 25 citations,
May 2019 in “Heliyon”
25 citations,
May 2019 in “Heliyon” Hair treatments cause significant structural changes, especially with excessive heat, regardless of ethnicity.
 January 2017 in “Clinical approaches and procedures in cosmetic dermatology”
January 2017 in “Clinical approaches and procedures in cosmetic dermatology” Cosmetic procedures can harm hair, but damage can be minimized with knowledge and care; however, once hair is damaged, it cannot be reliably repaired.
 1 citations,
January 2017 in “Clinical approaches and procedures in cosmetic dermatology”
1 citations,
January 2017 in “Clinical approaches and procedures in cosmetic dermatology” Hair can't be reliably repaired once damaged; prevention and proper product use are key to maintaining hair health.
 40 citations,
June 2013 in “Molecular Pharmaceutics”
40 citations,
June 2013 in “Molecular Pharmaceutics” The gelatin/β-TCP scaffold with nanoparticles improves wound healing and skin regeneration.
13 citations,
March 2017 in “Skin Research and Technology” Formaldehyde damages curly hair more than glyoxylic acid.
1 citations,
December 2022 in “Applied Sciences”  September 2020 in “Benha Journal of Applied Sciences”
September 2020 in “Benha Journal of Applied Sciences” Protein hair straighteners damage the hair more than hair dyes.
 5 citations,
September 2015 in “BMC Medical Genetics”
5 citations,
September 2015 in “BMC Medical Genetics” The EDAR gene mutation leads to thinner and more deformed hair shafts.
 3 citations,
January 2015 in “Mathematical problems in engineering”
3 citations,
January 2015 in “Mathematical problems in engineering” Hair damage increases significantly with higher temperatures and longer heating times.
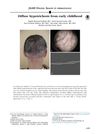 September 2016 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
September 2016 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” The girl has a genetic hair condition causing thin hair since childhood.
 41 citations,
November 2020 in “Colloids and surfaces. B, Biointerfaces”
41 citations,
November 2020 in “Colloids and surfaces. B, Biointerfaces” Different hair protein amounts change the strength of keratin/chitosan gels, useful for making predictable tissue engineering materials.
 17 citations,
June 2021 in “Molecules”
17 citations,
June 2021 in “Molecules” Melatonin-loaded nanocarriers improve melatonin delivery and effectiveness for various medical treatments.
 8 citations,
November 2022 in “International Journal of Cosmetic Science”
8 citations,
November 2022 in “International Journal of Cosmetic Science” Human hair varies widely and should be classified by curl type rather than race.
 December 2013 in “Biomedical and biopharmaceutical research”
December 2013 in “Biomedical and biopharmaceutical research” Nanotechnology shows promise for better drug delivery and cancer treatment.
 August 2023 in “European Journal of Plastic Surgery”
August 2023 in “European Journal of Plastic Surgery” 3D bioprinting is advancing in plastic and reconstructive surgery, especially for creating tissues and improving surgical planning, but faces challenges like vascularization and material development.
 231 citations,
October 1999 in “Journal of Clinical Investigation”
231 citations,
October 1999 in “Journal of Clinical Investigation” Activating the Sonic hedgehog gene in mice can start the hair growth phase.
 3 citations,
February 2023 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
3 citations,
February 2023 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” Autologous Platelet and Extracellular Vesicle-Rich Plasma (PVRP) has potential in enhancing tissue regeneration and improving hair conditions, but its effectiveness varies due to individual differences.
2 citations,
January 2022 in “Anais brasileiros de dermatologia/Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia” Chemical hair straighteners can cause scalp and hair damage, but long-term effects are unclear.
1 citations,
October 2018 in “InTech eBooks” Ethosomes are a promising method for treating hair loss by delivering drugs directly to the scalp.
 January 2025 in “Clinical Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology”
January 2025 in “Clinical Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology” Genetic testing is crucial for diagnosing rare hair loss disorders.
 13 citations,
January 2017 in “Cosmetics”
13 citations,
January 2017 in “Cosmetics” Different tests are used to see how hair care products affect hair, and choosing the right test is important for accurate results.
 January 2024 in “Molecules (Basel. Online)”
January 2024 in “Molecules (Basel. Online)” Juglone from walnut extracts may help repair damaged hair.
 4 citations,
March 2013 in “InTech eBooks”
4 citations,
March 2013 in “InTech eBooks” Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy (CLSM) is a useful tool for studying how drugs interact with skin and diagnosing skin disorders, despite some limitations.
 56 citations,
June 2015 in “Nature Protocols”
56 citations,
June 2015 in “Nature Protocols” Two-photon microscopy helps observe hair follicle stem cell behaviors in mice.

Proretinal nanoparticles are a safe and effective way to deliver retinal to the skin.
 January 2005 in “Seibutsu Butsuri/Seibutsu butsuri”
January 2005 in “Seibutsu Butsuri/Seibutsu butsuri” Chemical treatments damage hair more than UV exposure, making it thinner and less flexible.
 43 citations,
September 2001 in “Scanning”
43 citations,
September 2001 in “Scanning” Hair treatments like bleaching increase friction by exposing tiny pores on the hair surface.
 1 citations,
December 2014 in “Scanning”
1 citations,
December 2014 in “Scanning” Multiphoton microscopy effectively images rabbit skin structures in detail without staining and shows differences from human skin.
 35 citations,
July 2009 in “Optics express”
35 citations,
July 2009 in “Optics express” Researchers created a new light source that improves chemical imaging by removing background noise.
 1 citations,
May 2001 in “Proceedings of SPIE, the International Society for Optical Engineering/Proceedings of SPIE”
1 citations,
May 2001 in “Proceedings of SPIE, the International Society for Optical Engineering/Proceedings of SPIE” The system helps monitor hair properties using RGB video microscopy.


























