 3 citations,
May 2008 in “Hair transplant forum international”
3 citations,
May 2008 in “Hair transplant forum international” Common hair loss disorders may not need stem cell therapy, but could benefit from other treatments like hair cycle control and immune restoration therapy.
 12 citations,
May 1989 in “Postgraduate Medicine”
12 citations,
May 1989 in “Postgraduate Medicine” The document concludes that hair loss is common and can be treated with medications like minoxidil or surgical options, and it significantly affects people's psychological well-being.
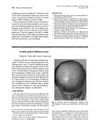 9 citations,
November 1993 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
9 citations,
November 1993 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Some men can have female pattern baldness without hormonal abnormalities or signs of feminization.
 February 2012 in “Expert Review of Endocrinology & Metabolism”
February 2012 in “Expert Review of Endocrinology & Metabolism” The document suggests more research is needed to understand the link between baldness and prostate cancer.
 March 2000 in “The Journal of pharmacy technology”
March 2000 in “The Journal of pharmacy technology” Finasteride effectively treats mild to moderate hair loss in men aged 18-41, with some side effects.
 26 citations,
January 2007 in “Organogenesis”
26 citations,
January 2007 in “Organogenesis” Bioengineering can potentially treat hair loss by regenerating hair follicles and cloning hair, but the process is complex and needs more research.
 50 citations,
March 2001 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
50 citations,
March 2001 in “Clinics in Dermatology” Genes and hormones cause hair loss, with four genes contributing equally.
 37 citations,
June 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
37 citations,
June 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Blocking a protein called CXXC5 with a specific peptide can stimulate hair regrowth and new hair growth in wounds.
 27 citations,
March 2014 in “Experimental Dermatology”
27 citations,
March 2014 in “Experimental Dermatology” IGF-1 affects hair loss and could be a potential treatment.
 21 citations,
November 2017 in “Scientific Reports”
21 citations,
November 2017 in “Scientific Reports” Different human hair follicle stem cells grow at different rates and respond differently to a baldness-related compound.
 3 citations,
November 2021 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
3 citations,
November 2021 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Androgenetic alopecia, a genetic disorder affecting up to 50% of adults, is caused by an excessive response to androgens leading to hair follicle shrinkage. Treatments include FDA-approved drugs, other therapies like low-dose oral minoxidil, and hair transplantation.
 2 citations,
April 2012 in “Science-business Exchange”
2 citations,
April 2012 in “Science-business Exchange” Blocking a protein called prostaglandin D2 might help treat hair loss.
 1 citations,
April 2016 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
1 citations,
April 2016 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Blocking Prostaglandin D₂ may help treat hair loss.
October 2022 in “The Korean Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology” Targeting the PGD2-DP2 pathway may help treat hair loss.
 58 citations,
January 2006 in “Skin Pharmacology and Physiology”
58 citations,
January 2006 in “Skin Pharmacology and Physiology” High levels of testosterone and 5α-DHT can lead to cell death in cells important for hair growth.
 20 citations,
August 2005 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology”
20 citations,
August 2005 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology” The protein ARA70/ELE1 is involved in male pattern baldness, and lower levels of its short form may lead to hair thinning.
 June 2012 in “Nature digest”
June 2012 in “Nature digest” A substance called prostaglandin D2 is linked to stopping hair growth in men with common baldness.
 86 citations,
July 2020 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
86 citations,
July 2020 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” Activating the Wnt/β-catenin pathway could lead to new hair loss treatments.
 40 citations,
July 2008 in “Drug Discovery Today”
40 citations,
July 2008 in “Drug Discovery Today” Current treatments for male pattern baldness include minoxidil and finasteride, with new options being developed.
 30 citations,
November 2013 in “PLOS ONE”
30 citations,
November 2013 in “PLOS ONE” Androgen receptor signaling causes early aging of cells important for hair growth by damaging their DNA.
 17 citations,
December 2004 in “The Journal of Men's Health & Gender”
17 citations,
December 2004 in “The Journal of Men's Health & Gender” Male pattern baldness involves hormone-related hair thinning, shorter hair, and inflammation.
 1 citations,
September 1997 in “PubMed”
1 citations,
September 1997 in “PubMed” The uniform density approach in hair restoration is less noticeable in situations like wind or exercise.

Androgenetic alopecia, or hair loss, is caused by a mix of genetics, hormones, and environment, where testosterone affects hair growth and causes hair to become smaller and grow for a shorter time.
 July 2016 in “Experimental Dermatology”
July 2016 in “Experimental Dermatology” New treatments for hair growth and psoriasis may be possible, and gene differences could affect baldness and the severity of skin conditions.
 July 2016 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
July 2016 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” R-spondin2 may help treat hair loss, gene differences could explain baldness, a peptide's regulation is linked to psoriasis, B-defensin gene copies may affect a skin condition's risk and severity, and potential markers and targets for alopecia areata were identified.
 October 2015 in “Journal of Bioresource Management”
October 2015 in “Journal of Bioresource Management” Growing hair cells in the lab from plucked hairs could lead to a new, less invasive, and cheaper baldness treatment.
 January 2022 in “Stem cell biology and regenerative medicine”
January 2022 in “Stem cell biology and regenerative medicine” The document concludes that hair follicle regeneration involves various factors like stem cells, noncoding dsRNA, lymphatic vessels, growth factors, minoxidil, exosomes, and induced pluripotent stem cells.
 June 1996 in “Archives of Dermatology”
June 1996 in “Archives of Dermatology” Using a mix of finasteride and minoxidil can significantly regrow hair in men with pattern baldness.
 19 citations,
July 2009 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology”
19 citations,
July 2009 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology” The study found that long-term sun exposure does not significantly affect follicular plugs on the scalp, and the scalp's appearance is unique compared to other body parts.
 54 citations,
June 1985 in “American Journal of Dermatopathology”
54 citations,
June 1985 in “American Journal of Dermatopathology” Minoxidil helps grow longer, thicker hair in bald scalps of stumptailed macaques, and early treatment is more effective.




























