 139 citations,
December 1998 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
139 citations,
December 1998 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” K6hf is a unique protein found only in a specific layer of hair follicles.
 122 citations,
November 1984 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
122 citations,
November 1984 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” No single treatment is consistently effective for alopecia areata, and more research is needed.
 105 citations,
September 1995 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
105 citations,
September 1995 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Recombinant cytokine therapy can cause skin reactions ranging from mild to severe.
 80 citations,
April 2018 in “Trends in Molecular Medicine”
80 citations,
April 2018 in “Trends in Molecular Medicine” Lichen Planopilaris and Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia may help us understand hair follicle stem cell disorders and suggest new treatments.
 74 citations,
April 2005 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
74 citations,
April 2005 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Minoxidil and finasteride are effective for male hair loss, minoxidil for female hair loss, and various treatments like corticosteroids work for alopecia areata; treatment should be tailored to the individual.
 70 citations,
January 2000 in “Hormone Research in Paediatrics”
70 citations,
January 2000 in “Hormone Research in Paediatrics” SAHA syndrome is a condition in women involving skin and hair issues, often related to hormonal imbalances, and is treated based on the underlying cause.
 70 citations,
June 2010 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
70 citations,
June 2010 in “Clinics in Dermatology” Certain groups may need vitamin supplements to improve hair health and prevent other health problems.
 68 citations,
September 2003 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
68 citations,
September 2003 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Shrinking skin cancer increases the chance of cancer in nearby lymph nodes.
 67 citations,
May 2010 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
67 citations,
May 2010 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Some chemotherapy can cause permanent hair loss.
 64 citations,
March 2005 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
64 citations,
March 2005 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) slows down hair growth and promotes hair follicle regression.
 61 citations,
June 2014 in “Scientific Reports”
61 citations,
June 2014 in “Scientific Reports” Wnt1a-conditioned medium from stem cells helps activate cells important for hair growth and can promote hair regrowth.
 52 citations,
February 2006 in “Archives of Dermatology”
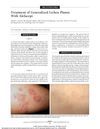
52 citations,
February 2006 in “Archives of Dermatology” Alefacept may effectively treat severe lichen planus, with patients showing significant improvement and no side effects.
 52 citations,
November 2003 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
52 citations,
November 2003 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Different harmful mutations in the CDH3 gene cause HJMD, but symptoms vary among individuals.
 51 citations,
January 2014 in “Pediatric Clinics of North America”
51 citations,
January 2014 in “Pediatric Clinics of North America” The guide explains how to identify and treat children's hair loss, including fungal infections, autoimmune disorders, hairstyle changes, self-correcting conditions, and behavioral therapy for hair-pulling.
 51 citations,
July 2010 in “Trends in Endocrinology and Metabolism”
51 citations,
July 2010 in “Trends in Endocrinology and Metabolism” Prolactin may play a significant role in skin and hair health and could be a target for treating skin and hair disorders.
 46 citations,
April 2008 in “Archives of Dermatological Research”
46 citations,
April 2008 in “Archives of Dermatological Research” Substance P may worsen acne by increasing inflammation, but corticosteroids might help by reducing this effect.
 45 citations,
May 2018 in “Stem Cell Research & Therapy”
45 citations,
May 2018 in “Stem Cell Research & Therapy” Using patients' own fat-derived cells to treat alopecia areata significantly improved hair growth and was safe.
 45 citations,
January 2010 in “International journal of trichology”
45 citations,
January 2010 in “International journal of trichology” Topical immunotherapy, especially with DPCP, is effective for treating severe alopecia areata.
 42 citations,
November 2018 in “Archives of dermatological research”
42 citations,
November 2018 in “Archives of dermatological research” Apremilast was not effective in treating moderate-to-severe alopecia areata.
 42 citations,
April 2011 in “Annals of Pharmacotherapy”
42 citations,
April 2011 in “Annals of Pharmacotherapy” Flutamide effectively treats female pattern hair loss with low doses showing good liver tolerance.
 41 citations,
June 2003 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
41 citations,
June 2003 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Long-term minoxidil use can cause pseudoacromegaly, but stopping it improves symptoms.
 36 citations,
May 2011 in “The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism”
36 citations,
May 2011 in “The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism” Treatment with a hormone agonist can reduce excess male hormones in postmenopausal women without surgery.
 36 citations,
May 2011 in “Dermatologic therapy”
36 citations,
May 2011 in “Dermatologic therapy” No treatments fully cure or prevent alopecia areata; some help but have side effects or need more research.
 32 citations,
December 2009 in “Archives of Dermatological Research”
32 citations,
December 2009 in “Archives of Dermatological Research” Dihydrotestosterone increases certain inflammatory signals in skin cells, potentially contributing to acne.
 31 citations,
August 2005 in “The American Journal of Dermatopathology”
31 citations,
August 2005 in “The American Journal of Dermatopathology” The study concluded that PKP1 is essential for skin integrity and hair growth, and its dysfunction causes the symptoms of ectodermal dysplasia/skin fragility syndrome.
 30 citations,
July 2019 in “Endocrinology”
30 citations,
July 2019 in “Endocrinology” Certain HSD3B1 gene types are linked to worse prostate cancer outcomes and affect treatment response and other health conditions.
 30 citations,
December 1999 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings”
30 citations,
December 1999 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings” Steroids, particularly estrogens and 5α-reductase inhibitors, affect blood vessel-related hair growth processes in hair follicle cells.
 29 citations,
September 2012 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
29 citations,
September 2012 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Hair disorders are caused by a complex mix of biology, genetics, hormones, and environmental factors, affecting hair growth and leading to conditions like alopecia.
 28 citations,
November 2013 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
28 citations,
November 2013 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” GMG-43AC may help reduce unwanted hair growth and treat certain hair loss conditions.
 26 citations,
June 2019 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
26 citations,
June 2019 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Regenerative therapies show promise for treating vitiligo and alopecia areata.






























