 3 citations,
February 2018 in “Australian Veterinary Journal”
3 citations,
February 2018 in “Australian Veterinary Journal” Veterinarians could test positive for ketamine from work exposure, not just substance abuse.
 48 citations,
March 2003 in “BJOG: An International Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology”
48 citations,
March 2003 in “BJOG: An International Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology” Mothers and newborns with dental fillings had higher mercury in their hair, but getting fillings during pregnancy didn't raise mercury levels further.
 February 2010 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
February 2010 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” A woman with Degos disease managed her condition for nine years with medications and had two healthy pregnancies, while a separate finding suggests a possible link between female pattern hair loss and high blood pressure.
 59 citations,
August 2007 in “Clinical Endocrinology”
59 citations,
August 2007 in “Clinical Endocrinology” The current methods for diagnosing polycystic ovary syndrome are too vague and may lead to misdiagnosis and problems in research.
 34 citations,
July 1999 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
34 citations,
July 1999 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Iron deficiency is not a significant cause of hair loss in women.
 28 citations,
August 2009 in “Nursing for Women's Health”
28 citations,
August 2009 in “Nursing for Women's Health” Cognitive behavioral strategies help women with PCOS make lifestyle changes to improve their health.
 4 citations,
July 2005 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
4 citations,
July 2005 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Topical PUVA and tacrolimus ointment can effectively and safely treat infant alopecia universalis.
 40 citations,
March 1982 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
40 citations,
March 1982 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Young women with diffuse hair loss may have low SHBG levels, which could lead to more active testosterone and contribute to their hair loss.
 218 citations,
April 2012 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
218 citations,
April 2012 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Guidelines suggest various treatments for alopecia areata, but leaving it untreated is also an option as 80% cases may recover on their own.
 23 citations,
October 1971 in “BMJ”
23 citations,
October 1971 in “BMJ” Stopping the pill and giving birth both caused hair loss.
 2 citations,
September 2008 in “Fertility and Sterility”
2 citations,
September 2008 in “Fertility and Sterility” Clinical signs of excess male hormones and actual hormone levels in the blood do not always match in women with polycystic ovary syndrome.
 October 1971 in “The BMJ”
October 1971 in “The BMJ” Hair loss can be linked to hormonal changes, and physical conditions like heart defects can cause depression.
 63 citations,
January 2012 in “The European Journal of Contraception & Reproductive Health Care”
63 citations,
January 2012 in “The European Journal of Contraception & Reproductive Health Care” Some birth control pills have a higher risk of blood clots than others.
 36 citations,
November 2009 in “European Radiology”
36 citations,
November 2009 in “European Radiology” The study found that women with PCOS have more and larger ovarian follicles and differences in ovarian structure, but these features alone can't always diagnose PCOS.
 30 citations,
October 2014 in “PLOS ONE”
30 citations,
October 2014 in “PLOS ONE” BAF200 is essential for proper heart and coronary artery formation.
 28 citations,
April 1936 in “Journal of the American Medical Association”
28 citations,
April 1936 in “Journal of the American Medical Association” Aloe vera healed severe skin damage and restored normal skin in five weeks.
 5 citations,
May 2019 in “Hormone and Metabolic Research”
5 citations,
May 2019 in “Hormone and Metabolic Research” Women with nonclassic 21-hydroxylase deficiency can have successful pregnancies through IVF, with certain factors affecting their chances.
 June 1995 in “International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics”
June 1995 in “International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics” Higher doses of oestradiol implants improve bone density in postmenopausal women.
 260 citations,
July 2010 in “Cell”
260 citations,
July 2010 in “Cell” Mutations in the SRD5A3 gene cause a new type of glycosylation disorder by blocking the production of a molecule necessary for protein glycosylation.
 215 citations,
January 2011 in “Reproductive Biology and Endocrinology”
215 citations,
January 2011 in “Reproductive Biology and Endocrinology” About 7% to 15% of Iranian women have polycystic ovary syndrome, depending on the criteria used to diagnose it.
 158 citations,
May 1968 in “The journal of nutrition/The Journal of nutrition”
158 citations,
May 1968 in “The journal of nutrition/The Journal of nutrition” Zinc is crucial for growth and health in rats.
 120 citations,
June 2008 in “American Journal of Epidemiology”
120 citations,
June 2008 in “American Journal of Epidemiology” A simple screening method found that 6.3% of women in a semiurban area in Sri Lanka have polycystic ovary syndrome, with most showing menstrual irregularities.
 62 citations,
February 2011 in “Expert review of dermatology”
62 citations,
February 2011 in “Expert review of dermatology” Scalp cooling can reduce chemotherapy-induced hair loss and should be available in all hospitals.
 61 citations,
February 2001 in “American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology”
61 citations,
February 2001 in “American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology” Metabolic syndrome and PCOS are related but separate conditions, with metabolic syndrome increasing the risk of heart disease and diabetes.
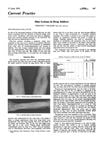 56 citations,
June 1970 in “The BMJ”
56 citations,
June 1970 in “The BMJ” Drug addicts often have scars, skin color changes, blocked veins, and bruising, with severe ulcers from barbiturate injections.
 40 citations,
March 2016 in “The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism”
40 citations,
March 2016 in “The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism” Young girls whose mothers have PCOS may have higher activity of a specific enzyme that could lead to developing PCOS later.
 39 citations,
January 2012 in “Reproductive Biology and Endocrinology”
39 citations,
January 2012 in “Reproductive Biology and Endocrinology” About 8.5% of women in Salvador, Brazil, have Polycystic Ovary Syndrome.
 36 citations,
January 2014 in “The Journal of Sexual Medicine”
36 citations,
January 2014 in “The Journal of Sexual Medicine” Testosterone may help increase sexual events for women with low libido due to antidepressants.
 35 citations,
October 2004 in “Biology of Reproduction”
35 citations,
October 2004 in “Biology of Reproduction” PNU157706 reduced rat sperm movement and fertility without affecting offspring health.
 33 citations,
March 2017 in “Dermatologic Surgery”
33 citations,
March 2017 in “Dermatologic Surgery” Low-level laser therapy effectively treats female hair loss, increasing hair count by 51%.






























