 56 citations,
August 2019 in “Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology”
56 citations,
August 2019 in “Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology” The document concludes that Telogen Effluvium is a hair loss disorder that can be assessed with the modified wash test and may be treated with clobetasol foam, with patient management being important.
1 citations,
January 2021 in “Skin appendage disorders” Alopecia areata in children is usually mild and effectively treated with strong topical steroids.
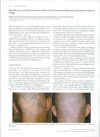 10 citations,
January 2010 in “Acta dermato-venereologica”
10 citations,
January 2010 in “Acta dermato-venereologica” Light therapy can effectively treat vitiligo and hair loss caused by a specific medication.
 37 citations,
June 2018 in “Clinical and Experimental Medicine”
37 citations,
June 2018 in “Clinical and Experimental Medicine” People with alopecia areata often have lower vitamin D levels and more inflammation, suggesting vitamin D might be involved in the condition.
 1 citations,
May 2022 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
1 citations,
May 2022 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Some overweight or obese men with long-term frontal fibrosing alopecia may have abnormal sex hormone levels.
 9 citations,
June 2019 in “Archives of Dermatological Research”
9 citations,
June 2019 in “Archives of Dermatological Research” Both topical calcipotriol and narrowband UVB improved alopecia, but combining them didn't enhance the effect on hair loss severity, despite higher vitamin D3 levels.
 14 citations,
January 2020 in “Mediterranean Journal of Rheumatology”
14 citations,
January 2020 in “Mediterranean Journal of Rheumatology” New JAK inhibitor drugs show promise for treating skin diseases but need more research on safety and effectiveness.
 9 citations,
September 2016 in “Dermatologic Surgery”
9 citations,
September 2016 in “Dermatologic Surgery” New LPP subtype affects vellus hairs, mimics AGA, and needs biopsy for diagnosis.
 1 citations,
January 2015 in “Advanced techniques in biology & medicine”
1 citations,
January 2015 in “Advanced techniques in biology & medicine” Down Syndrome patients with Alopecia Areata often have hypothyroidism and specific immune abnormalities.
 45 citations,
August 2018 in “Stem Cells International”
45 citations,
August 2018 in “Stem Cells International” Stem cells, especially from fat tissue and Wharton's jelly, can potentially regenerate hair follicles and treat hair loss, but more research is needed to perfect the treatment.
 2 citations,
January 2017 in “Journal of Pigmentary Disorders”
2 citations,
January 2017 in “Journal of Pigmentary Disorders” Vitiligo causes white skin patches and can lead to psychological stress.
 1 citations,
December 2010 in “InnovAiT”
1 citations,
December 2010 in “InnovAiT” The document concludes that accurate diagnosis and appropriate management are crucial for treating various hair disorders, which have significant psychological impacts.
 24 citations,
January 2008 in “KARGER eBooks”
24 citations,
January 2008 in “KARGER eBooks” The document concludes that ongoing research using animal models is crucial for better understanding and treating Alopecia Areata.
40 citations,
October 2012 in “Dermatologic clinics” More research is needed to understand the genetic causes of Alopecia areata to develop better treatments.
 48 citations,
May 2008 in “Drug Discovery Today: Disease Mechanisms”
48 citations,
May 2008 in “Drug Discovery Today: Disease Mechanisms” Hair follicles offer promising targets for delivering drugs to treat hair and skin conditions.
 20 citations,
July 2009 in “Journal of Pediatric and Adolescent Gynecology”
20 citations,
July 2009 in “Journal of Pediatric and Adolescent Gynecology” Quick treatment of hair disorders in teenage girls is important because of the emotional effects.
 290 citations,
December 2017 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
290 citations,
December 2017 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Alopecia areata is an autoimmune condition causing hair loss, influenced by genetics, stress, and diet, and may be prevented by a high soy oil diet.
 67 citations,
January 2013 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology”
67 citations,
January 2013 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology” The document concludes that alopecia areata is an autoimmune disease without a definitive cure, but treatments like corticosteroids are commonly used.
 8 citations,
January 2003 in “Pharmacotherapy: The Journal of Human Pharmacology and Drug Therapy”
8 citations,
January 2003 in “Pharmacotherapy: The Journal of Human Pharmacology and Drug Therapy” Chemotherapy may cause recurring hair loss due to an autoimmune response.
 80 citations,
April 2018 in “Trends in Molecular Medicine”
80 citations,
April 2018 in “Trends in Molecular Medicine” Lichen Planopilaris and Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia may help us understand hair follicle stem cell disorders and suggest new treatments.
 July 2018 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
July 2018 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Hair regrowth was seen in 83% of children with alopecia, immune system plays a role in the condition, and various treatments showed effectiveness for hair and nail disorders.
 1 citations,
July 2020 in “Journal of cosmetic dermatology”
1 citations,
July 2020 in “Journal of cosmetic dermatology” A woman on immunosuppressants developed two rare scalp conditions, which improved with specific treatments.
 12 citations,
May 2017 in “Pharmacology & therapeutics”
12 citations,
May 2017 in “Pharmacology & therapeutics” Targeting immune tolerance issues in Alopecia Areata could restore hair growth and maintain remission.
 47 citations,
December 2019 in “Frontiers in immunology”
47 citations,
December 2019 in “Frontiers in immunology” A new mutation in the STING protein causes a range of symptoms and its severity may be affected by other genetic variations; treatment with a specific inhibitor showed improvement in one patient.
 3 citations,
July 2017 in “Elsevier eBooks”
3 citations,
July 2017 in “Elsevier eBooks” Skin reactions are a common reason for emergency visits due to drug allergies, with some severe cases needing intensive care.
 1 citations,
August 2018 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)”
1 citations,
August 2018 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)” A new mutation in the TMEM173 gene and a risk allele in IFIH1 cause a unique set of immune-related symptoms.
75 citations,
September 2009 in “Dermato-endocrinology” The skin produces and processes hormones, affecting both local and overall body functions.
 9 citations,
November 2012 in “Hepatology Research”
9 citations,
November 2012 in “Hepatology Research” A man lost all his hair permanently after hepatitis C treatment, a side effect not seen before.
 6 citations,
November 2007 in “Archives of Disease in Childhood: Education & Practice”
6 citations,
November 2007 in “Archives of Disease in Childhood: Education & Practice” The document concludes that accurate diagnosis of alopecia in children relies on thorough examination and history, and while treatments exist, none can alter the course of alopecia areata, which can significantly affect a child's psychological well-being.
 September 2009 in “Dermato-endocrinology”
September 2009 in “Dermato-endocrinology” Good nutrition and vitamins are important for healthy skin and can prevent diseases.


























