July 2024 in “Journal of Controlled Release” Nanostructured lipid carriers effectively deliver tofacitinib to hair follicles, reversing hair loss in alopecia areata.
 December 2024 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology”
December 2024 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology” Switching to ritlecitinib improves hair regrowth and well-being in severe alopecia areata patients.
 January 2016 in “Journal of clinical & experimental dermatology research”
January 2016 in “Journal of clinical & experimental dermatology research” New methods can diagnose hair loss by examining the scalp and can treat it with a mix of oral and topical medications, along with cosmetic procedures like hair transplants.
 1 citations,
October 2013 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas”
1 citations,
October 2013 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas” Customized medications made through compounding can be beneficial for various skin conditions but require careful regulation and collaboration between doctors and pharmacists.
 38 citations,
March 2017 in “Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs”
38 citations,
March 2017 in “Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs” Bimatoprost is promising for treating some types of hair loss but needs more testing for androgenetic alopecia.
 9 citations,
December 2017 in “The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology”
9 citations,
December 2017 in “The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology” New targeted therapies for hair loss from alopecia areata show promise, with personalized treatment expected in the future.
 14 citations,
July 2016 in “Pediatric Dermatology”
14 citations,
July 2016 in “Pediatric Dermatology” A 9-year-old girl with alopecia areata had successful hair regrowth using bimatoprost after other treatments failed.
January 2020 in “Indian Journal of Forensic Medicine & Toxicology” Oral cyclosporine is an effective and safe treatment for severe alopecia areata.
December 1977 in “Archives of Dermatology” Most patients with small patches of hair loss usually regrow hair.
11 citations,
December 2013 in “International Journal of Dermatology” IL16 gene variations may affect the risk of alopecia areata in Koreans.
15 citations,
October 2013 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Vitiligo patients should be routinely screened for thyroid disease and, if extensive or prolonged, also for RA, PA, and type 2 diabetes.
 December 2024 in “Journal of Dermatological Treatment”
December 2024 in “Journal of Dermatological Treatment” Early treatment can help reverse hair loss caused by cosmetic fillers.
 4 citations,
September 2011 in “Expert Review of Dermatology”
4 citations,
September 2011 in “Expert Review of Dermatology” Various treatments exist for alopecia areata, but none are completely satisfactory; choice depends on age, disease extent, and preference.
 55 citations,
March 2009 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
55 citations,
March 2009 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Topical latanoprost and bimatoprost eye solutions don't help eyelash growth in people with alopecia areata.
 20 citations,
November 2009 in “European Journal of Dermatology”
20 citations,
November 2009 in “European Journal of Dermatology” Latanoprost, a glaucoma treatment, was found ineffective in treating hair loss in eyebrows and eyelashes.
 16 citations,
July 2020 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
16 citations,
July 2020 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” Ruxolitinib may help treat hair loss by reducing inflammation, promoting hair growth signals, and protecting hair follicle immunity.
 1 citations,
April 2020 in “Plastic and Aesthetic Nursing”
1 citations,
April 2020 in “Plastic and Aesthetic Nursing” PRP therapy might help increase hair growth for nonscarring alopecia, but more research is needed to confirm its effectiveness.
 April 2020 in “Rheumatology”
April 2020 in “Rheumatology” Rituximab therapy successfully treated a patient's complete body hair loss and was effective for six years.
 67 citations,
January 2013 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology”
67 citations,
January 2013 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology” The document concludes that alopecia areata is an autoimmune disease without a definitive cure, but treatments like corticosteroids are commonly used.
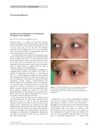 15 citations,
November 2009 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology”
15 citations,
November 2009 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology” Bimatoprost helped a girl grow her eyelashes back quickly and without serious side effects.
244 citations,
January 2010 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” The document says current treatments for alopecia areata do not cure or prevent it, and it's hard to judge their effectiveness due to spontaneous remission and lack of studies.
 13 citations,
April 2020 in “Dermatology and therapy”
13 citations,
April 2020 in “Dermatology and therapy” Cyclosporine combined with corticosteroids is more effective for severe alopecia areata than cyclosporine alone.
1 citations,
January 2023 in “Skin Appendage Disorders” Radiofrequency devices can help remove or grow hair, but more research is needed.
18 citations,
January 2010 in “Dermatology Research and Practice” DPCP treatment for alopecia areata can sometimes cause vitiligo.
 April 2016 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
April 2016 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Alopecia areata affects quality of life more than androgenetic alopecia.
 1 citations,
November 2023 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
1 citations,
November 2023 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Baricitinib helps with early hair regrowth in people with alopecia areata.
21 citations,
December 2005 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” T-cells in alopecia areata scalp show abnormal regulation, leading to less inflammation.
5 citations,
April 2019 in “Journal of Nepal Health Research Council” People with Alopecia areata often have lower vitamin D levels, which may be linked to the severity of their condition.
14 citations,
January 2019 in “PubMed” Vitamin D might be involved in the development of alopecia areata and could help in its treatment.
48 citations,
September 2011 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Epigenetic changes in blood cells may contribute to alopecia areata.

















