Search
for
Sort by
Research
270-300 / 1000+ results
research Ulcerative Colitis and Total Alopecia in a Mother and Her Son
A mother and son both had ulcerative colitis and alopecia, suggesting a genetic link in autoimmune disorders and successful treatment with cyclosporine.

research Steroid-Resistant Nephrotic Syndrome Associated with Steroid Sulfatase Deficiency—X-Linked Recessive Ichthyosis: A Case Report and Review of Literature
A boy with a rare skin condition and kidney disease improved with cyclosporine after steroids failed, suggesting a new treatment approach.

research Tacrolimus in Dermatology
Tacrolimus is an effective treatment for several skin conditions with fewer side effects than cyclosporine.
research Answer
Cyclosporine-A can cause excessive hair growth, which usually stops after discontinuing the drug.

research CsA-Induced Hypertrichosis Might Be Caused in Part by Inhibition of TGF-β2 Expression in Dermal Papilla Cells
The medicine Cyclosporin A might cause excessive hair growth by reducing a protein that controls hair growth.
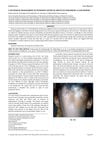
research A Successful Management of Extensive Alopecia Areata in Childhood: A Case Report
Combining OMP with cyclosporine can effectively treat severe alopecia areata in children.

research Wound Healing, Cutaneous Therapy, Hair
A device was made in 2008 to measure hair loss severity. Other findings include: frizzy mutation in mice isn't related to Fgfr2, C/EBPx marks preadipocytes, Cyclosporin A speeds up hair growth in mice, blocking plasmin and metalloproteinases hinders healing, hyperbaric oxygen helps ischemic wound healing, amniotic membranes heal wounds better than polyurethane foam, rhVEGF165 from a fibrin matrix improves tissue flap viability and induces VEGF-R2 expression, and bFGF enhances wound healing and reduces scarring in rabbits.

research Abstracts
Finasteride is effective for male hair loss, teledermatology is accurate and accepted, and cyclosporin helps treat toxic epidermal necrolysis.

research Tacrolimus in Dermatology
Tacrolimus is effective for various skin conditions with fewer side effects than cyclosporine.
research Lichen Planopilaris: Retrospective Study on the Characteristics and Treatment of 291 Patients
Women are more likely to have Lichen planopilaris, and treatments with cyclosporine and methotrexate are most effective but less safe than mycophenolate mofetil.

research Alopecia Areata: Overview and Treatment Options
Alopecia areata causes hair loss, has no cure, and various treatments exist.

research Drug-Induced Hair Loss and Hair Growth
Some drugs can cause hair loss or increase hair growth, but these effects are usually reversible when the drug is stopped.

research Psoriasis of the Scalp: Diagnosis and Management
Coal tar shampoos, salicylic acid, and topical corticosteroids are effective for scalp psoriasis, with Vitamin D3 analogues also showing benefits; severe cases may require stronger medication with more risks.

research Treatment of Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia and Lichen Planopilaris: A Systematic Review
No effective treatment for frontal fibrosing alopecia was found, but oral 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors had the best response; for lichen planopilaris, topical corticosteroids were commonly used but had a high relapse rate.

research Protection Against Chemotherapy-Induced Alopecia
No treatment fully prevents hair loss from chemotherapy yet.

research Primary Cicatricial Alopecia: Treatment Approaches and Classification
Treatments for permanent hair loss from scarring aim to stop further loss, not regrow hair, and vary by condition, with partial success common.

research The Pathogenesis of Alopecia Areata
Alopecia areata is likely caused by a combination of genetic factors and immune system dysfunction, and may represent different diseases with various causes.

research Drug Reactions Affecting Hair: Diagnosis
Some drugs can cause hair loss, change hair color and shape, or increase hair growth, and treatment may involve stopping the drug or using specific hair growth treatments.

research Clinical Findings, Cutaneous Pathology, and Response to Therapy in 21 Patients With Keratosis Pilaris Atrophicans
The study found that Keratosis Pilaris Atrophicans is a genetic skin condition that starts in childhood, involves inflammation and scarring, and current treatments are only somewhat effective.

research Alopecia: Evaluation and Treatment
The document concludes that proper diagnosis and FDA-approved treatments for different types of hair loss exist, but treatments for severe cases often fail and future improvements may focus on hair follicle stem cells.

research Safety of Dermatologic Medications in Pregnancy and Lactation
Most dermatologic medications are safe during pregnancy and breastfeeding, but some should be avoided due to potential risks.
research Alopecia Areata: A New Treatment Plan
The document suggests a personalized treatment plan for alopecia areata based on the patient's age and hair loss severity, using a range of therapies ranked by effectiveness and safety.

research Anagen Effluvium: A Review of Rapid Hair Loss During Growth Phase and Loose Anagen Hair Syndrome
Hair usually grows back 1-3 months after treatment for anagen effluvium, and children with Loose Anagen Hair Syndrome often improve by adolescence.

research Early Diagnosis and Treatment of Discoid Lupus Erythematosus
Early diagnosis and treatment of discoid lupus erythematosus improve outcomes.

research Alopecia Areata: A Review on Diagnosis, Immunological Etiopathogenesis, and Treatment Options
The document concludes that while there are various treatments for Alopecia Areata, there is no cure, and individualized treatment plans are essential due to varying effectiveness.

research Effects of Dermatological Medications on Male Fertility
Some dermatological medications can impair male fertility, so consult a doctor before trying to conceive.
research Gsdma3 Mutation Causes Bulge Stem Cell Depletion and Alopecia Mediated by Skin Inflammation
A Gsdma3 mutation causes hair loss due to stem cell damage from skin inflammation.
research Review of Treatment for Alopecia Totalis and Alopecia Universalis
No treatment is completely effective for alopecia totalis and alopecia universalis.

research Use of Dermatoscopy and Videodermatoscopy in Therapeutic Follow-Up: A Review
Dermatoscopy and videodermatoscopy are useful and reliable for tracking treatment progress in various skin conditions.