 12 citations,
July 2014 in “International Journal of STD & AIDS”
12 citations,
July 2014 in “International Journal of STD & AIDS” HIV patients with lower CD4 T cell counts often have more skin problems.
May 2024 in “Journal of Fungi” Tinea capitis in adults, especially postmenopausal Black women, needs prompt treatment with oral antifungals to avoid scarring.
 2 citations,
October 2021 in “Journal of skin and stem cell”
2 citations,
October 2021 in “Journal of skin and stem cell” Nail disorders are often related to jobs like housework and manual labor, with cosmetic issues being the main concern, and are commonly caused by skin diseases like psoriasis.
 48 citations,
October 2011 in “Sports Medicine”
48 citations,
October 2011 in “Sports Medicine” Ice-skating athletes often have skin problems due to cold, infections, and inflammation, needing careful treatment and prevention.
 28 citations,
August 2001 in “Journal of cutaneous medicine and surgery”
28 citations,
August 2001 in “Journal of cutaneous medicine and surgery” People with Down's syndrome often have more skin problems due to a weak immune system.
 January 2015 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology”
January 2015 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology” The document concludes that various skin conditions have specific characteristics and treatments, and highlights the importance of vitamin D in managing these dermatological issues.
March 2023 in “Authorea (Authorea)” Early diagnosis and treatment of systemic-onset juvenile idiopathic arthritis are crucial for improvement.
 40 citations,
July 2007 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
40 citations,
July 2007 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Systemic glucocorticosteroids are a primary treatment for various skin conditions but require careful management due to potential side effects and relapses.
 2 citations,
January 2014 in “Springer eBooks”
2 citations,
January 2014 in “Springer eBooks” The book details skin conditions in older adults, their link to mental health, cancer treatment importance, hair loss remedies, and managing autoimmune and itchy skin.
 32 citations,
June 2017 in “Journal of infection/The Journal of infection”
32 citations,
June 2017 in “Journal of infection/The Journal of infection” The document concludes that terbinafine is effective for treating scalp fungal infections in children and recommends not excluding them from school during treatment, while also highlighting the need for updated treatment guidelines due to changing infection patterns.
 October 2022 in “Gadua Journal of Pure and Allied Science”
October 2022 in “Gadua Journal of Pure and Allied Science” Terbinafine is the most effective treatment for tinea capitis, a scalp infection often confused with other conditions.
 January 2025 in “Journal of Fungi”
January 2025 in “Journal of Fungi” Advanced dermoscopy techniques improve diagnosis and treatment monitoring for Kerion celsi but don't guarantee full hair regrowth.
 32 citations,
August 2003 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
32 citations,
August 2003 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Tinea capitis can be misdiagnosed as bacterial infection in adult women but is treatable with antifungal medication.
 33 citations,
February 1996 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
33 citations,
February 1996 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Treat scalp and beard fungal infections early with oral antifungal medication and sometimes topical therapy, avoiding unnecessary allergy tests and surgery.
 156 citations,
September 2014 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement”
156 citations,
September 2014 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement” Accurate diagnosis and effective oral treatment are key to managing tinea capitis and preventing its spread.
 1 citations,
January 2019 in “International Journal of ChemTech Research”
1 citations,
January 2019 in “International Journal of ChemTech Research” Eclipta prostrata has many medicinal benefits, but more research is needed to understand how it works.
 April 1955 in “Archives of pediatrics & adolescent medicine”
April 1955 in “Archives of pediatrics & adolescent medicine” Children's skin diseases need special care and treatment.
 41 citations,
September 2007 in “Pediatric emergency care”
41 citations,
September 2007 in “Pediatric emergency care” Oral medication is necessary to treat scalp fungus in children, with griseofulvin being the usual choice.
 May 2023 in “Pharma innovation”
May 2023 in “Pharma innovation” Ringworm in cattle can be effectively treated with Povidone iodine and Whitefield ointment.
 14 citations,
January 2008 in “Medical mycology”
14 citations,
January 2008 in “Medical mycology” Canadian porcupines in a Japanese zoo passed a skin fungus to each other.
 7 citations,
May 2012 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas”
7 citations,
May 2012 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas” Scalp fungus infections in Spain are a health concern, with changing causes and a need for better treatment and prevention.
 1 citations,
December 2007 in “Drug and therapeutics bulletin”
1 citations,
December 2007 in “Drug and therapeutics bulletin” New treatments for children's scalp ringworm are recommended based on recent data.
6 citations,
November 1977 in “Archives of Dermatology” A 6-year-old girl in the U.S. had a rare scalp infection caused by *Trichophyton soudanense*.
 March 2014 in “Pediatric Clinics of North America”
March 2014 in “Pediatric Clinics of North America” The document discusses how to identify and manage common skin conditions in children.
 2 citations,
September 2013 in “Serbian Journal of Dermatology and Venereology”
2 citations,
September 2013 in “Serbian Journal of Dermatology and Venereology” HIV-positive patients, especially men who have sex with men, had a high rate of skin diseases and sexually transmitted infections.
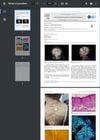 September 2022 in “International journal of infectious diseases”
September 2022 in “International journal of infectious diseases” A woman with a rare scalp infection was cured after one month of medication.
 1 citations,
January 2023 in “Advances in animal and veterinary sciences”
1 citations,
January 2023 in “Advances in animal and veterinary sciences” Most cats with dermatophytosis had fungal infections, mainly caused by M. canis.
 June 2023 in “Deleted Journal”
June 2023 in “Deleted Journal” Healthy dogs and cats can carry and spread skin infections without showing symptoms.
 36 citations,
October 2016 in “Medical mycology”
36 citations,
October 2016 in “Medical mycology” PCR-ELISA is better for identifying the fungus causing scalp infections in Ugandan children than traditional methods.
7 citations,
September 2021 in “Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy” Olorofim effectively treats fungal skin infections.


























