January 2023 in “Journal of Integrative Medicine and Research” Vitiligo and lupus can occur together, requiring careful treatment to manage both conditions.
 January 2014 in “European Geriatric Medicine”
January 2014 in “European Geriatric Medicine” A postmenopausal woman's virilization was caused by a rare ovarian tumor that was hard to detect but was successfully treated with surgery.
 16 citations,
January 2008 in “Acta dermato-venereologica”
16 citations,
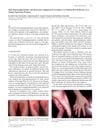
January 2008 in “Acta dermato-venereologica” Vitamin B12 deficiency can cause skin darkening and increased blood vessels, but treatment can improve symptoms.
December 2013 in “American journal of transplantation” The patient improved after antiviral treatment for a viral infection.
October 1984 in “Kidney international” The patient had complex urinary tract issues and ambiguous genitalia, with physical features suggesting a hormonal imbalance.
 25 citations,
July 1991 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
25 citations,
July 1991 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis is a rare, serious skin condition that can affect anyone, is more common in women, and may be linked to genetics, with a 20% mortality rate mainly due to sepsis.
 32 citations,
March 2021 in “Journal of cosmetic dermatology (Print)”
32 citations,
March 2021 in “Journal of cosmetic dermatology (Print)” COVID-19 infection may trigger alopecia areata in some patients.
July 2024 in “Vestnik dermatologii i venerologii” Post-COVID-19 hair loss is different from androgenetic alopecia and can be identified by lower copper and higher selenium levels.
 January 2021 in “Scandinavian journal of clinical and laboratory investigation”
January 2021 in “Scandinavian journal of clinical and laboratory investigation” The document describes a way to measure biotin in blood to prevent wrong test results in hormone level testing.
 March 2014 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
March 2014 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Vitamin D deficiency is common in temporary hair loss, and stress is often a suspected cause.
 June 2011 in “The Journal for Nurse Practitioners”
June 2011 in “The Journal for Nurse Practitioners” Up to half of adult women may experience hair loss, and doctors should use medical history, exams, and tests to find the cause and treat it.
July 2022 in “Dermatologica Sinica” Many women with hair loss also have zinc deficiency, iron depletion, or thyroid issues.
 December 2022 in “Cureus”
December 2022 in “Cureus” Low iron levels are linked to hair loss in women.
 42 citations,
February 1985 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
42 citations,
February 1985 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Excessive hair growth can be assessed by history, exam, and blood tests, and treated with medication like dexamethasone, birth control pills, and spironolactone.
13 citations,
September 2009 in “Heart & Lung” Kawasaki's disease can occur in adults and should be considered with specific symptoms and high ferritin levels.
 27 citations,
September 2012 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
27 citations,
September 2012 in “Dermatologic Clinics” The document concludes that using specific tools and tests is essential for identifying the cause of hair loss and deciding on the right treatment.
 10 citations,
June 2000 in “Primary Care”
10 citations,
June 2000 in “Primary Care” The document explains different hair loss types and treatments, emphasizing diagnosis through examination and tests, and specific treatments for each condition.
 1 citations,
March 2022 in “Clinical and Experimental Obstetrics & Gynecology”
1 citations,
March 2022 in “Clinical and Experimental Obstetrics & Gynecology” Ovarian volume is significantly related to higher levels of certain hormones in Korean women with PCOS.
 7 citations,
October 2019 in “Case reports in endocrinology”
7 citations,
October 2019 in “Case reports in endocrinology” A young woman's symptoms suggested PCOS, but tests and surgery confirmed and treated a rare ovarian tumor, resolving her condition.
 2 citations,
October 2015 in “Primary Care: Clinics in Office Practice”
2 citations,
October 2015 in “Primary Care: Clinics in Office Practice” Doctors should diagnose hair loss by examining the patient and possibly doing tests, and then treat it based on the type, which may prevent permanent hair loss.
 October 2017 in “Iranian Journal of Dermatology”
October 2017 in “Iranian Journal of Dermatology” Clinical exams are good for diagnosing some women's hair loss, but lab tests aren't always needed.
 63 citations,
March 2011 in “Clinical Endocrinology”
63 citations,
March 2011 in “Clinical Endocrinology” Evaluate postmenopausal women with high androgen levels using medical history, physical exams, lab tests, and imaging to manage health risks.
 4 citations,
January 2019 in “Clinical Chemistry”
4 citations,
January 2019 in “Clinical Chemistry” Diagnosing Polycystic Ovary Syndrome is hard due to varying symptoms, no set criteria, and the need for better tests and education.
 35 citations,
January 2014 in “BioMed Research International”
35 citations,
January 2014 in “BioMed Research International” Female pattern hair loss involves hormonal factors, genetics, and may be linked to low ferritin levels.
 21 citations,
March 2006 in “Seminars in Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
21 citations,
March 2006 in “Seminars in Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” Most hair loss disorders can be accurately diagnosed and treated in an outpatient setting.
 January 2020 in “Kocatepe Tıp Dergisi”
January 2020 in “Kocatepe Tıp Dergisi” Not all hair loss patients need lab tests; patient history and physical exams are key to deciding who does.
 18 citations,
May 2016 in “Annals of Medicine”
18 citations,
May 2016 in “Annals of Medicine” The article concludes that correctly diagnosing systemic causes of hair loss requires a detailed clinical evaluation and a systematic diagnostic approach.
 10 citations,
November 2018 in “Physiological Research”
10 citations,
November 2018 in “Physiological Research” The conclusion is that standardizing testosterone measurement methods is essential for better diagnosis accuracy in women.
 10 citations,
February 2007 in “Clinical techniques in small animal practice”
10 citations,
February 2007 in “Clinical techniques in small animal practice” Dogs with sex hormone imbalances may not drink or pee a lot but often lose hair on their body and can have reproductive system issues.
 3 citations,
February 2008 in “Basic and clinical dermatology”
3 citations,
February 2008 in “Basic and clinical dermatology” Telogen Effluvium is a hair loss condition where treatment involves identifying and managing its triggers.























