 64 citations,
January 2004 in “American journal of clinical dermatology”
64 citations,
January 2004 in “American journal of clinical dermatology” Folliculitis is an inflammation of hair follicles that requires proper diagnosis and treatment based on the specific cause.
9 citations,
January 2014 in “World journal of clinical cases” Neomycin is a common cause of follicular contact dermatitis, which is treated by avoiding the allergen and using creams.
 24 citations,
August 2005 in “The American Journal of Dermatopathology”
24 citations,
August 2005 in “The American Journal of Dermatopathology” Vertical sections are better than horizontal sections for diagnosing alopecia.
 30 citations,
May 2014 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology”
30 citations,
May 2014 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology” The conclusion is that better understanding and more research are needed to effectively manage follicular and scarring disorders in skin of color, with an emphasis on patient education and cultural awareness.
 March 2021 in “CRC Press eBooks”
March 2021 in “CRC Press eBooks” The document concludes that different patterns of hair thickness and scalp changes can help diagnose types of non-scarring hair loss.
 13 citations,
January 2013 in “International Journal of Trichology”
13 citations,
January 2013 in “International Journal of Trichology” Inflammation around hair follicles may worsen hair loss; evaluating and treating it can improve transplant results.
 90 citations,
June 2006 in “The American Journal of Dermatopathology”
90 citations,
June 2006 in “The American Journal of Dermatopathology” The document concludes that accurate diagnosis of different types of hair loss requires careful examination of hair and scalp tissue, considering both clinical and microscopic features.
 February 2013 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
February 2013 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” A woman's hair loss looked like a different condition due to her hairstyle, and treatment stopped further hair loss but didn't regrow hair.
 March 2020 in “Clinical research in dermatology”
March 2020 in “Clinical research in dermatology” Two unusual cases showed that Lichen Planopilaris can look like other skin conditions and need early treatment to protect hair.
 158 citations,
February 2000 in “Archives of dermatology”
158 citations,
February 2000 in “Archives of dermatology” Some people with pattern hair loss may also have scalp inflammation and scarring similar to lichen planopilaris.
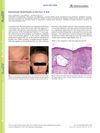 1 citations,
January 2019 in “Acta dermato-venereologica”
1 citations,
January 2019 in “Acta dermato-venereologica” The woman's skin and hair symptoms were confirmed as frontal fibrosing alopecia, and while facial papules are common in such cases, there's no effective local treatment, but systemic treatments can help.
 April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks”
April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks” Lichen planopilaris is a rare, chronic condition causing hair loss, mainly in middle-aged women, and early treatment is important to prevent permanent baldness.
 129 citations,
January 2009 in “International Journal of Trichology”
129 citations,
January 2009 in “International Journal of Trichology” Trichoscopy can diagnose female hair loss with high accuracy by looking for specific patterns in hair and scalp appearance.
3 citations,
January 2021 in “Medicinski arhiv” Trichoscopy, a hair loss evaluation technique, found that people with Androgenetic Alopecia have more thin hairs, yellow dots, and perifollicular discoloration than healthy individuals.
 13 citations,
January 2016 in “Journal of cosmetology & trichology”
13 citations,
January 2016 in “Journal of cosmetology & trichology” Alternative treatments show promise for hair growth beyond traditional methods.
 March 2024 in “Journal of clinical medicine”
March 2024 in “Journal of clinical medicine” Trichoscopy shows hair diameter variability, vellus hairs, and the peripilar sign are key indicators for diagnosing Androgenetic Alopecia.
 5 citations,
May 2008 in “Nature Precedings”
5 citations,
May 2008 in “Nature Precedings” Trichoscopy is a useful non-invasive method to diagnose female hair loss with high accuracy.
 2 citations,
July 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks”
2 citations,
July 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks” Trichoscopy is a useful tool for diagnosing and managing hair and scalp conditions, often better than traditional methods.
 9 citations,
August 2013 in “Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America”
9 citations,
August 2013 in “Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America” Recognize and treat hair loss conditions that mimic androgenetic alopecia by identifying warning signs and using proper tools.
 66 citations,
March 2018 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement”
66 citations,
March 2018 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement” An imbalance between certain immune cells is linked to a chronic skin condition and may be influenced by obesity, smoking, and autoimmune issues.
 39 citations,
January 2011 in “Archives of Dermatology”
39 citations,
January 2011 in “Archives of Dermatology” Reflectance confocal microscopy confirms that yellow dots are signs of damaged hair follicles in alopecia areata.
 21 citations,
September 2015 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
21 citations,
September 2015 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Yellow and orange colors are important for diagnosing certain skin conditions.
 4 citations,
November 2016 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology”
4 citations,
November 2016 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology” Three characteristics of plasmacytoid dendritic cells help tell apart lupus-related hair loss from LPP.
 62 citations,
March 2012 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
62 citations,
March 2012 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Using dermoscopy to guide scalp biopsies is an effective way to diagnose cicatricial alopecia.
November 2021 in “Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology” An elderly woman with cancer improved after treatment for a rare skin condition with coiled hairs.
8 citations,
January 2017 in “Indian dermatology online journal” Traumatic anserine folliculosis is a skin condition caused by friction, treatable with topical cream and avoiding trauma.
 90 citations,
July 2008 in “Dermatologic therapy”
90 citations,
July 2008 in “Dermatologic therapy” Lichen planopilaris is a chronic, scarring hair loss condition with no definitive cure, requiring accurate diagnosis and treatment to manage symptoms.
 178 citations,
December 2011 in “Journal of Dermatological Case Reports”
178 citations,
December 2011 in “Journal of Dermatological Case Reports” Trichoscopy is a useful tool for diagnosing different hair and scalp diseases by their unique visual features.
 15 citations,
July 1999 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
15 citations,
July 1999 in “Dermatologic Clinics” The document concludes that immune system abnormalities cause alopecia areata, but the exact process is still not completely understood.
 1 citations,
May 2003 in “Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine”
1 citations,
May 2003 in “Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine” The boy had trichotillomania, causing hair loss, and treatment focused on habit reversal and support.


























