Finasteride may help reduce COVID-19 infection by altering a key gene.
 142 citations,
December 1991 in “Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy”
142 citations,
December 1991 in “Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy” Dextran sulfate was found to be toxic and ineffective for treating HIV.
 34 citations,
April 2008 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
34 citations,
April 2008 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Skin problems like itching, dry skin, and hair loss are more common in hepatitis C patients after interferon treatment, but lichen planus is not linked to the infection.
10 citations,
June 2019 in “Transplant infectious disease” The virus linked to a rare disease was found in a patient's blood and urine before skin symptoms appeared.
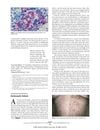 10 citations,
February 2006 in “Archives of dermatology”
10 citations,
February 2006 in “Archives of dermatology” A man's chest hair turned white after a shingles infection, possibly due to virus-damaged pigment cells.
19 citations,
August 2017 in “American journal of clinical dermatology” Hepatitis B virus exposure may be linked to increased risk of alopecia areata.
5 citations,
August 2021 in “Experimental dermatology” Overexpressing Merkel cell virus proteins in human hair follicles can create clusters of cells that resemble Merkel cell cancer.
 July 2022 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
July 2022 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” The early genes of a specific virus can cause abnormal skin cell growth and hair follicle changes.
8 citations,
January 2013 in “Australasian journal of dermatology” Trichodysplasia spinulosa is a rare skin condition caused by a virus, treatable with antiviral medication.
 3 citations,
January 2022 in “Journal of Infection”
3 citations,
January 2022 in “Journal of Infection” Some early COVID-19 mutations in patients predicted future common virus mutations.
 2 citations,
July 2020 in “Research Square (Research Square)”
2 citations,
July 2020 in “Research Square (Research Square)” Some Moroccan medicinal plants may contain compounds that can inhibit the virus causing COVID-19.
 November 2022 in “Revista Hospital Clínico Universidad de Chile”
November 2022 in “Revista Hospital Clínico Universidad de Chile” COVID-19 may cause hair loss due to the virus's effects and stress from the pandemic.
71 citations,
January 2011 in “Journal of cutaneous pathology” A rare skin condition was confirmed to be associated with a specific virus in a young girl.
19 citations,
March 2016 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement” Trichodysplasia spinulosa is a rare skin disease in immunocompromised patients caused by a specific virus targeting hair follicle cells.
 13 citations,
July 2020 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)”
13 citations,
July 2020 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)” Four drugs were found that could potentially treat COVID-19 by inhibiting the virus in lab tests.
 8 citations,
May 2021 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
8 citations,
May 2021 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” A COVID-19 patient had unusual nail discoloration and nail separation possibly due to the virus's effects on small blood vessels.
 80 citations,
June 2020 in “Dermatopathology”
80 citations,
June 2020 in “Dermatopathology” COVID-19 can cause various skin lesions, which may result from the virus and immune response, and are not directly linked to illness severity.
 26 citations,
December 2022 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
26 citations,
December 2022 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Monkeypox skin lesions show full-thickness skin death and swollen skin cells, with the virus found in affected cells.
 7 citations,
January 2021 in “Biology”
7 citations,
January 2021 in “Biology” Some COVID-19 patients have different skin problems, which might be the only sign of the virus or related to other health issues.
 March 2023 in “Медицинский совет”
March 2023 in “Медицинский совет” COVID-19 may cause different types of hair loss, and the virus's effects on hair could help understand its impact on other body parts.

The document suggests using convalescent plasma to treat COVID-19 Long Hauler Syndromes because it may contain beneficial elements that target the virus.
 43 citations,
July 2020 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
43 citations,
July 2020 in “Dermatologic Therapy” During the COVID-19 pandemic, a clinic in Turkey saw fewer patients but more cases of certain skin conditions, possibly linked to the virus and stress.
10 citations,
February 2022 in “Epidemiologia” One-third of COVID-19 patients had long-term symptoms like hair loss and fatigue, with women, older individuals, blood group B, smokers, and those with more virus exposure at higher risk.
 7 citations,
July 2020 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
7 citations,
July 2020 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Skin symptoms linked to COVID-19 are hard to confirm, and more testing is needed to identify which are truly caused by the virus.
 1 citations,
February 2022 in “The Journal of Urology”
1 citations,
February 2022 in “The Journal of Urology” Certain drugs like Dutasteride and Finasteride might help fight SARS-CoV-2 by increasing levels of a steroid called DHEA, which can protect the heart and increase nitric oxide to counteract the virus.
 September 2022 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
September 2022 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Different types of hair loss are linked to COVID-19, with some types possibly increasing risk of getting the virus, while others may be triggered or worsened by the virus.
 December 2011 in “Asia-Pacific biotech news”
December 2011 in “Asia-Pacific biotech news” In 2011, there were major scientific breakthroughs in cancer treatment, immunity, Parkinson's, virus simulation, schizophrenia, hair growth, lung cancer, and medical grafts.
 July 2005 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
July 2005 in “British Journal of Dermatology” New gene mutations linked to skin conditions were found, bacteria and chemicals may worsen acne, a dog mutation could exist in humans, virus-like elements might be involved in psoriasis, and a vitamin D3 treatment doesn't prevent chemotherapy-related hair loss.
 July 1993 in “Inpharma Weekly”
July 1993 in “Inpharma Weekly” Dicentrine reduced heart disease risk factors in rats, T-588 protected mice brains without side effects, Provir blocked herpes virus and lessened mouse symptoms, and LY191704 could treat hair loss and prostate issues.
December 2020 in “American Journal of Transplantation” Early recognition and treatment of VATS in transplant patients improve outcomes.




















