 October 2020 in “Veterinary Dermatology”
October 2020 in “Veterinary Dermatology” New treatments and diagnostic methods for various animal skin conditions showed promising results.
 August 2019 in “International journal of contemporary pediatrics”
August 2019 in “International journal of contemporary pediatrics” A child with a rare type of rickets showed some improvement with high doses of vitamin D, but such conditions often respond poorly to treatment.
 August 2019 in “Journal of Medical Histology”
August 2019 in “Journal of Medical Histology” EMT helps heal tissues but can cause scarring and other issues if prolonged.
July 2019 in “Dermatology practical & conceptual” The study found that alopecia areata is strongly linked to autoimmune diseases and may indicate a genetic predisposition to such conditions.
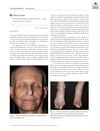 March 2019 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft”
March 2019 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft” Rothmund-Thomson syndrome type 2 can cause chronic, poorly healing wounds.
 April 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Ovol2 is important for proper skin healing and hair growth.
 April 2018 in “The Journal of Urology”
April 2018 in “The Journal of Urology” Imipramine and pseudoephedrine treatment can effectively restore normal ejaculation in patients with diabetes, increasing their chances for pregnancy.
April 2017 in “Al-Azhar Medical Journal” PRP is an effective and safe treatment for alopecia areata.
 December 2016 in “Springer eBooks”
December 2016 in “Springer eBooks” Chrousos Syndrome is caused by mutations that make the body less sensitive to glucocorticoids, leading to various symptoms and requiring high-dose treatment.
 December 2016 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
December 2016 in “British Journal of Dermatology” The meeting highlighted the importance of genetic testing and multidisciplinary approaches in pediatric dermatology.
August 2016 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” The infant likely has Hay-Wells syndrome and needs genetic testing and heart screening.
 April 2016 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
April 2016 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” The study found that severe alopecia areata affects any age, treatments often give temporary results, and some factors predict worse outcomes.
 April 2016 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
April 2016 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” People with certain allergic conditions or higher white blood cell counts have more severe hair loss, and treating hair and nail side effects early in melanoma therapy can improve quality of life.

A new mutation in the CYP11B1 gene was found in a woman with mild hyperandrogenemia, a rare cause of non-classic congenital adrenal hyperplasia.
 November 2015 in “Hair transplant forum international”
November 2015 in “Hair transplant forum international” Early attempts at using cloned cells for hair transplants failed, but 3D cell growth showed some promise.
 December 2014 in “Endocrinología y nutrición”
December 2014 in “Endocrinología y nutrición” The woman's rare combination of diseases suggests an unknown factor may predispose individuals to multiple endocrine diseases.
November 2012 in “Annales de Dermatologie et de Vénéréologie” Frontal fibrosing alopecia can occur in children, not just postmenopausal women.
 September 2009 in “European journal of paediatric neurology”
September 2009 in “European journal of paediatric neurology” Biotin supplements did not significantly reduce hair loss in rats on valproic acid.
 June 2005 in “British Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery”
June 2005 in “British Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery” Advancements in aesthetic surgery from 2002-2003 include improved skin resurfacing, effective migraine surgery, satisfying hair transplants, alternative treatments for skin nevi, successful endoscopic midface enhancement, and safe techniques for facial rejuvenation.
 January 2001 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology”
January 2001 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology” A test for nail fungus was most accurate with PAS stain, low-dose spironolactone helped two-thirds of acne patients, metformin reduced symptoms of HIV-related fat distribution changes with some side effects, and skin examination with dermoscopy was better at detecting abnormal moles, while temporary tattoos can cause skin reactions.
 November 1998 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
November 1998 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” A man's skin cancer improved and some of his hair grew back after treatment with a special light therapy and a medication.
 February 1961 in “The Lancet”
February 1961 in “The Lancet” Some new drugs show potential for treating blood cancers but have serious side effects and need more research.
October 2022 in “The Journal of Clinical Pharmacology” Men with early-onset hair loss have less cardiometabolic benefit from bromocriptine.
 January 2022 in “Journal of Healthcare Sciences”
January 2022 in “Journal of Healthcare Sciences” Male Androgenetic Alopecia, a common hair loss in men, can be slowed and partially restored with treatments like minoxidil and finasteride, or hair transplantation. Serenoa repens may be an alternative treatment. More research is needed for new treatments.
January 2020 in “International Journal of Trichology” Androgen-producing ovarian tumors can cause male-pattern hair loss in women.

The herbal mixture Xiantene may help treat common baldness, and men who grey early tend to be less bald but more grey.
 June 2007 in “Advances in Dermatology and Allergology/Postępy Dermatologii i Alergologii”
June 2007 in “Advances in Dermatology and Allergology/Postępy Dermatologii i Alergologii” Finasteride is effective in stopping hair loss and promoting regrowth in most men with mild side effects.
 61 citations,
January 2019 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology”
61 citations,
January 2019 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology” The cause of Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia is unclear, diagnosis involves clinical evaluation and various treatments exist, but their effectiveness is uncertain.
 11 citations,
October 2001 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
11 citations,
October 2001 in “Dermatologic Clinics” The document concludes that DAB389-IL2 is promising for treating refractory cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, but more research is needed on its effectiveness and side effect management.
 2 citations,
September 2017 in “Plastic and reconstructive surgery. Global open”
2 citations,
September 2017 in “Plastic and reconstructive surgery. Global open” Nanofat injections can significantly improve hair growth in men with hair loss for up to a year.
























