuticals may improve skin health and protect against aging, but more research is needed on their optimal use and possible health risks.
 51 citations,
May 2010 in “Journal of Drug Targeting”
51 citations,
May 2010 in “Journal of Drug Targeting” Transcutol-containing vesicles improve minoxidil's skin penetration and hair growth promotion.
 15 citations,
September 2014 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
15 citations,
September 2014 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Seven patients were misdiagnosed with discoid lupus instead of lichen planopilaris due to similar symptoms, showing the need for careful diagnosis in scarring hair loss conditions.
 13 citations,
December 2010 in “Archives of Dermatology”
13 citations,
December 2010 in “Archives of Dermatology” Minoxidil use can cause trichostasis spinulosa in long-term hair loss patients.
[object Object]  12 citations,
January 2007 in “Current problems in dermatology”
12 citations,
January 2007 in “Current problems in dermatology” Environmental and cosmetic factors, including heat, chemicals, and sun exposure, can cause hair loss and damage.
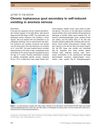 6 citations,
May 2010 in “The Journal of Dermatology”
6 citations,
May 2010 in “The Journal of Dermatology” A woman with anorexia developed gout from self-induced vomiting.
 6 citations,
December 1966 in “Textile Research Journal”
6 citations,
December 1966 in “Textile Research Journal” Animal hair fibers like wool and mohair are strong when dry, but vicuna fibers are very brittle.
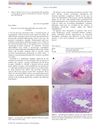 5 citations,
August 2014 in “Australasian journal of dermatology”
5 citations,
August 2014 in “Australasian journal of dermatology” Sorafenib can cause delayed skin problems, so patients need careful monitoring.
 2 citations,
December 2008 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology”
2 citations,
December 2008 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology” A small forehead lesion led to the discovery of a significant brain arteriovenous malformation in a young girl.
 1 citations,
October 2012 in “Elsevier eBooks”
1 citations,
October 2012 in “Elsevier eBooks” Skin stem cells can help improve skin repair and regeneration.
 September 2016 in “Journal of Dermatological Science”
September 2016 in “Journal of Dermatological Science” A specific mutation known for causing cancer is also found to cause a skin condition in a young girl.
 September 2016 in “Journal of Dermatological Science”
September 2016 in “Journal of Dermatological Science” Golden oyster mushroom extract may protect skin cells from aging by its antioxidant properties.
 February 2006 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
February 2006 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Terbinafine is more effective than itraconazole for toenail fungus, especially in older patients, and debridement improves its effectiveness.
 March 1998 in “Dermatologic Surgery”
March 1998 in “Dermatologic Surgery” The Miniflap Hair Restoration method effectively restores hair and reduces baldness, but may cause some hair loss and increased baldness in the crown, with the Juri flap method suggested as a quicker, less risky alternative.
 June 1996 in “Journal of Dermatological Science”
June 1996 in “Journal of Dermatological Science” Two new compounds were found that could promote hair growth as well or better than minoxidil.
 September 2016 in “Journal of Dermatological Science”
September 2016 in “Journal of Dermatological Science” The protein aPKCλ is crucial for keeping hair follicle stem cells inactive and for hair growth and regeneration.
 418 citations,
September 2012 in “Nature”
418 citations,
September 2012 in “Nature” African spiny mice can regenerate skin, hair, and cartilage, but not muscle, and their unique abilities could be useful for regenerative medicine.
 276 citations,
December 2017 in “Journal of Dermatological Science”
276 citations,
December 2017 in “Journal of Dermatological Science” The document concludes that mouse models are helpful but have limitations for skin wound healing research, and suggests using larger animals and genetically modified mice for better human application.
 83 citations,
June 2020 in “Materials & Design”
83 citations,
June 2020 in “Materials & Design” Sponge helps heal wounds faster with less inflammation and better skin/hair growth.




























