3 citations,
March 2022 in “Medicine” Systemic lupus erythematosus treatment can restore vision in patients with retinal artery occlusion.
 May 2023 in “Elsevier eBooks”
May 2023 in “Elsevier eBooks” Systemic immunotherapies are used for immune-related hair loss but not usually for genetic hair loss, unless the patient has both conditions.
 April 2005 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
April 2005 in “Dermatologic Clinics” The document summarizes recent dermatological treatments and advances in areas like pediatric care, wound healing, skin closure, light-based therapies, pigment disorders, hair loss, immunotherapy, infection management, melanoma, drug reactions, and facial rejuvenation.
[object Object]  122 citations,
November 1984 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
122 citations,
November 1984 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” No single treatment is consistently effective for alopecia areata, and more research is needed.
 45 citations,
January 2010 in “International journal of trichology”
45 citations,
January 2010 in “International journal of trichology” Topical immunotherapy, especially with DPCP, is effective for treating severe alopecia areata.
20 citations,
March 2021 in “Drug design, development and therapy” Topical immunotherapy can treat alopecia areata, but its effectiveness varies and the exact mechanism is unclear.
 2 citations,
January 2018 in “International journal of research in dermatology”
2 citations,
January 2018 in “International journal of research in dermatology” Intralesional corticosteroids are the best for limited alopecia areata, oral steroids are less effective, and PRP is safe and promising, especially for children and severe cases.
 23 citations,
July 2008 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement”
23 citations,
July 2008 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement” Topical contact sensitizers can treat certain skin conditions but are rarely used in the U.K.
 September 2022 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
September 2022 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Patient-reported outcomes better reflect the quality of life impact of alopecia areata than traditional severity scores.
 4 citations,
September 2011 in “Expert Review of Dermatology”
4 citations,
September 2011 in “Expert Review of Dermatology” Various treatments exist for alopecia areata, but none are completely satisfactory; choice depends on age, disease extent, and preference.
[object Object]  April 2024 in “International Journal of Research Publication and Reviews”
April 2024 in “International Journal of Research Publication and Reviews” Alopecia areata causes hair loss with varied treatment responses and frequent relapses.
 October 2023 in “Frontiers in medicine”
October 2023 in “Frontiers in medicine” Targeted immunotherapy could be a promising new treatment for hair regrowth.
 April 2024 in “Dermatology and therapy”
April 2024 in “Dermatology and therapy” There are significant gaps and inconsistencies in diagnosing and treating alopecia areata in Greece and Italy.
 December 2019 in “Journal of pediatrics & neonatology”
December 2019 in “Journal of pediatrics & neonatology” A 13-year-old boy had a rare, stable type of hair loss with little chance of regrowth, but treatment is available for looks.
 July 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks”
July 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks” The most common cause of hair loss in children is tinea capitis, followed by alopecia areata and telogen effluvium.
 1 citations,
January 2023 in “Przegląd Dermatologiczny”
1 citations,
January 2023 in “Przegląd Dermatologiczny” The Polish Society of Dermatology recommends treatments for alopecia areata that vary by severity, including topical and systemic medications, with long-term maintenance important for management.
 16 citations,
January 2015 in “Current problems in dermatology”
16 citations,
January 2015 in “Current problems in dermatology” Alopecia Areata is an autoimmune hair loss condition that needs more research for better treatments.
 1 citations,
September 2020 in “Cochrane library (CD-ROM)”
1 citations,
September 2020 in “Cochrane library (CD-ROM)” The analysis aims to identify the most effective and safest treatments for alopecia areata.
 15 citations,
April 2011 in “Pediatric Nephrology”
15 citations,
April 2011 in “Pediatric Nephrology” New treatments for lupus show promise, but more research is needed, especially for children.
 95 citations,
November 2018 in “Australasian journal of dermatology”
95 citations,
November 2018 in “Australasian journal of dermatology” Alopecia areata treatment varies, with no optimal method established yet.
 9 citations,
December 2017 in “The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology”
9 citations,
December 2017 in “The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology” New targeted therapies for hair loss from alopecia areata show promise, with personalized treatment expected in the future.
 15 citations,
January 2014 in “Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia”
15 citations,
January 2014 in “Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia” Lupus treatment requires a combination of drugs and therapies, with research needed for new options.
 17 citations,
March 2018 in “Pediatric dermatology”
17 citations,
March 2018 in “Pediatric dermatology” Hydroxychloroquine may help treat alopecia areata in children.
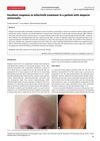 16 citations,
January 2017 in “Acta dermatovenerologica Alpina, Pannonica et Adriatica (Tiskana izd.)”
16 citations,
January 2017 in “Acta dermatovenerologica Alpina, Pannonica et Adriatica (Tiskana izd.)” A patient with complete hair loss regrew all her hair using tofacitinib.
 8 citations,
December 2018 in “Journal of Dermatological Treatment”
8 citations,
December 2018 in “Journal of Dermatological Treatment” The PRP-like cosmetic with biomimetic peptides is potentially effective and safe for treating alopecia areata.
 5 citations,
July 2020 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
5 citations,
July 2020 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Adding antihistamines to topical corticosteroid and cryotherapy may improve hair regrowth in alopecia areata patients.
 5 citations,
January 2010 in “International journal of trichology”
5 citations,
January 2010 in “International journal of trichology” PUVASOL might effectively treat complete scalp baldness.
 47 citations,
October 2014 in “Expert Opinion on Emerging Drugs”
47 citations,
October 2014 in “Expert Opinion on Emerging Drugs” New alopecia treatments aim for better results and fewer side effects.
 4 citations,
January 2022 in “Drug design, development and therapy”
4 citations,
January 2022 in “Drug design, development and therapy” Intramuscular corticosteroids are effective and safe for severe alopecia areata, with most patients regrowing hair, but nearly half may relapse.
 11 citations,
February 2021 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
11 citations,
February 2021 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” Oral tofacitinib helped regrow hair in over half of the patients with severe alopecia, but relapses and side effects were common.



























