June 2021 in “International journal of cosmetics and dermatology” Vitamin C and E may help with certain skin and hair conditions, but more research is needed to confirm their effectiveness.
 July 2011 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
July 2011 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Dermatologists give better information on pathology forms, hypersensitivity vasculitis is a common skin issue, misdiagnoses can occur, and various skin conditions are linked to loss of elastin or genetic factors.
 42 citations,
January 1998 in “BioDrugs”
42 citations,
January 1998 in “BioDrugs” Azathioprine's effectiveness and safety require careful monitoring and more research, especially regarding its use with corticosteroids and the role of TPMT status in patients.
[object Object]  67 citations,
September 2003 in “Journal of cutaneous pathology”
67 citations,
September 2003 in “Journal of cutaneous pathology” Skin problems are very common in people with end-stage kidney disease.

An 11-year-old female Pinscher with Pemphigus Foliaceus was successfully diagnosed and treated.
 9 citations,
July 2002 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
9 citations,
July 2002 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” The document concludes that fexofenadine reduces inflammation in chronic hives, cholestyramine helps half of pregnant women with itchy rashes, and relaxing incisions are a good alternative in facial surgery for the elderly.
 September 1999 in “The Journal of The British Menopause Society”
September 1999 in “The Journal of The British Menopause Society” The document concludes that skin aging in women can be caused by UV exposure and hormonal changes, and treatments like hormone replacement therapy and various skin therapies can help.
 September 2019 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
September 2019 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Dermal Papilla Cells grown in 3D and with stem cells better mimic natural hair growth conditions than cells grown in 2D.

Microneedle technology is effective for skin rejuvenation and enhancing cosmeceutical delivery, with ongoing innovation and increasing commercialization.
 January 2024 in “Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology”
January 2024 in “Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology” Dermatologists should customize cosmetic treatments for dark-skinned patients to minimize risks and complications.
 24 citations,
July 2011 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
24 citations,
July 2011 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Men with hair loss have more DNA changes in back-of-head hair follicles, possibly protecting them from thinning.
 August 2023 in “JOJ dermatology & cosmetics”
August 2023 in “JOJ dermatology & cosmetics” Antibiotics often cause skin reactions, making them a major health concern.
 January 2023 in “Indian dermatology online journal”
January 2023 in “Indian dermatology online journal” A boy with Pachyonychia congenita has a confirmed gene mutation, highlighting the need for a local genetic database in India.
 7 citations,
May 2022 in “International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health”
7 citations,
May 2022 in “International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health” Isotretinoin therapy for acne can cause many reversible side effects, mainly mild skin conditions, and patient understanding of these effects can improve treatment adherence.

The document is a detailed guide on skin conditions and treatments for dermatologists.
 August 2007 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
August 2007 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” The meeting discussed vitamin D3's role in fighting tuberculosis, potential treatments for skin conditions like psoriasis, and hair follicle regeneration as a possible solution for hair loss.
 January 1998 in “Lasers in Surgery and Medicine”
January 1998 in “Lasers in Surgery and Medicine” Lasers are effective and safe for various medical treatments, including cancer, wound healing, and skin conditions.
 22 citations,
September 2004 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
22 citations,
September 2004 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Bimatoprost can cause longer, thicker, darker eyelashes and eyebrows.
 5 citations,
October 2015 in “The American journal of pathology”
5 citations,
October 2015 in “The American journal of pathology” Mice with a mutated Dsg3 gene showed severe symptoms but not the typical blistering of pemphigus vulgaris.
 13 citations,
January 2018 in “BioMed Research International”
13 citations,
January 2018 in “BioMed Research International” Scalp involvement is common in pemphigus and can lead to hair loss, with the severity of scalp lesions linked to overall disease severity.
 7 citations,
June 1994 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
7 citations,
June 1994 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Obesity may contribute to female hair loss by increasing male hormone levels that affect hair follicles.
 April 2024 in “Oral Surgery Oral Medicine Oral Pathology and Oral Radiology”
April 2024 in “Oral Surgery Oral Medicine Oral Pathology and Oral Radiology” The patient was diagnosed with oral lichen sclerosus and needs long-term monitoring.
 March 2012 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
March 2012 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” African Americans lack knowledge about laser hair removal safety, Nd:Yag laser treatment is effective with high satisfaction, pressure during surgery can cause hair loss, and treating ovarian inflammation may help with alopecia areata.
 March 2012 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
March 2012 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Treating ovarian-related inflammation may help hair regrowth in women with alopecia areata.
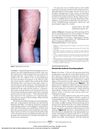 10 citations,
June 2011 in “Archives of Dermatology”
10 citations,
June 2011 in “Archives of Dermatology” Finasteride caused blisters on hands and feet.
 183 citations,
January 2018 in “Cosmetics”
183 citations,
January 2018 in “Cosmetics” Essential oils in cosmetics can offer benefits but may cause allergies and should be used carefully.
[object Object] 9 citations,
August 2021 in “Journal of clinical medicine” Pili torti is a rare condition where hair is twisted and breaks easily, often linked to genetic disorders or other health issues.
 84 citations,
April 2005 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
84 citations,
April 2005 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Treatments for melanin disorders exist, but more effective options needed.
 25 citations,
March 2017 in “Journal of Dermatological Treatment”
25 citations,
March 2017 in “Journal of Dermatological Treatment” Platelet-rich plasma treatment for non-scarring hair loss shows mixed results and needs more research.
 29 citations,
January 2007 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
29 citations,
January 2007 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Photodynamic Therapy is an effective treatment for mild to severe acne.



























