 86 citations,
January 2019 in “Frontiers in Immunology”
86 citations,
January 2019 in “Frontiers in Immunology” The document concludes that diagnosing and treating Human African Trypanosomiasis is challenging, but new treatments like fexinidazole are promising.
1 citations,
March 2019 in “American journal of geriatric psychiatry/The American journal of geriatric psychiatry” The case shows the need for psychiatrists to manage end-of-life care for dementia patients, including respecting patients' wishes and using hospice services.
3 citations,
February 2002 in “The American journal of psychiatry” Stopping birth control pills may have triggered a manic episode in a woman with HAIR-AN syndrome.

People with Down syndrome have a higher risk of skin disorders and need better screening and treatment.
 88 citations,
October 2002 in “Journal of Dermatology”
88 citations,
October 2002 in “Journal of Dermatology” Finasteride for hair loss may cause depression, affecting sleep and relationships.
 11 citations,
February 2003 in “Baillière's best practice & research. Clinical obstetrics & gynaecology/Baillière's best practice and research in clinical obstetrics and gynaecology”
11 citations,
February 2003 in “Baillière's best practice & research. Clinical obstetrics & gynaecology/Baillière's best practice and research in clinical obstetrics and gynaecology” Acne and increased body hair in teenage girls are normal but severe cases may need hormone evaluation and treatment can prevent diabetes linked to PCO.
 2 citations,
January 1998 in “Dermatology”
2 citations,
January 1998 in “Dermatology” Stopping forehead irritation and using hydrocortisone helped a man's skin, Martinique has lower melanoma rates, a man had an allergy to a specific antifungal, another had unexplained cysts, certain drugs can cause skin reactions without always being interrelated, a link between Fanconi anemia and a skin condition was suggested, high levels of a certain protein may play a role in a type of psoriasis, and there's a need to study the connection between scalp pain and hair loss.
 July 2021 in “Journal of dermatology research and therapy”
July 2021 in “Journal of dermatology research and therapy” COVID-19 may worsen hair loss, and Nourkrin® could be a safe treatment option, but more research is needed.
 1 citations,
June 2023 in “Genes”
1 citations,
June 2023 in “Genes” Hair loss from Alopecia Areata is caused by both genes and environment, with several treatments available but challenges in cost and relapse remain.
 July 2004 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
July 2004 in “Clinics in Dermatology” The Third World Congress of the International Academy of Cosmetic Dermatology discussed various topics like hair disorders, skin conditions, wound healing, shampoo technology, acne treatment, and the use of lasers in dermatology.
 September 2003 in “Clinics in Family Practice”
September 2003 in “Clinics in Family Practice” Different hair diseases affect people during childbearing years, with treatments ranging from medication to psychological support.
8 citations,
January 2016 in “Case Reports in Psychiatry” Trichotillomania in dementia may be better treated with dopamine blockers like quetiapine than with SSRIs.
 10 citations,
January 2017 in “Skin Pharmacology and Physiology”
10 citations,
January 2017 in “Skin Pharmacology and Physiology” Finasteride may cause vitiligo, sexual issues, and depression; better treatments and predicting side effects needed.
 May 2024 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology”
May 2024 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology” Androgenetic alopecia in men is genetic and linked to health issues like obesity and heart disease, with treatments including minoxidil, finasteride, and hair transplants.
 3 citations,
June 2023 in “Frontiers in medicine”
3 citations,
June 2023 in “Frontiers in medicine” Oxidative stress may contribute to hair loss in alopecia areata and antioxidants could potentially help as a treatment.
 9 citations,
January 2017 in “International Journal of Trichology”
9 citations,
January 2017 in “International Journal of Trichology” The study suggests that mast cells might be involved in the hair loss condition telogen effluvium and could be a target for treatment.
 2 citations,
July 2014 in “Irish Journal of Medical Science”
2 citations,
July 2014 in “Irish Journal of Medical Science” The meeting discussed medical findings, including benefits of certain treatments for cancer and heart conditions, and highlighted issues like poor adherence to preventive measures and skill gaps among interns.
 9 citations,
January 2013 in “Acta dermato-venereologica”
9 citations,
January 2013 in “Acta dermato-venereologica” The conclusion is that "trichoknesis" should be recognized as a separate condition from trichodynia, characterized by itching instead of pain.
 January 2013 in “Psychiatry and clinical neurosciences”
January 2013 in “Psychiatry and clinical neurosciences” Physical symptoms in depression can reveal underlying medical conditions.
 1 citations,
October 2016 in “Iranian journal of psychiatry and behavioral sciences”
1 citations,
October 2016 in “Iranian journal of psychiatry and behavioral sciences” Sertraline, an antidepressant, may rarely cause hair loss.
 219 citations,
March 2004 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
219 citations,
March 2004 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” 5% and 2% minoxidil solutions effectively promote hair growth and reduce hair loss, with 5% being slightly more effective but having more side effects.
 January 2017 in “International journal of science and research”
January 2017 in “International journal of science and research” Trichotillomania is a chronic hair-pulling disorder, more common in females, treated with therapy and sometimes medication.
 26 citations,
January 2017 in “Acta dermato-venereologica”
26 citations,
January 2017 in “Acta dermato-venereologica” Antidepressants might help with skin inflammation and improve conditions like psoriasis and eczema.
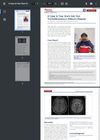 1 citations,
July 2022 in “Movement disorders clinical practice”
1 citations,
July 2022 in “Movement disorders clinical practice” A patient with Wilson's disease showed hair-pulling behavior as an initial symptom.
 13 citations,
September 2011 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology”
13 citations,
September 2011 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology” The oral contraceptive ethinylestradiol/chlormadinone acetate is effective in reducing acne and improving other skin conditions related to high androgen levels.
9 citations,
September 2019 in “Journal of clinical sleep medicine” Vitamin B12 deficiency can rarely cause excessive daytime sleepiness.
 86 citations,
July 1993 in “Drugs”
86 citations,
July 1993 in “Drugs” Finasteride treats enlarged prostate, shrinks it, improves urination, but may cause sexual dysfunction and isn't for women or children.
 1 citations,
December 2021 in “Androgens”
1 citations,
December 2021 in “Androgens” Testosterone and its metabolites affect brain functions and could help treat neurological disorders.
9 citations,
February 2018 in “Journal of Patient-Reported Outcomes” New tools were created to help lupus patients report their symptoms and impacts more accurately.
 13 citations,
August 2005 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
13 citations,
August 2005 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Doctors should consider psychological factors when treating skin conditions and work with mental health experts.

























