 102 citations,
December 2017 in “The journal of investigative dermatology. Symposium proceedings/The Journal of investigative dermatology symposium proceedings”
102 citations,
December 2017 in “The journal of investigative dermatology. Symposium proceedings/The Journal of investigative dermatology symposium proceedings” Restoring hair bulb immune privilege is crucial for managing alopecia areata.
 12 citations,
May 2017 in “Pharmacology & therapeutics”
12 citations,
May 2017 in “Pharmacology & therapeutics” Targeting immune tolerance issues in Alopecia Areata could restore hair growth and maintain remission.
 23 citations,
April 2021 in “Journal of Clinical Medicine”
23 citations,
April 2021 in “Journal of Clinical Medicine” Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia's cause is unclear, affects mainly postmenopausal women, and current treatments focus on stopping hair loss rather than regrowth.
 14 citations,
January 2020 in “Mediterranean Journal of Rheumatology”
14 citations,
January 2020 in “Mediterranean Journal of Rheumatology” New JAK inhibitor drugs show promise for treating skin diseases but need more research on safety and effectiveness.
 1 citations,
December 2010 in “InnovAiT”
1 citations,
December 2010 in “InnovAiT” The document concludes that accurate diagnosis and appropriate management are crucial for treating various hair disorders, which have significant psychological impacts.
 July 2018 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
July 2018 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Hair regrowth was seen in 83% of children with alopecia, immune system plays a role in the condition, and various treatments showed effectiveness for hair and nail disorders.
 3 citations,
May 2023 in “Biomedicines”
3 citations,
May 2023 in “Biomedicines” PCOS causes infertility mainly due to hormonal imbalances, insulin resistance, and chronic inflammation.
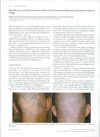 10 citations,
January 2010 in “Acta dermato-venereologica”
10 citations,
January 2010 in “Acta dermato-venereologica” Light therapy can effectively treat vitiligo and hair loss caused by a specific medication.
 9 citations,
June 2019 in “Archives of Dermatological Research”
9 citations,
June 2019 in “Archives of Dermatological Research” Both topical calcipotriol and narrowband UVB improved alopecia, but combining them didn't enhance the effect on hair loss severity, despite higher vitamin D3 levels.
 December 2023 in “Research Square (Research Square)”
December 2023 in “Research Square (Research Square)” These specific gene polymorphisms are not linked to Alopecia Areata in Egyptians.
 4 citations,
July 2015 in “Case Reports in Dermatology”
4 citations,
July 2015 in “Case Reports in Dermatology” A woman with unexplained hair loss was found to have harmless skin tumors and a scarring hair loss condition, but the tumors didn't cause the hair loss.
February 2025 in “PLoS ONE” Androgenetic alopecia starts earlier in males than females, with different treatments, and is linked to income, education, alcohol use, and mental health.
17 citations,
December 2013 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings” Autoimmune and metabolic issues are linked, and treating one may worsen another.
15 citations,
October 2013 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Vitiligo patients should be routinely screened for thyroid disease and, if extensive or prolonged, also for RA, PA, and type 2 diabetes.
 5 citations,
July 2020 in “Curēus”
5 citations,
July 2020 in “Curēus” Beard hair loss can signal early diabetes and thyroid issues, treatable with specific cream.
 April 2020 in “Journal of the Endocrine Society”
April 2020 in “Journal of the Endocrine Society” A patient with myotonic dystrophy had several autoimmune disorders and thyroid cancer, suggesting a possible link between these conditions.
155 citations,
December 2002 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Thyroid-related genes are active in skin cells and may affect autoimmune conditions.
 April 2020 in “IP Indian journal of clinical and experimental dermatology”
April 2020 in “IP Indian journal of clinical and experimental dermatology” Many children with alopecia areata also have other autoimmune diseases.
 9 citations,
January 2020 in “Postepy Dermatologii I Alergologii”
9 citations,
January 2020 in “Postepy Dermatologii I Alergologii” Frontal fibrosing alopecia is a poorly understood condition with increasing cases and unclear treatment effectiveness.
1 citations,
August 2005 in “Springer eBooks” Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disease with genetic links, treatable with certain medications, and can affect mental health.
110 citations,
December 2013 in “The journal of investigative dermatology. Symposium proceedings/The Journal of investigative dermatology symposium proceedings” Alopecia areata is a genetic and immune-related hair loss condition that is often associated with other autoimmune diseases and does not typically cause permanent damage to hair follicles.

Hair loss can be caused by hormones, illness, autoimmune disorders, or vitamin deficiencies, and treatments vary depending on the type.
 21 citations,
February 2012 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
21 citations,
February 2012 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Late-onset alopecia areata in Taiwanese patients is more common in women, usually starts at age 57, often involves less than 10% hair loss, and may have a minimal link to thyroid issues.
 9 citations,
January 2007 in “Gynecological Endocrinology”
9 citations,
January 2007 in “Gynecological Endocrinology” A woman was the first known case to have both polycystic ovary syndrome and autoimmune polyglandular syndrome type 2, suggesting a need to check for both conditions in similar patients.
 3 citations,
June 2020 in “Cureus”
3 citations,
June 2020 in “Cureus” A woman's hair loss led to discovering she had lupus.
 2 citations,
February 2023 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
2 citations,
February 2023 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” People with autism are more likely to develop alopecia areata than those without autism.
 2 citations,
April 2023 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
2 citations,
April 2023 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Hispanic/Latinx patients with alopecia areata often have it before age 40, with females and certain health conditions like rheumatoid arthritis more commonly affected.
 7 citations,
May 1978 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
7 citations,
May 1978 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Recent hair loss research shows some progress, especially in understanding male pattern baldness, but effective treatments for many types of hair loss are still lacking.
 March 2022 in “Research Square (Research Square)”
March 2022 in “Research Square (Research Square)” A girl with severe hair loss saw hair regrowth after using cannabis.
9 citations,
January 2015 in “Annals of dermatology/Annals of Dermatology” Alopecia areata in elderly people is usually mild and responds well to treatment.























