 3 citations,
November 2015 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
3 citations,
November 2015 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Testosterone can both promote hair growth and cause baldness by affecting hair growth signals.
 6 citations,
January 2016 in “Skin appendage disorders”
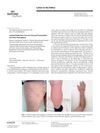
6 citations,
January 2016 in “Skin appendage disorders” A man with rare Lichen Planopilaris lost body hair, not scalp hair, and treatment stopped itching but didn't regrow hair.
 24 citations,
April 2007 in “European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics”
24 citations,
April 2007 in “European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics” Microparticles containing artocarpin extract could effectively treat hair loss and acne with minimal side effects.
 1 citations,
November 2017 in “Skin appendage disorders”
1 citations,
November 2017 in “Skin appendage disorders” Ingrown hairs are a common feature in scarring alopecias due to follicular damage.
 100 citations,
November 1996 in “Molecular Medicine Today”
100 citations,
November 1996 in “Molecular Medicine Today” Growth factors and cytokines are important for hair growth and could potentially treat hair loss, but more research is needed to overcome challenges before they can be used in treatments.
 12 citations,
October 1995 in “The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism”
12 citations,
October 1995 in “The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism” Skin changes can indicate hormonal imbalances and help diagnose endocrine disorders.
 17 citations,
January 2015 in “Current problems in dermatology”
17 citations,
January 2015 in “Current problems in dermatology” Understanding and treating hair disorders in different ethnic groups requires knowledge of specific hair care practices and hair characteristics.
 3 citations,
October 1995 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
3 citations,
October 1995 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Finasteride helps treat skin issues like acne and baldness by blocking testosterone conversion.
 54 citations,
August 2017 in “Gynecological Endocrinology”
54 citations,
August 2017 in “Gynecological Endocrinology” Lifestyle changes and weight loss are key for treating PCOS-related metabolic issues and infertility, with various medications available for specific symptoms.
 143 citations,
October 1996 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
143 citations,
October 1996 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Too much androgen can cause hair loss; finasteride may help.
 67 citations,
July 2016 in “Reviews in Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders”
67 citations,
July 2016 in “Reviews in Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders” Stress can worsen skin conditions by affecting hormone levels and immune response.
 159 citations,
December 2007 in “American Journal of Pathology”
159 citations,
December 2007 in “American Journal of Pathology” Stress-related substance P may lead to hair loss and negatively affect hair growth.
 41 citations,
June 2016 in “Reviews in endocrine and metabolic disorders”
41 citations,
June 2016 in “Reviews in endocrine and metabolic disorders” Hidradenitis suppurativa may be related to hormones and patients often have metabolic disorders; more research is needed to understand this connection.
 11 citations,
May 2022 in “Journal of immunology research”
11 citations,
May 2022 in “Journal of immunology research” Breast implants are linked to autoimmune symptoms, with over half of patients feeling better after removal, but the exact cause is unclear and may involve bacterial biofilm.
 41 citations,
November 2011 in “The Journal of Dermatology”
41 citations,
November 2011 in “The Journal of Dermatology” Some hair loss disorders are caused by genetic mutations affecting hair growth.
 January 2014 in “Journal of Pigmentary Disorders”
January 2014 in “Journal of Pigmentary Disorders” Women's hair gets thinner and grayer as they age, with treatments available for hair loss and graying.
 56 citations,
October 2018 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
56 citations,
October 2018 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Androgens play a complex role in skin conditions like acne and hair loss in women, and normal blood levels don't always show true androgen status.
 10 citations,
January 2009 in “Elsevier eBooks”
10 citations,
January 2009 in “Elsevier eBooks” Hair growth is influenced by hormones and goes through different phases; androgens can both promote and inhibit hair growth depending on the body area.
 2 citations,
January 2014 in “Hair therapy & transplantation”
2 citations,
January 2014 in “Hair therapy & transplantation” New treatments for hair growth disorders are needed due to limited current options and complex hair follicle biology.
 38 citations,
June 2003 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings”
38 citations,
June 2003 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings” Accurate clinical, histological, and genetic methods are key for understanding and treating hair disorders.
 July 2023 in “Al-Azhar Assiut Medical Journal”
July 2023 in “Al-Azhar Assiut Medical Journal” Trichoscopy helps diagnose and manage hair and scalp disorders in children.
 2 citations,
August 2021 in “Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy”
2 citations,
August 2021 in “Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy” Using 5-aminolevulinic acid photodynamic therapy for hair loss didn't increase hair growth but slightly reduced scalp oiliness, and it was safe with mild side effects.
 January 2020 in “Open Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology”
January 2020 in “Open Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology” All women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) in a study had at least one skin disorder, with the most common being excessive hair growth, acne, dark skin patches, hair loss, and oily skin.
 December 2015 in “JAMA Dermatology”
December 2015 in “JAMA Dermatology” Dermatologists can help diagnose endocrine disorders like PCOS and metabolic syndrome by looking at skin symptoms.
 November 2013 in “John Wiley & Sons, Ltd eBooks”
November 2013 in “John Wiley & Sons, Ltd eBooks” Skin symptoms can indicate endocrine disorders and have various treatments.
 129 citations,
January 2009 in “International Journal of Trichology”
129 citations,
January 2009 in “International Journal of Trichology” Trichoscopy can diagnose female hair loss with high accuracy by looking for specific patterns in hair and scalp appearance.
 3 citations,
October 2003 in “Annals of Oncology”
3 citations,
October 2003 in “Annals of Oncology” A woman with low thyroid function did not lose her hair during chemotherapy, possibly because her hair follicles were less affected by the treatment.
 31 citations,
May 2008 in “Drug Discovery Today: Disease Mechanisms”
31 citations,
May 2008 in “Drug Discovery Today: Disease Mechanisms” Different hair growth problems are caused by genetic issues or changes in hair growth cycles, and new treatments are being developed.
 124 citations,
July 2012 in “Archives of Dermatological Research”
124 citations,
July 2012 in “Archives of Dermatological Research” Targeting androgen receptors could be a promising way to treat skin disorders with fewer side effects.
 11 citations,
September 1997 in “Archives of Dermatology”
11 citations,
September 1997 in “Archives of Dermatology” Reduced androgens linked to kinky hair disorder and hair loss; 5a-reductase inhibitors may help.






























