
Vitamin D is crucial for skin health and managing skin diseases.
 January 2022 in “Acta Scientific Women's Health”
January 2022 in “Acta Scientific Women's Health” Early diagnosis and treatment of PCOS can prevent complications and improve symptoms.
[object Object]  November 2020 in “Elsevier eBooks”
November 2020 in “Elsevier eBooks” Antiandrogens and androgen inhibitors like spironolactone, finasteride, and dutasteride can treat hair loss and skin conditions, but they have risks and side effects, including potential harm to pregnant women and risks of cancer and heart issues. Herbal remedies also have antiandrogenic effects but lack safety validation.
 March 2020 in “International journal of contemporary medical research”
March 2020 in “International journal of contemporary medical research” Patients with metabolic syndrome often have skin problems like acanthosis nigricans and skin tags, and early treatment is important to prevent serious issues.
 April 2019 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
April 2019 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Keloids significantly reduce quality of life, and treating symptoms should be prioritized.
 March 2019 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
March 2019 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Seborrheic dermatitis is influenced by diet, genetics, and psychological factors.
 January 2019 in “ISGE series”
January 2019 in “ISGE series” The document concludes that effectively managing PCOS requires a multifaceted approach.
 January 2018 in “Springer eBooks”
January 2018 in “Springer eBooks” Athletes need effective management of skin disorders for their performance and well-being.

Tailored nonsurgical cosmetic procedures are crucial for safely treating diverse skin types, especially skin of color.
 January 2018 in “Deleted Journal”
January 2018 in “Deleted Journal” Managing PCOS effectively requires focusing on psychological health, lifestyle changes, and medication.
[object Object]  November 2017 in “Elsevier eBooks”
November 2017 in “Elsevier eBooks” PCOS is a genetic disorder affecting women's reproductive health, with treatments focused on symptoms like insulin resistance and fertility.
 January 2017 in “Springer eBooks”
January 2017 in “Springer eBooks” The document explains various skin conditions and their treatments.
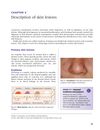
The document explains different types of skin lesions and their characteristics, causes, and related conditions.
 December 2016 in “John Wiley & Sons, Ltd eBooks”
December 2016 in “John Wiley & Sons, Ltd eBooks” The document concludes that proper recognition and treatment of skin appendage disorders are important for management.
 October 2016 in “Journal of the Dermatology Nurses’ Association”
October 2016 in “Journal of the Dermatology Nurses’ Association” Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) affects 6%-15% of women of reproductive age, causing symptoms like acne and hair loss, and increasing the risk of type 2 diabetes and heart disease; it's managed through diet, exercise, and medications like Metformin and hormonal contraceptives.
 July 2015 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
July 2015 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Treating skin conditions with both psychological and dermatological care improves patient outcomes and can save costs.
 January 2008 in “The European Journal of Contraception & Reproductive Health Care”
January 2008 in “The European Journal of Contraception & Reproductive Health Care” Non-daily contraceptives cause fewer side effects and are more satisfying to women, and certain oral contraceptives can treat acne and seborrhoea, with a combination of chlormadinone acetate and ethinyl estradiol being highly effective and safe.
 November 2021 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
November 2021 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Different stages and types of female hair loss are linked with age, menopause, high blood pressure, and skin conditions like acne and hirsutism.
 222 citations,
September 2016 in “JCI insight”
222 citations,
September 2016 in “JCI insight” Tofacitinib is safe and effective for severe alopecia areata, but hair loss may return 2 months after stopping treatment.
 130 citations,
February 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
130 citations,
February 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Tofacitinib may help treat severe hair loss, but more research is needed.
 66 citations,
June 2021 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
66 citations,
June 2021 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Baricitinib is effective and safe for treating severe alopecia areata.
 52 citations,
June 1981 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
52 citations,
June 1981 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Oral retinoids are effective for severe skin conditions but require careful use due to side effects.
 10 citations,
January 2023 in “Acta dermato-venereologica”
10 citations,
January 2023 in “Acta dermato-venereologica” Baricitinib and deuruxolitinib are effective for treating alopecia areata, but their efficacy depends on the dose.
 April 2024 in “Frontiers in medicine”
April 2024 in “Frontiers in medicine” Alopecia Areata significantly lowers quality of life and current treatments are inadequate, highlighting a need for better therapies and standardized treatment protocols.
 April 2024 in “Frontiers in pharmacology”
April 2024 in “Frontiers in pharmacology” Brepocitinib 30mg is most effective for moderate-to-severe alopecia areata, but ritlecitinib 50mg may offer a better balance of safety and effectiveness.
 March 2024 in “Clinical and experimental dermatology”
March 2024 in “Clinical and experimental dermatology” Topical corticosteroids may be a safe and effective treatment for severe alopecia areata in children.
 29 citations,
October 2020 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
29 citations,
October 2020 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Women with high androgen levels may have more severe COVID-19 symptoms.
 157 citations,
August 2010 in “Lupus”
157 citations,
August 2010 in “Lupus” The document concludes that recognizing and treating cutaneous lupus erythematosus early is crucial for managing the skin and potential systemic symptoms.
7 citations,
October 2018 in “South African journal of botany” Clausena anisata may be effective in treating acne due to its ability to fight bacteria, reduce inflammation, and possibly lower sebum production.
23 citations,
October 2020 in “Anais brasileiros de dermatologia/Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia” Tailored treatments for alopecia areata are recommended based on severity and patient needs.




























