 197 citations,
June 2009 in “American journal of human genetics”
197 citations,
June 2009 in “American journal of human genetics” WNT10A mutations often cause ectodermal dysplasias, with males showing more tooth issues than females.
[object Object]  31 citations,
August 2020 in “EClinicalMedicine”
31 citations,
August 2020 in “EClinicalMedicine” Male cancer patients have a higher risk of severe illness and death from COVID-19 than female patients.
 27 citations,
August 2015 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
27 citations,
August 2015 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” The document concludes that there is a significant lack of reporting on the sex and age of cells in skin research, which could affect clinical trials and treatments.
 11 citations,
May 2021 in “Journal of Medical Virology”
11 citations,
May 2021 in “Journal of Medical Virology” Men are more likely to have severe respiratory viral infections like COVID-19 due to hormonal and genetic differences, while women generally have stronger immune responses.
 34 citations,
July 2020 in “Frontiers in immunology”
34 citations,
July 2020 in “Frontiers in immunology” Androgens may influence T cells, contributing to higher autoimmune liver disease risk in women.
 30 citations,
June 2021 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
30 citations,
June 2021 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Mutations in the WNT10A gene can cause skin, hair, teeth, and other disorders, and may also affect other areas like kidney and cancer, with potential for targeted treatments.
 197 citations,
January 2019 in “Neuropsychopharmacology”
197 citations,
January 2019 in “Neuropsychopharmacology” Male and female bodies respond differently to stress, influenced by hormones and development stages, with implications for stress-related diseases.
 125 citations,
August 2020 in “Frontiers in Immunology”
125 citations,
August 2020 in “Frontiers in Immunology” Men generally have more severe COVID-19 cases and higher death rates than women due to biological differences.
[object Object]  113 citations,
July 2020 in “Communications biology”
113 citations,
July 2020 in “Communications biology” Men, especially older ones with health issues like prostate cancer, may have worse COVID-19 outcomes and could benefit from therapies targeting male hormones.
 47 citations,
May 2020 in “Cardiovascular Research”
47 citations,
May 2020 in “Cardiovascular Research” The document concludes that future heart disease research should account for sex-specific differences to improve diagnosis, treatment, and outcomes.
 16 citations,
December 2021 in “Frontiers in Endocrinology”
16 citations,
December 2021 in “Frontiers in Endocrinology” Sex hormones may affect COVID-19 severity, with estrogen possibly reducing risk and testosterone potentially increasing it.
 June 2023 in “Pharmaceuticals”
June 2023 in “Pharmaceuticals” Men and women respond differently to drugs for COVID-19, high cholesterol, and diabetes, which suggests a need for personalized treatments.
 1 citations,
April 2024 in “Science Advances”
1 citations,
April 2024 in “Science Advances” Female cuckoo color differences are linked to their unique genes and help avoid male harassment.
 48 citations,
April 2010 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
48 citations,
April 2010 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Men are more likely to get infectious skin diseases, while women are more prone to autoimmune and pigment-related skin conditions, influenced by biological and environmental factors.
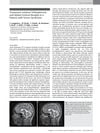 2 citations,
July 2016 in “Pharmacopsychiatry”
2 citations,
July 2016 in “Pharmacopsychiatry” A person with Turner Syndrome showed severe schizophrenia that didn't respond to treatment and had brain shrinkage.
 2 citations,
February 2019 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)”
2 citations,
February 2019 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)” The Asiatic lion has very low genetic diversity and unique genetic traits, highlighting the need for its conservation.
 25 citations,
February 2022 in “JAAD International”
25 citations,
February 2022 in “JAAD International” Some COVID-19 patients lose hair, with the most common type linked to male hormones and possibly increasing the risk of severe illness.
April 2023 in “Andrologia” American men are older, more obese, and have longer infertility than Canadian men.
 29 citations,
March 2019 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
29 citations,
March 2019 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Acne is significantly influenced by genetics, and understanding its genetic basis could lead to better, targeted treatments.
 21 citations,
January 2021 in “Therapeutic Advances in Endocrinology and Metabolism”
21 citations,
January 2021 in “Therapeutic Advances in Endocrinology and Metabolism” Testosterone may have a dual role in COVID-19, potentially worsening outcomes in men, and testosterone therapy could help some patients, but more research is needed.
 9 citations,
January 2016 in “Skin Pharmacology and Physiology”
9 citations,
January 2016 in “Skin Pharmacology and Physiology” The study concluded that both estrogen and androgen receptors, which decrease with age, are linked to skin aging and may be hormonally regulated.
 5 citations,
December 2017 in “The Journal of Dermatology”
5 citations,
December 2017 in “The Journal of Dermatology” A new gene mutation caused a man's rare skin condition, Schöpf-Schulz-Passarge syndrome.
 4 citations,
April 2021 in “Experimental and Molecular Medicine”
4 citations,
April 2021 in “Experimental and Molecular Medicine” The conclusion is that certain genetic factors and blood types may affect COVID-19 severity, but changes in ACE2 and TMPRSS2 genes are not clearly linked to it.
 August 2017 in “International journal of research in dermatology”
August 2017 in “International journal of research in dermatology” 0.05% betamethasone dipropionate is the most effective treatment for mild alopecia areata.
 16 citations,
April 2012 in “Journal of mammalogy”
16 citations,
April 2012 in “Journal of mammalogy” Young female Australian fur seals are losing hair due to low tyrosine and zinc levels and high pollution exposure.
 9 citations,
April 2018 in “Journal of trace elements in medicine and biology”
9 citations,
April 2018 in “Journal of trace elements in medicine and biology” Hair analysis can show nutritional status and environmental exposure, with phosphorus being very stable in hair and differences found based on gender and conditions like depression and autism.
 January 2023 in “Journal of men's health”
January 2023 in “Journal of men's health” Higher dihydrotestosterone may be linked to more inflammation in COVID-19 patients with low testosterone.
 July 2020 in “Environmental Science and Pollution Research”
July 2020 in “Environmental Science and Pollution Research” Finasteride harms invertebrates' survival and burial ability.
 383 citations,
February 2011 in “Nature Reviews Genetics”
383 citations,
February 2011 in “Nature Reviews Genetics” DNA profiling in forensics has improved, but predicting physical traits and ancestry from DNA has limitations and requires ethical consideration.
 96 citations,
June 2017 in “Nature Communications”
96 citations,
June 2017 in “Nature Communications” A WNT10A gene mutation leads to ectodermal dysplasia by disrupting cell growth and differentiation.




























