 3 citations,
July 2015 in “Dermatologica Sinica”
3 citations,
July 2015 in “Dermatologica Sinica” About half of Taiwanese dermatologists use dermoscopy, mainly to improve diagnosis and detect cancer early, but cost and lack of training limit its wider use.
 97 citations,
September 2011 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
97 citations,
September 2011 in “British Journal of Dermatology” The human hair follicle can store topical compounds and be targeted for drug delivery with minimal side effects.
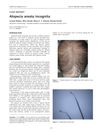 19 citations,
January 2011 in “Clinics”
19 citations,
January 2011 in “Clinics” A young woman with a rare hair loss condition improved with steroid and biotin treatment.
 15 citations,
August 2015 in “Scanning”
15 citations,
August 2015 in “Scanning” Corkscrew and cigarette-ash-shaped hairs in tinea capitis are caused by internal hair degradation and external resistance.
 9 citations,
January 2019 in “American Journal of Dermatopathology”
9 citations,
January 2019 in “American Journal of Dermatopathology” DKK-1 gene linked to hair loss in AGA and AA patients; more research needed for potential therapy.
 2 citations,
October 2017 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
2 citations,
October 2017 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Focal atrichia helps diagnose female pattern hair loss.
 1 citations,
May 2023 in “Curēus”
1 citations,
May 2023 in “Curēus” A man had a benign pilar cyst on his face, which is rare and was successfully removed by surgery.
 1 citations,
April 2022 in “The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine ”
1 citations,
April 2022 in “The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine ” Fractional laser therapy may help regrow hair in alopecia areata.
 December 2020 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)”
December 2020 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)” Stress can cause a type of hair loss in mice lacking the CCHCR1 gene.
 July 2008 in “Expert Review of Dermatology”
July 2008 in “Expert Review of Dermatology” Proper planning for hair transplants is crucial for natural results, with careful patient selection and strategic graft placement being key factors.
 March 2004 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
March 2004 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Women with lupus experienced non-scarring hair loss with fewer hair follicles, and the test for lupus in hair was not helpful.
 140 citations,
August 2011 in “Biomaterials”
140 citations,
August 2011 in “Biomaterials” Keratose, derived from human hair, is a non-toxic biomaterial good for tissue regeneration and integrates well with body tissues.
 49 citations,
February 2019 in “The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism”
49 citations,
February 2019 in “The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism” Use "female pattern hair loss" term, assess androgen excess, treat with minoxidil and other medications if needed.
 26 citations,
July 2021 in “Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology”
26 citations,
July 2021 in “Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology” The review suggests that a special cell-derived treatment shows promise for various skin conditions and hair growth but needs more research for confirmation.
 15 citations,
November 2019 in “Cutaneous and Ocular Toxicology”
15 citations,
November 2019 in “Cutaneous and Ocular Toxicology” Minoxidil tretinoin liposomal based hydrogel shows promise for effective treatment of hair loss by delivering both drugs at the same time.
 11 citations,
May 2009 in “Medical Hypotheses”
11 citations,
May 2009 in “Medical Hypotheses” Male pattern baldness is an unintended side effect of the body's use of androgens for muscle growth, especially in those genetically prone to it.
 7 citations,
April 2015 in “Plastic and Aesthetic Nursing”
7 citations,
April 2015 in “Plastic and Aesthetic Nursing” Hair transplantation can effectively restore a natural-looking hairline when properly planned and executed.
 5 citations,
October 2018 in “Dermatologic therapy”
5 citations,
October 2018 in “Dermatologic therapy” Recognizing congenital triangular alopecia is crucial to avoid unnecessary treatments.
 4 citations,
December 2017 in “American Journal of Dermatopathology”
4 citations,
December 2017 in “American Journal of Dermatopathology” Naked hair shafts are significantly associated with scarring hair loss and may help diagnose it, especially when multiple are found.
 3 citations,
May 2018 in “InTech eBooks”
3 citations,
May 2018 in “InTech eBooks” Animal models, especially mice, are essential for advancing hair loss research and treatment.
 3 citations,
July 1997 in “Current problems in dermatology”
3 citations,
July 1997 in “Current problems in dermatology” Hair restoration surgery has evolved over time, with a focus on natural-looking results and managing patient expectations, while also considering potential complications and the lifelong progression of male pattern baldness.
 2 citations,
March 2021 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
2 citations,
March 2021 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” Umbilical cord-derived media is safe and effective for hair growth.
 July 2015 in “Cambridge University Press eBooks”
July 2015 in “Cambridge University Press eBooks” The document concludes that careful history and physical exams are crucial for accurately diagnosing polycystic ovary syndrome and distinguishing it from other similar conditions.
 July 2011 in “Springer eBooks”
July 2011 in “Springer eBooks” The document concluded that FDA-approved treatments like minoxidil and finasteride are effective for hair loss, while the effectiveness of natural remedies and other non-approved treatments is not well-supported by evidence.
 July 2007 in “Clinical Risk”
July 2007 in “Clinical Risk” The claimant sued for negligence after a hair treatment caused harm and distress, and the defendant responded after legal action started.
115 citations,
August 2004 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Modulating Cytochrome P450 activity could help develop new skin disease treatments.
 9 citations,
July 2002 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
9 citations,
July 2002 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” The document concludes that fexofenadine reduces inflammation in chronic hives, cholestyramine helps half of pregnant women with itchy rashes, and relaxing incisions are a good alternative in facial surgery for the elderly.
 7 citations,
October 2018 in “Journal of Craniofacial Surgery”
7 citations,
October 2018 in “Journal of Craniofacial Surgery” About 21.3% of young, healthy Chinese men experience hair loss. Hairlines are mostly linear or have a central protrusion. Hair is densest on the top and back of the head, and hair follicles usually have 1 or 2 hairs. This information can help in designing hair restoration procedures.
 5 citations,
February 2004 in “Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology”
5 citations,
February 2004 in “Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology” Multiple eye conditions were studied, highlighting the importance of various imaging methods for diagnosis, the vision side effects of drugs tamoxifen and Propecia, and the usefulness of optical coherence tomography for diagnosing and monitoring macular and retinal diseases.
 3 citations,
June 1997 in “Veterinary Dermatology”
3 citations,
June 1997 in “Veterinary Dermatology” Minoxidil treatment can stimulate hair growth in hairless puppies if applied early.





























