 21 citations,
January 2022 in “Pharmaceutics”
21 citations,
January 2022 in “Pharmaceutics” Colchicine might help treat different skin diseases, but more research is needed to confirm its effectiveness and safe dosage.
1 citations,
May 2022 in “International journal of molecular sciences” Faulty LEF1 activation causes faster skin cell differentiation in premature aging syndrome.
 1 citations,
January 2021 in “Skin appendage disorders”
1 citations,
January 2021 in “Skin appendage disorders” Chemotherapy patients don't all lose their hair due to factors like hair growth rates, age, genetics, and the type of drugs used.
 40 citations,
January 2010 in “International Journal of Trichology”
40 citations,
January 2010 in “International Journal of Trichology” Loose Anagen Syndrome is a hair condition where hairs can be easily pulled out, mainly affecting young girls, and may improve on its own or with treatment.
 391 citations,
January 2010 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
391 citations,
January 2010 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Half of people with Alopecia Areata may see hair regrowth within a year without treatment, but recovery is unpredictable.
 96 citations,
January 2013 in “International Journal of Trichology”
96 citations,
January 2013 in “International Journal of Trichology” Trichoscopy is a useful, non-invasive way to diagnose different types of hair loss.
 December 2017 in “The journal of investigative dermatology. Symposium proceedings/The Journal of investigative dermatology symposium proceedings”
December 2017 in “The journal of investigative dermatology. Symposium proceedings/The Journal of investigative dermatology symposium proceedings” The summit aimed to speed up finding treatments for alopecia areata.
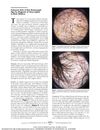 108 citations,
March 2011 in “Archives of Dermatology”
108 citations,
March 2011 in “Archives of Dermatology” Corkscrew hair may be a new sign for quickly diagnosing scalp fungus in black children.
 29 citations,
October 2012 in “Anais Brasileiros De Dermatologia”
29 citations,
October 2012 in “Anais Brasileiros De Dermatologia” Diagnosing hair loss disorders needs clinical, dermoscopic, and histological differences, and checking menstrual cycle, weight changes, drug therapy, and nail changes.
 165 citations,
June 2007 in “European Journal of Cell Biology”
165 citations,
June 2007 in “European Journal of Cell Biology” Hair follicle stem cells are key for hair and skin regeneration, can be reprogrammed, and have potential therapeutic uses, but also carry a risk of cancer.
 212 citations,
September 2015 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
212 citations,
September 2015 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” The document provides a method to classify human hair growth stages using a model with human scalp on mice, aiming to standardize hair research.
 1 citations,
April 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
1 citations,
April 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” CCL5 is important for the hair growth potential of human dermal papilla cells.
 April 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Deleting the CRIF1 gene in mice disrupts skin and hair formation, certain proteins affect hair growth, a new compound may improve skin and hair health, blood cell-derived stem cells can create skin-like structures, and hair follicle stem cells come from embryonic cells needing specific signals for development.
 April 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Applying pseudoceramide improved skin and hair health.
 April 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Stem cells can create hair follicles, potentially treating permanent hair loss, and healthy skin and hair depend on mitochondrial function and special fats.
 October 2023 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)”
October 2023 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)” Immune cells are essential for early hair and skin development and healing.
 28 citations,
January 2015 in “Skin appendage disorders”
28 citations,
January 2015 in “Skin appendage disorders” Children with trichotillomania often pull hair from their scalp, and parents may not notice; stress can trigger it, and asking detailed questions helps in diagnosis and treatment.
 April 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Removing the Crif1 gene in mouse skin disrupts skin balance and hair growth.
 April 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Blood cells turned into stem cells can become skin cells similar to normal ones, potentially helping in skin therapies.
 76 citations,
February 2021 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
76 citations,
February 2021 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” Mesenchymal stem cells show potential for skin healing and anti-aging, but more research is needed for safe use, especially regarding stem cells from induced pluripotent sources.
22 citations,
November 2016 in “International journal of molecular sciences” Vitamin D receptor is important for regulating hair growth and wound healing in mice.
 April 2016 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2016 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” The symposium showed that stem cells are key for understanding and treating skin diseases and for developing new skin models and therapies.
November 2022 in “Regenerative Therapy” Advancements in tissue engineering show promise for hair follicle regeneration to treat hair loss.
17 citations,
January 2007 in “Annals of Medicine” Cutaneous gene therapy could become a viable treatment for skin and hair disorders with improved vector development and gene expression control.
 30 citations,
November 2012 in “Anais Brasileiros De Dermatologia”
30 citations,
November 2012 in “Anais Brasileiros De Dermatologia” Diagnosing diffuse alopecia, a hair loss condition, can be challenging and may require a scalp biopsy or tracking the disease's progression when symptoms and skin tests aren't enough.
15 citations,
July 2014 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” iPSCs can help treat genetic skin disorders by creating healthy skin cells from a small biopsy.
 1 citations,
December 2022 in “Frontiers in Immunology”
1 citations,
December 2022 in “Frontiers in Immunology” Tissue environment greatly affects the unique epigenetic makeup of regulatory T cells, which could impact autoimmune disease treatment.
 August 2023 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
August 2023 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” Human skin xenografting could improve our understanding of skin development, renewal, and healing.
 21 citations,
December 2016 in “PLOS ONE”
21 citations,
December 2016 in “PLOS ONE” Scientists made skin stem cells from other human cells with over 97% efficiency, which could help treat skin conditions.
 24 citations,
May 2016 in “Stem Cell Reviews and Reports”
24 citations,
May 2016 in “Stem Cell Reviews and Reports” The document concludes that understanding how adult stem and progenitor cells move is crucial for tissue repair and developing cell therapies.

























